You carbohydrates are the main energy sources of a cell, in addition to being part of the composition of nucleic acids and of the cell wall. Also called carbohydrates, carbohydrates and sugars, these substances are generally found in foods of plant origin, such as potatoes and beans, and present in their composition the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. We can sort the carbohydrates into three groups, using as a criterion their size and organization, they are: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
What are carbohydrates?
You carbohydrates are biomolecules of great biological importance and form the most abundant class of biomolecules of our planet. These molecules are fundamentally formed bycarbon, hydrogen and oxygen, hence the denomination of carbohydrates. It is worth noting, however, that other atoms may be present in their molecules, such as the nitrogen found in chitin, which forms the exoskeleton of arthropods.
Read too: Proteins - main nutrients present in building foods
Function of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates have several functions, but the main function attributed to these biomolecules is to Energy supply. It is also worth noting that carbohydrates act as flags in the body, participate in the cell wall structure, gives exoskeleton structure of arthropods and the formation of nucleic acids.
Carbohydrate Sources

When talking about carbohydrates, many people only remember foods, such as breads, cakes, pasta and sweets. However, these foods are not the only ones that contain these biomolecules. As we know, vegetables perform photosynthesis and store carbohydrates at the end of this process as a source of energy for the plant. Therefore, all plant foods have carbohydrates, including fruits. Foods dairy and honey they also have carbohydrates.
See too: Unconventional Food Plants (PANCs): what are they and what are they for?
Carbohydrate classification
Carbohydrates can be classified into three main classes, using the size of their carbon chain as a criterion: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.

monosaccharides
The simplest carbohydrates are called monosaccharides, which are monomers (units that form polymers) that form the most complex carbohydrates. Monosaccharides, also called simple sugars, are classified according to the number of carbons they have in their molecule, which has a general formula (CH2O)n. So we have the trioses with three, the tetroses with four, the pentoses with five, the hexoses with six and the heptosis with seven carbon atoms.
As an example of monosaccharide we should highlight two pentoses that participate in the formation of DNA and RNA: a deoxyribose and the ribose, respectively. In addition, we have the glucose and fructose, two extremely important hexoses for living beings. It is important to note that glucose, which has formula C6H12O6, is the main carbohydrate used by cells to obtain energy.
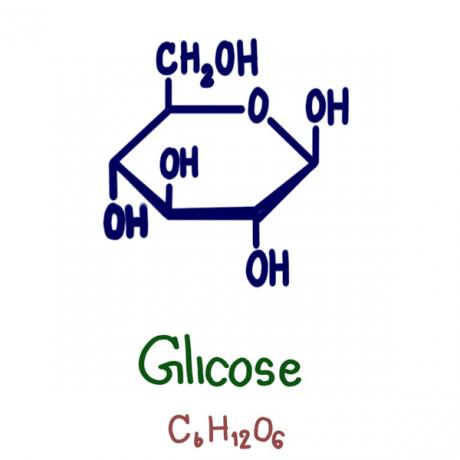
Disaccharides
You disaccharides are carbohydrates formed by two molecules of monosaccharides, linked by glycosidic bonds, and are soluble in water. Among the main examples, we can mention the sucrose, which is the result of a molecule of glucose with one of fructose. In addition to sucrose, we have lactose (glucose + galactose) and maltose (glucose + glucose).
An important feature of disaccharides is that they need to be broken down to be used as an energy source, unlike monosaccharides.
Polysaccharides
You polysaccharides they are formed by the joining of hundreds and even thousands of monosaccharides. Unlike disaccharides, they are not soluble in water. This insolubility is important for several organisms, such as arthropods, for example, which have an exoskeleton formed by a polysaccharide (chitin) that protects them against dissection. In addition to chitin, we can cite as examples of polysaccharides:
- Cellulose: Major component of the cell wall of plant cells. It is considered the most abundant carbohydrate in nature. Although not digested by humans, cellulose is important in the diet as fiber.
- THEkid: Main energy reserve of vegetables. It is formed by glucose molecules linked together.
- Glycogen:Reserve carbohydrate found in animals. Glycogen is stored in the liver and muscles, and when the body needs energy it is broken down into glucose molecules. Like starch and cellulose, glycogen is the result of the union of several glucose molecules.
Polysaccharides, when formed by only one type of monosaccharide, are called homopolysaccharides, this being the case for starch and glycogen. When polysaccharides have two or more different monosaccharides, they are called heteropolysaccharide. As an example of heteropolysaccharide, we can mention the peptidoglycan, which forms the cell wall of bacteria.
by Vanessa dos Santos
Biology teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/biologia/o-que-e-carboidrato.htm

