A Victorian age It was the period in which Queen Victoria reigned, from June 1837 to January 1901. It was a time marked by the power of England, which became the richest country in the world through colonialism and industrialization. It is also recognized that culture in general, especially fashion, literature, music and architecture, received great attention. On the other hand, it was also a period of great social inequality, since the poorest population did not have access to all of this English apogee.
Read too: British royal family — the family currently occupying the British throne
Topics of this article
- 1 - Summary about the Victorian Era
- 2 - Historical context of the Victorian Era
- 3 - Main characteristics of the Victorian Era
- 4 - Fashion in the Victorian Era
- 5 - Art in the Victorian Era
- 6 - Architecture in the Victorian Era
- 7 - Society in the Victorian Era
- 8 - Population of the Victorian Era
- 9 - Economy in the Victorian Era
- 10 - Culture in the Victorian Era
- 11 - Literature in the Victorian Era
- 12 - Importance of the Victorian Era
- 13 - Who was Queen Victoria?
Summary about the Victorian Era
- The Victorian Era was the period of reign of Queen Victoria of England, from June 1837 to January 1901.
- In this period, England it was the richest country in the world.
- Its end coincides with the French Belle Époque.
- Women's fashion had great prominence in the period and, for the rich, it was composed of corsets and skirts and pompous dresses, thus having a great contrast in relation to the clothes of the poor.
- Art and architecture in the Victorian Era was influenced by Gothic and Classical styles.
- Society was profoundly unequal.
- The population has increased a lot.
- England dominated the world economy.
- The culture was greatly encouraged and lived a heyday
- Great names in literature emerged in the period, such as Oscar Wilde.
- It was very important in several aspects, such as economic, political and cultural.
- Queen Victoria she was the last of the House of Hanover to obtain the throne, which she received from her uncle Wilhelm IV. She was born in 1819 and died in 1901.
Historical context of the Victorian Era
Victorian Era was the period in which Queen Victoria reigned, from June 1837 until January 1901, the date of her death. The end of the era coincides with the Belle-Époque in Europe. Victoria's England dominated ¼ of the world, and industrialization brought technological advances and income to part of the country. Thus, birth rates rose in the period.
Do not stop now... There's more after the publicity ;)
Main characteristics of the Victorian Era
The main characteristics of the Victorian Era were:
- England was portrayed as the model country, being the most powerful nation in the world.
- There was the expansion of the UK colonies in Africa, Asia and the Middle East.
- The Berlin Conference and the consolidation of neocolonialism took place.
- English imperialism expanded and consolidated.
- occurred to Second Industrial Revolution.
- The development of transport has expanded.
- Electricity and photography were invented.
- Social inequality has increased.
- Artistic activities were encouraged.
- There was great emphasis on fashion and literature.
- The stereotype that “the English people are polite” arose.
Fashion in the Victorian Era
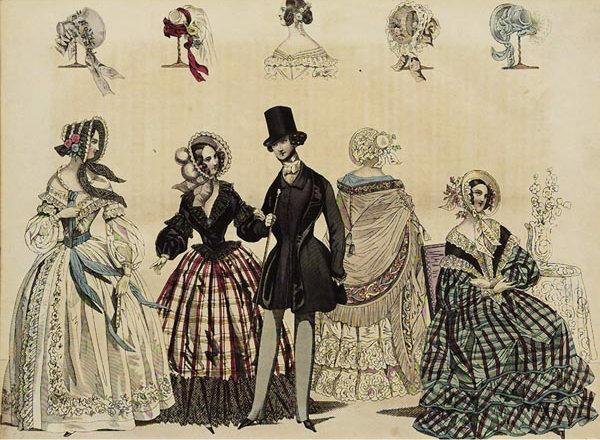

Fashion in the Victorian Era consisted of various trends in British clothing from the 1830s to the 1890s. In women's fashion, corsets became famous, which made women have thin waists. Some, so tight, caused health problems. In any case, they limited his movements. The dresses had several layers, which formed wide skirts. Hats were also widely used.

For those who could pay for it, it was a fashion for clothes of great volume, puffy shapes, fluffy sleeves, high collar, ruffles and lace. The colors were in dark tones, and the trend at the time was green. To obtain it in the tonality requested by the nobles, many died in production, due to the toxicity of the arsenic used.
In the fashion of wealthy men, men's clothing would necessarily include a vest, coat and hat, quite formally.

Poor people got their clothes secondhand or even made them themselves.. In the case of donations, many were contaminated with lice and other pests, which caused illness and death due to the hygiene habits of the time. That's the not-so-glamorous part of Victorian fashion.

Art in the Victorian Age
In the visual arts, the Victorian Era was deeply influenced by realism, in an attempt to faithfully portray the nature and society of the time. Afterwards, they were heavily influenced by mythology and fantasy, with the presence of fairies, landscapes and nudity.
Architecture in the Victorian Era
In architecture, There was a conflict over whether to adopt Gothic or classical theory.. In fact, some experts claim that there was no Victorian architecture par excellence, but rather a reinterpretation of existing styles, which, together, were baptized with the name of the monarch. Just as there was Gregorian architecture, executed during the reigns of George I, George II, George III and George IV, there was Victorian architecture.

