We know that the social inequality It is a problem of a social nature that is present in all countries of the world.
Therefore, the Escola Educação team selected some questions about social inequality for you to answer. Let's go?
see more
Teacher performance is a key factor for the full inclusion of students…
Scientists use technology to unlock secrets in ancient Egyptian art…
Questions about social inequality
1- What are the indicators that help to identify the level of social inequality within a country?
a) They are the Human Development Index (HDI), income per capita and the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
b) Are the Human Development Index (HDI), income per capita and the level of education of the population.
c) They are the Human Development Index (HDI), Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and the level of education of the population.
d) They are the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), income per capita and the level of education of the population.
2- What is social inequality?
a) Social inequality is the economic difference between the lower social classes.
b) Social inequality is the economic difference between the higher social classes.
c) Social inequality is the economic difference between the groups of people that make up society
d) Social inequality is the economic difference existing only in republican countries.
3- Check the alternative that contains the main causes of social inequality.
the corruption; lack of social investments (culture, education and health); intense income distribution; accumulation of wealth.
b) Corruption; lack of social investments (culture, education and health); bad income distribution; distribution of wealth.
c) Corruption; lack of investment in the economy; bad income distribution; accumulation of wealth.
d) Corruption; lack of social investments (culture, education and health); bad income distribution; accumulation of wealth.
4- Check the alternative that contains the main consequences of social inequality.
a) Poverty, misery, hunger, infant mortality, unemployment, marginalization, violence.
b) Poverty, misery, hunger, infant mortality, employment, marginalization, violence.
c) Poverty, misery, hunger, increased child life expectancy, unemployment, marginalization, violence.
d) Poverty, misery, hunger, infant mortality, unemployment, marginalization of the upper classes, violence.
5- (Unicentro) Regarding the caste system of a society, mark the correct alternative.
a) There is social mobility within a caste society.
b) Exogamy is part of marriages performed in caste societies.
c) There is no social mobility within a caste society.
d) Within a caste system, heredity is not important.
e) In a caste system there is no division between upper and lower castes.
6- (Ufub) According to Marx's theory, social inequality can be explained:
a) For the distribution of wealth according to the effort of each one in the performance of his work.
b) By the division of society into social classes, resulting from the separation between owners and non-owners of the means of production.
c) Due to differences in the innate intelligence and ability of individuals, determined biologically.
d) For the appropriation of working conditions by the most capable men in historical contexts, marked by equal opportunities.
7- (UPE 2013) – Observe the cartoon below:
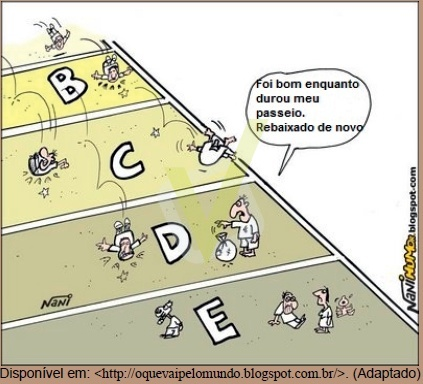
It refers to a form of inequality. About the characteristics of this social structure, analyze the alternatives and mark the CORRECT one.
a) Hierarchization is rigid, based on hereditary, professional, ethnic, religious criteria that determine relationships between people.
b) Tradition is a fundamental element in defining the relationships established between different groups.
c) Mobility from one stratum to another in this structure is possible, but it is controlled by individuals at the top of the organization.
d) People differ from one another by the place occupied by them in a historically determined by social production, by its relationship with the means of production and by its role in social organization from work.
e) The choice of spouse must be made exclusively within the social organization, based on hereditary criteria.
8- (UPE SSA 2 2016) – Observe the charge below:

Social structure is a theme present in sociological studies. Based on the charge, it is CORRECT to state that:
a) social inequality is based on housing, as obtaining other elements of survival depends exclusively on individuals.
b) social movements function as mechanisms that encourage the creation of social spaces, as shown in the cartoon.
c) the stratification of Brazilian society is divided into social classes, which are determined by economic and social conditions of life.
d) the resident of one of the houses in the cartoon compares his residence with that of a higher social class. This fact makes him satisfied with his social status.
e) the middle class in Brazil is characterized by having a large accumulation of money that makes it a fragile social structure, if compared to other social organizations.
9- What are the factors that the Human Development Index (HDI) considers fundamental to measure the degree of human development of a country?
a) Transport, health and economy.
b) Education, health and economy.
c) Education, health and sustainability.
d) Education, housing and sustainability.
10- (UEG 2011) –Some people achieve more than others in societies – more money, more prestige, more power, more life, and everything that men value. Such inequalities create divisions in society – divisions with respect to age, sex, wealth, power and other resources. Those at the top of these divisions want to maintain their advantage and privilege; those at the bottom want more and must live in a constant state of anger and frustration […]. Thus, inequality is a machine that produces tension in human societies. It is the source of energy behind social movements, protests, riots and revolutions. Societies may, for a period of time, stifle these separatist forces, but if severe inequalities persist, tension and conflict will punctuate and sometimes dominate social life. TURNER, Jonathan H. Sociology: Concepts and applications. São Paulo: Pearson, 2000. P. 111. (Adapted).
Observing the figure and reading the text allow us to infer:
a) on the social level, human equality is explicit in two well-defined sectors: in justice, according to which all are equal before the law, and in education, in which all must have opportunities equals; these practices are experienced by Brazilian society.
b) according to Karl Marx, those who own or control the means of production have power, being able to manipulate cultural symbols through the creation of ideologies that justify their power and privileges.
c) class stratification exists when income, power and prestige are given equally to members of a society, thus generating cultural, behavioral and organizational groups similar.
d) stratification, in Karl Marx's view, shows that the class struggle is not polarized between having and not having and involves more than the economic order.
feedback
1- B
2-C
3- D
4- A
5-C
6- B
7-D
8-C
9- B
10-B
Learn more at:
- List of questions about terrorism
- List of questions about capitalism
- List of History of Brazil questions
