To determine the opposite, the conjugate and the equality of any complex number, we need to know some fundamentals.
Opposite
The opposite of any real number is its symmetric, the opposite of 10 is -10, the opposite of -5 is +5. The opposite of a complex number respects this same condition, as the opposite of the complex number z will be –z.
For example: Given the complex number z = 8 – 6i, its opposite will be:
- z = - 8 + 6i.
Conjugated
To determine the conjugate of a complex number, it is enough to represent the complex number through the opposite of the imaginary part. The conjugate of z = a + bi will be: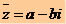
Example:
z = 5 – 9i, its conjugate will be:
z = – 2 – 7i, its conjugate will be
Equality
Two complex numbers will be the same if, and only if, they meet the following condition:
equal imaginary parts
Real equal parts
Given the complex numbers z1 = a + bi and z2 = d + ei, z1 and z2, they will be equal if only if a = d and bi = ei.
Comments:
The sum of opposite complex numbers will always equal zero.
z + (-z) = 0.
The conjugate of the conjugate of a complex number will be the complex number itself.
There is no order relationship in the set of complex numbers, so we cannot establish who is greater or less.
Example 1
Given the complex number z = - 2 + 6i, calculate its opposite, its conjugate and the opposite of the conjugate.
Opposite
- z = 2 - 6i
Conjugated
opposite of the conjugate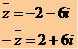
Example 2
Determine a and b so that 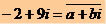 .
.
-2 + 9i = a - bi
We need to establish ownership of the relationship of equality between them. Then:
a = - 2
b = - 9
by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/oposto-conjugado-igualdade-numeros-complexos.htm
