The elements of family 17 or VII A of the Periodic Table are called Halogens, represented by the five elements listed below: Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Iodine (I) and Astatine (At). They are often generically represented by the letter X.

The most important ones, due to their daily applications, are chlorine, bromine and iodine.
This name "halogen" means "salt forming".
All of them have 7 electrons in the valence shell (electronic shell outermost to the nucleus and more energetic). Generically: ns2 np5. As a result, they tend to receive an electron and form negative monovalent ions (X-1), reacting mainly with alkali metals (family 1 metals), which tend to donate an electron. Thus, they give rise to compounds with formulas of the MX type.

By gaining this electron, the halogens are stable, as their valence shell is complete (with eight electrons) and their characteristics change completely. For example, chlorine gas (Cl2) is a greenish-yellow, dense, highly toxic and reactive gas, sparingly soluble in water and explosively reacting with hydrogen. However, when the
chlorine (Cl) receives an electron from sodium (Na), they become ions, forming sodium chloride (NaCl), or table salt, which we ingest daily and which is necessary to sustain our lives. Chlorine especially becomes the chloride ion (Cl-) which is necessary in our body for the formation of hydrochloric acid (HCl), the main component of our gastric juice.In fact, chlorine is the most abundant of the halogens and is used in the production of organic compounds, inorganics, in paper manufacturing (aiming at pulp bleaching) and in water and sewers. It is also common to use an aqueous solution of sodium hypochlorite (NaClO), which is called “liquid chlorine” and which is in the composition of bleach.
An interesting fact is that although some people say that “solid chlorine” is used in swimming pools, it is actually not just the element chlorine, but calcium hypochlorite (Ca (ClO)2).
Also, a similar case is the use of fluorine – which is actually not fluorine per se, but fluorides (ionic compounds that contain the element fluorine) – in drinking water treatment and in oral care products.
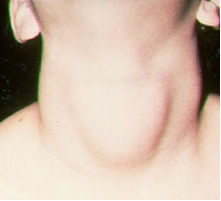
With respect to the iodine, an important application is their addition (in the form of iodides or sodium and potassium iodates), required by law, to table salt. This is because the lack of iodine in the body can cause a disease called goiter, popularly known as papo.
O bromine it is a red liquid, at room temperature, dense and unstable and, as it is volatile, it can evaporate, forming a reddish vapor. It is not found in nature in isolation, nor is it used in industry in this way. The main applications of its compounds are: as catalysts for organic reactions, mixed with fuels, in photographic developments, among others.
already the astatine it is a radioactive element. Its origin is usually as a result of the radioactive decay of uranium and thorium isotopes. It forms at least 20 isotopes, with At-210 being the most stable, with a half-life of 8.3 hours. It's a very rare element.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
