Urban mobility is defined as the conditions present in space that enable the circulation of people, goods and cargo in cities. Mobility has become a challenge for large urban centers, which have experienced rapid expansion of their urban fabric and fleet of private vehicles, contrasting with transport Insufficient and low-quality roads and public roads in many cases. Ensuring urban mobility means providing greater fluidity to urban space and making the city more accessible to those who inhabit it, ensuring a better quality of life for the population.
Check it out on our podcast: Challenges of urban mobility in Brazil
Topics of this article
- 1 - Summary on urban mobility
- 2 - What is urban mobility?
- 3 - Problems of urban mobility
- 4 - Importance of urban mobility
- 5 - Challenges of urban mobility
- 6 - Consequence of lack of urban mobility
- 7 - Urban mobility in Brazil
- 8 - Urban mobility in the world
- 9 - Sustainable urban mobility
- 10 - Possible solutions for urban mobility
- 11 - Resolved exercises on urban mobility
Summary on urban mobility
Urban mobility is the capacity that people, goods and loads have to circulate through urban space. taking into account the available infrastructure, current regulations and conditions intrinsic to these agents.
The rapid growth of cities and the car fleet and issues such as lack of planning are causes of urban mobility problems.
The dynamization of urban space, carrying out activities in cities and access to all the services they offer depend on urban mobility, hence its importance.
The slowness in traffic at peak hours (time of shift) is a consequence of the lack of urban mobility. rush), congestion, delays and increased air and noise pollution.
In Brazil, the intense migratory flow towards the cities from the second half of the 20th century and the fact that the infrastructure and the transport system has not been expanded are factors that create problems for urban mobility in the country at the moment.
There are forums dedicated to debates on urban mobility worldwide and studies being carried out by companies on urban mobility in the main cities of the world.
According to Here's Urban Mobility Index, the five cities with the best urban mobility in the world are, respectively: Copenhagen, Brussels, Vancouver, Vienna and Zurich.
Urban mobility combined with the preservation of the environment and improvement in the quality of life of the population of cities is called sustainable urban mobility.
Improvements and solutions for urban mobility include urban planning, expansion of the public transport, adoption of intermodality in urban transport, expansion of roads and flexibility in schedules.
What is urban mobility?
urban mobility is the capacity to carry out displacements in the cities and urbanized areas. This is a concept that has been extensively worked on in the context of urban geography and applied mainly in urban planning and policies aimed at cities, referring to the set of normative conditions and infrastructural, as well as individual, which allow the movement of people and also cargo in cities, thus ensuring the fluidity of space urban.
This definition is very close to that presented in the National Urban Mobility Policy (Law No. 12,587 of January 3, 2012), one of the legal provisions that deal with this issue in the Brazil.
Do not stop now... There's more after the publicity ;)
Urban mobility problems
Cities around the world, especially metropolises, face a series of problems linked to urban mobility and also the lack of it. This happens especially in those places that went through a quick process of urbanization, marked by the disorderly growth of cities, that is, without any kind of planning that would prepare the space for the intensification of flows in general.
Another important aspect to be considered in the study of urban mobility problems is the use of individual transport to the detriment of public transport, such as buses and subways. The population's preference for vehicles such as cars or motorcycles is due to several reasons ranging from greater flexibility of use to scrapping of urban public transport, which includes broken or low-quality vehicles and fares high. Thus, there is a growth in the fleet of cars and motorcycles in cities.
Thus, we can state that you main problems of urban mobility stem fromm the lack of planning and the lack of adequate infrastructure that provides transportation in cities.
Taking this into account, we have listed below some of main problems of urban mobility:
slow traffic at peak hours rush) and increased congestion;
low coverage of public transport networks, that is, they do not reach all neighborhoods or streets in the city;
lack of integration of different urban modes;
poor quality of public transport and high fares;
low quality of urban asphalt, sidewalks and traffic routes in general;
lack of accessibility of places;
absence or inefficiency of bus lanes and cycle lanes.
Importance of urban mobility
Urban mobility is a fundamental aspect of cities and their respective population. She is important because provides greater fluidity of urban space, that is, under the right conditions, the flows of people and loads happen efficiently, making cities dynamic and functional spaces.
The importance of urban mobility is given because it enables thewhat we call it access to the city, providing citizens with mobility between different neighborhoods and locations, from the closest to those farthest from their place of residence, for different purposes, such as study, work or leisure. For this reason, urban mobility is an essential part of public policies that deal with the right to the city and the various plans aimed at the use and occupation of urban space.
Urban mobility challenges
Urban mobility offers a series of challenges to citizens, who face them on a daily basis, and also to public managers responsible for the administration and management of urban space. Such challenges become even greater in large urban centers and metropolises, which are highly populated spaces where the movement of people and in vehicles is intense.
Both aspects mentioned above configure two of the main challenges of urban mobility, together with the expansion of the urban fabric, that is, with the occurrence of a continuous growth of cities, which demands new infrastructure networks and an effective public transport system, with ample coverage capacity.
As we saw, the growth of the fleet of individual vehicles causes slow traffic and long congestion, imposing a challenge of improving circulation, with the expansion of roads and the creation of exclusive lanes for certain modes, such as buses and bicycles, and mainly in the quality and efficiency of public transport, thus attracting a greater number of users. Another challenge linked to the increase in the number of vehicles is the urban pollution, which affects not only cities, but the environmental balance as a whole.
Read too: Conurbation — when a city extends beyond its municipal boundaries due to its growth
Consequence of lack of urban mobility
The lack of urban mobility has consequences for its population and the dynamism of cities. Some of these impacts are:
limited access to the city, which prevents citizens from enjoying all the activities and services offered in the urban space and makes it difficult for them to get around;
delays due to inefficient public transport (need to use more than one bus or subway line to reach the destination, long waiting times, etc.) and/or traffic jams;
slow traffic and traffic jams at peak times rush);
increase of pollution atmospheric and sound in cities;
worsening of the quality of life of the population as a result of the problems mentioned above.
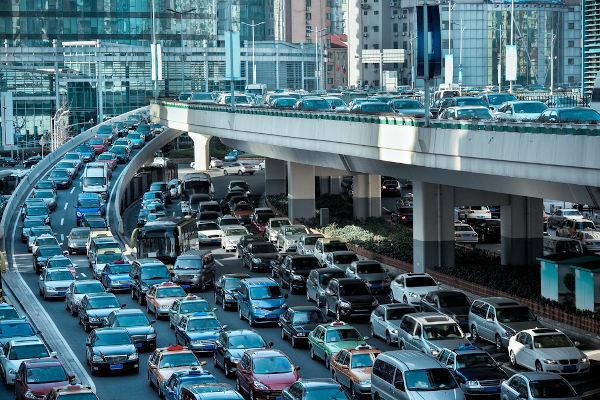

