A Yalta conference was the second conference held by the Allies at the end of World War II aiming to ensure a quick end to the war and the division of the zones of influence of the European continent between countries of the West and East. The leaders of the Allied nations came together to organize the war's final strategies: US President Franklin Roosevelt; the British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill; and the Soviet head of state, Joseph Stalin.
Read too: Paris Peace Conference and the treaty that sparked World War II
Topics of this article
- 1 - Summary of the Yalta Conference
- 2 - What were the objectives of the Yalta Conference?
- 3 - How was the Yalta Conference?
- 4 - What was decided at the Yalta Conference?
- 5 - Other World War II conferences
Summary of the Yalta Conference
- The Yalta Conference was the second conference held by the Allies at the end of World War II. World Cup aiming to ensure a quick end to the war and distribution of the continent's zones of influence European.
- Implicitly, this conference initiated the debates and tensions that culminated in the bipolarization of the world during the Cold War.
- The leaders of the Allied nations came together to organize the war's final strategies: US President Franklin Roosevelt; the British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill; and the Soviet head of state, Joseph Stalin.
- It was decided that Nazi Germany would be forced into unconditional surrender, and its territory would subsequently be divided among the Allies.
- The Potsdam Conference was the third conference held between the Allied nations with the aim of organizing the administration and occupation of defeated Germany.
- The Tehran Conference was the first of three major conferences held at the end of World War II. World Cup, in which the invasion of France (occupied by the Nazis) by British troops and American.
- The San Francisco Conference (April 25 and June 26, 1945) aimed at producing and approving the Charter of the United Nations (UN).
What were the objectives of the Yalta Conference?
The Yalta Conference took place between February 4 and 11, 1945, in the city of Yalta, Crimea, Ukraine. It was the second of three major conferences held by the Allied countries in the context of the end of World War II.
Your goals were ensure a quick end to the war and the distribution of the zones of influence of the European continent between West and East countries. Implicitly, this conference initiated the debates and tensions that culminated in the bipolarization of the world. during the cold war.
Do not stop now... There's more after the publicity ;)
How was the Yalta Conference?
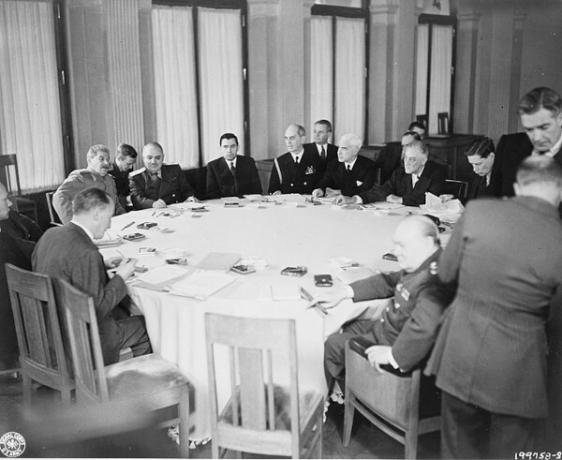

The leaders of the major Allied nations came together to negotiate, deliberate, and organize the war's final strategies. were present the president of the USA, Franklin Roosevelt; the British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill; and the Soviet head of state, Joseph Stalin. The meetings took place at the Palace of Livadia, in a resort area of Yalta, close to the Black Sea, and outlined the course for the end of the war.
The initiative to convene the first meeting between the leaders of the three major Allied powers from the president of the USA, Franklin Roosevelt. Initially, their intention was to host the meeting in a neutral location, such as the Mediterranean, Athens or Jerusalem. However, Stalin, leader from the USSR, rejected all proposals, under the allegation that long journeys would harm his health, which gave rise to a first tension. Stalin's suggestion to break the stalemate was to hold the conference in a city close to Russia, in Ukraine.
Each of the three leaders had their own political agenda, and the convergences leaned more towards British and American interests than towards the Soviets. An example of this is the discussion about what to do with Germany after the war:
- Roosevelt wanted Soviet support in the war against Japan in the Pacific, and his adherence to the then project of build the UN.
- Churchill intended that there should be free and democratic elections in the central and eastern European countries under Nazi rule after his liberation, especially in Poland.