Some elements are common to the buildings of that time, such as the recovery of styles from Asia and the Middle East; The valuation of historical items; and the revival of the Gothic style, for some time called neo-Gothic. The style spread throughout the United Kingdom and to English colonized countries.
The decoration of the houses had special prominence, especially in the dining rooms. Precious woods such as mahogany, walnut, rosewood, rosewood, oak and ebony were used, carefully cut and dressed with upholstery, usually with flower prints.
Society in the Victorian Age
Society in the Victorian Era, despite all the trappings of fashion and architecture and the grandeur of British imperialism of the period, remained divided into classes and profoundly unequal. The apogee of industrialization also corresponded to a period in which part of the population received very low wages for terrible working conditions and hours, including child labor. This population lived under precarious conditions.
Victorian Era Population
The population of the period increased. There was an increase in the birth rate, generating a population growth from 13.8 million (1831) to 32.5 million (1901).
Economy in the Victorian Era
The economy of the period was based on industry, especially textiles, which employed 40% of the industrial workforce. The steel industry boomed and then busted around this time. Exports increased. England was not involved in any military conflict in the period, which contributed to the economy. The country built transport systems in other countries, especially in its colonies.
The figures indicate that “between 1850 and 1873, the United Kingdom produced two thirds of the world's coal, half of the cotton and almost half of the metallic products”.|2| In protest of this and the working conditions, many miners' unions sprang up.
Culture in the Victorian Era
The Victorian Era was very culturally relevant. The culture of the period revived the gothic, which came to be called neo-Gothic, and was mainly marked by the apogee of various branches of art, such as the plastic arts, literature and music. There was also a peculiarity of the cult of death in the period.
Literature in the Victorian Era
The literature of the period was very rich, both in novels, generally portraying typical dilemmas of the bourgeois class, and in science fiction. The following stood out: Charlotte, Emily and Anne Brontë; George Eliot; Charles Dickens; and oscar wilde.
See too:William Shakespeare — an English poet and playwright of the Elizabethan period
Importance of the Victorian Era
The Victorian Era was culturally important, but mainly in economic terms. Culturally, because several branches of art had great prominence; and economically, as it was when England became the richest country in the world, due to industrial development and colonialism.
Who was Queen Victoria?
Queen Victoria was the last of the House of Hanover and the only one to reign. Her name was Alexandrina Vitória Regina, and she was born on May 24, 1819. Her parents were the Duke of Kent, who died when she was still a baby, and the former Princess of Leininge.
Vitória assumed the reign of her uncle Guilherme IV, aged 18, and remained in it for more than six decades, being the second longest reign in England, behind only the reign of Elizabeth II. During this period, from 1837 to 1850, she had to deal with the chartist movement, which claimed the political rights of workers.
In her personal life, she was married to Prince Albert, from 1840, her cousin, with whom she had nine children. He greatly influenced her reign, especially in encouraging science and the arts, in addition to the army. He died in the year 1861, leaving the Queen in deep mourning.
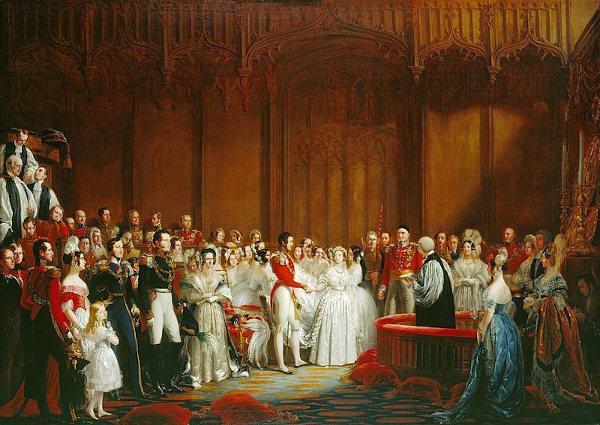

Queen Victoria was fluent in German and French; she played the piano; and studied History, Geography and Literature diligently, in addition to having been a painter.
During her reign, England experienced the height of colonialism and bourgeois industrial policy.. Still during her governance, the abolition of slavery in the British Empire (1838) took place; the reduction of the working day in the textile industry to 10 hours (1847); the Crimean War (1853-1856) and the Boer War in South Africa (1899-1901); and the Third Reform Act (voting rights, in 1884).
He died in 1901, aged 81. He suffered from rheumatism and died as a result of general health complications.
Note
|1| CROUZET, F. From the superiority of l’Angleterre sur la France. Paris: Perrin, 1982.
image credit
[1] Adam Calaitzis / Shutterstosck
Sources
HOBSBAWN, E. j. The Age of Revolutions. Rio de Janeiro: Paz e Terra, 1977.
MEIRA, J. P. G. Historiographic note on the concept of class: English Social History and the Victorian Era in England. Available in: http://www.anpuhpb.org/anais_xiii_eeph/textos/ST%2014%20-%20Jean%20Paul%20Gouveia%20Meira%20%20TC.PDF.
THOMPSON, E. P. The Formation of the Working Class. Rio de Janeiro: Peace and Land, 1987.
By Mariana de Oliveira Lopes Barbosa
History teacher
Discover the main characteristics of the Belle Époque, the period between the Franco-Prussian War and the First World War.
Get more information about Henry VIII's rule and Queen Elizabeth's reign during the religious conflicts in Europe here.
Access and discover the life of Elizabeth II, such as her marriage, her participation in the Second World War and her coronation as Queen of the United Kingdom.
Click on the link to learn more about the British monarchy, ruled by the British royal family. See when the Windsor dynasty emerged and who its members are.
Click to know the geography of England. Find out what the difference is between this country and the United Kingdom, understanding a better correlation between them.
See here the story of Queen Victoria, responsible for the English industrial acceleration, for the end of slavery in the British Empire and for laws that helped workers.