Chocolate is a food loved by most people, and for many, especially women, it is considered irresistible. Others, however, need to avoid it, some say that it is addictive and that it makes you fat. To see if these claims are really true and what the benefits and harms of eating chocolate are, it's important to know what the main components of this product are.
chocolate consists of 8% protein, 60% carbohydrates it's from 30% fat. As can be seen, the amount of fat is at an upper limit than what is desirable for a food. This can be translated into high calories, for example a 100g candy bar provides 520 calories. The least caloric are bitter and semisweet, followed by milk and, finally, white chocolate. In order not to get fat, it is recommended to ingest only 25 to 30 g a day, no more than three times a week.
This cocoa fat or butter is essentially saturated and does not lead to an increase in cholesterol levels.
But chocolate also provides minerals (potassium, chlorine, phosphorus, calcium, sodium, magnesium, iron, copper and zinc)
and vitamins (A, B1, B2, B3 and E, just do not contain vitamins C and D). That's why it is used as a food portion by soldiers and explorers in emergency situations.There are over 300 chemicals in chocolate, but there are three special substances that we want to draw attention to. They are not nutritious, but affect us and are closely related to the questions asked earlier, such as the question whether chocolate is really addictive.
The three substances are: phenylethylamine, oxalic acid and caffeine.
- Phenylethylamine (PEA, from English Phenylethylamine):
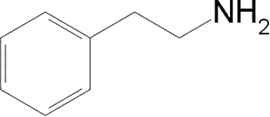
This is the substance responsible for causing the feeling of well-being in our brain, as it can trigger the release of dopamine, a chemical in the brain that causes the feeling of happiness.
It's true that chocolate can cause migraines in some people, and that's because it constricts the walls of the blood vessels in the brain. The human body has an enzyme (monoamine oxidase) that eliminates PEA when the person's body does not. can produce enough of this enzyme to prevent the increase of PEA in the body, there is the migraine.
- Oxalic acid:
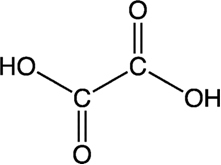
In every 100 g of cocoa there is 500 mg of this substance. It is present in many other foods such as rhubarb. If taken in doses above 1500 mg, it can even kill. Oxalic acid reacts with essential metals such as iron, magnesium and calcium in food and prevents them from nourishing the body.
Oxalic acid kills by decreasing below the tolerated level of calcium in our body.
Even in non-lethal doses, oxalic acid is dangerous because it forms calcium oxalate, which is insoluble, which can grow into painful stones in the bladder and kidneys.
- Caffeine:
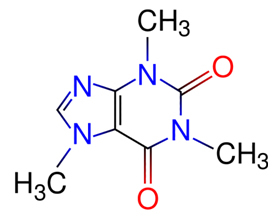
Chocolate contains a little caffeine which gives the feeling of recovering our energy and also has medicinal effects. To see the chemistry of this substance and its effects on our body, read the text “Caffeine Chemistry”.
It is interesting to note that although chocolate contains several active substances, none of them are addictive.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/composicao-quimica-chocolate.htm