- Stalin, on the other hand, demanded the construction of a Soviet sphere of political dominance in central and eastern Europe as a fundamental part of his national security strategy.
Thus, it became clear that the Allies of World War II would not remain allies much longer. In addition to these impasses, Stalin demanded that Poland be fully annexed to Soviet domains, as it was a "a matter of honor" for his government and for its strategic position as an obstacle to any country that wanted to invade the Russia.
Other discussions that occurred, revealed years later in secret documents, involved the situation in Korea and its eventual division — what was actually accomplished in the Korean War years later. As for the Soviet membership of the UN, it was established that the USSR would join as long as it obtained veto power over the Security Council, thus ensuring that it could block any unwanted decisions.
Know more: The Siege of Berlin, the Fall of Nazism, and the Death of Hitler—Last Chapters of the War
What was decided at the Yalta Conference?
During the Yalta Conference it was decided that:
- Nazi Germany would be forced into unconditional surrender and its territory would subsequently be divided among the Allies;
- Germany would be demilitarized and denazified;
- US President Franklin Roosevelt would organize the United Nations and would have the participation of the USSR;
- it would be necessary to force, through military attacks, the surrender of Japan.
Other World War II conferences
- Tehran Conference: was the first of three major conferences to take place at the end of World War II, held from November 28 to December 1, 1943 in Tehran, Iran. In it, the leaders of USA, USSR and England decided and organized the invasion of France (occupied by the Nazis) by British and American troops. To learn more about this conference, click here.
- Potsdam Conference: was the third major conference held between the three main allied nations, England, USA and USSR, in context of the end of World War II, which took place between July 17 and August 2, 1945 in Potsdam, Germany. The purposes of the Potsdam Conference were to organize the administration and occupation of Germany., recently defeated and who had signed their unconditional surrender on May 8.
- San Francisco Conference: took place between April 25 and June 26, 1945 in the city of San Francisco, USA. The objectives of the conference were the production and approval of the Charter of the United Nations by 50 allied nations. It is considered the inaugural landmark of the United Nations (UN).
Sources
MAGNOLI, Demetrio. History of Peace. São Paulo: Context, 2012.
MIRANDA, Monica; FARIA, Richard. From the Cold War to the New World Order. São Paulo: Context, 2003.
VASCONCELLOS, Carlos-Magno; MANSANI, Roberta. The international conferences of Yalta and Potsdam and their contribution to the construction of North American international economic hegemony in post-World War II capitalism. International Relations of the Current World Magazine. vol. 2, no. 16, 2013. Available in: http://revista.unicuritiba.edu.br/index.php/RIMA/article/view/731/557.
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
CAMPOS, Tiago Soares. "Yalta Conference"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/historiag/conferencia-de-yalta.htm. Accessed on August 17, 2023.
Learn once and for all the alliances formed in World War II and know the countries that make up the Axis and Allies.
See how the Battle of Berlin went, in which a small Nazi resistance fought against 2.5 million Soviets in the defense of the German capital.
Click here to understand what the Tehran Conference was and what its objectives were. See the importance of decisions made by the Allies in Tehran.
Learn more about the Cold War, a political-ideological conflict that polarized the world and resulted in a series of conflicts around the planet in the second half of the 20th century.
Korean War, World War II, Cold War, North Korea, South Korea, 38th parallel, Chinese Revolution of 1949, UN, war conflicts, nuclear hecatomb, Treaty of Pan-munjom.
Learn how the government of Japan managed to secure the population's devotion to the Emperor even after defeat in World War II.
See what happened in the final months of World War II, that is, the military actions that marked the end of that conflict.
Visit to learn more about the greatest conflict in human history: World War II. Also check out a video lesson on the topic and a mind map!
Cringe
The slang adapted from English is used to designate someone who is seen as tacky, shameful, outdated and out of fashion.
Neurodiversity
A term coined by Judy Singer, it is used to describe the wide variety of ways the human mind behaves.
PL of Fake News
Also known as PL2660, it is a bill that establishes mechanisms for the regulation of social networks in Brazil.
This Wednesday, August 16, Teresina, capital of Piauí, completes 171 years. Click and find out...