Urban mobility in Brazil
Urban mobility has become one of the main challenges in Brazilian cities, notably in the metropolises and metropolitan regions, which concentrate more than a third of the entire population of Brazil.
The modernization of agriculture and the development of industry Brazilian generated a intense migratory flow towards the cities from the second half of the 20th century, causing the growth of urbanized areas.
Although there has been expansion of the urban fabric and population growth in cities, the infrastructure and transport system has not been expanded or adapted accordingly, resulting in urban mobility problems in large Brazilian cities.
Among others, the common problems in Brazilian urban transport and, therefore, of urban mobility are:
overcrowding of public transport;
long waiting times;
need for transfer;
traffic jams;
scarcity of lines that serve the most distant areas of the city centers;
lack of maintenance of public roads.
It is also important to point out that the fleet of private vehicles, mainly cars, more than doubled in the last decade in Brazil, intensifying traffic in cities and affecting mobility in these spaces. While in 2001 the rate was 168 vehicles per thousand inhabitants, in 2020 this number jumped to 471 vehicles per thousand inhabitants.|1|
Brazilian legislation presents some legal devices that govern the use and occupation of urban land, which includes issues such as urban mobility. Among them are the City Statute (Law 10,257 of July 10, 2001) and the National Urban Mobility Plan (Law 12,587 of January 3, 2012), which provide for the elaboration and execution of urban mobility plans by Brazilian municipalities. To learn more, visit: Urban mobility in Brazil.
Urban mobility in the world

Improvements in urban mobility have become the big issue for cities around the planet, in view of population growth in urban areas, which continues on an upward curve. Today, more than 57% of the world's population lives in cities, while the population growth rate in urbanized areas is 1.73% per year.|2|
In addition to forums dedicated to debate of urban mobility on an international scale, considering the context of technological innovations and the need to seek more sustainable ways of life, one of them part of the World Economic Forum, companies carry out studies about urban mobility in the main world cities.
One of these studies is by an American technology company, Here, which created an Index of Urban Mobility based on four criteria: connectivity, sustainability, innovation and accessibility.
According to data from this index, the five cities with the best urban mobility in the world they are:
Copenhagen (Denmark)
Brussels (Belgium)
vancouver (Canada)
Vienna (Austria)
Zurich (Switzerland)
Sustainable urban mobility
Sustainable urban mobility combines the effectiveness of people's mobility in cities with less aggressive practices, means of transport and habits environment, promoting improvements in the quality of life in urban centers. In order to achieve more sustainable urban mobility, investments in the transport and urban accessibility sector are necessary, in addition to adequate planning measures.
Some practices that help make circulation in cities less harmful to the environment are:
expanding the use of bicycles and the construction of cycle lanes;
adoption of improvements in public transport, thus encouraging its use by a larger portion of the population;
expansion of rail networks in cities, with greater use of means of transport such as trains and subways;
adoption of electric vehicles or vehicles that use clean energy;
reducing the use of fossil fuels;
greater integration of urban transport.
Possible solutions for urban mobility
Some measures can be taken to improve urban mobility in cities in the medium and long term. Among them are:
diversification of the modes of transport used (subways, buses, trains, bicycles, cars);
flexibility of schedules for urban activities and services, avoiding traffic overload and the formation of traffic jams;
integration of different routes and modes of transport;
expanding the coverage of urban transport networks, increasing the integration of urban space;
adoption of improvements in roads and urban infrastructure in general, providing a greater degree of fluidity to the space.
Resolved exercises on urban mobility
question 1
(Fuvest)

The cartoon above, satirizing a problematic situation, common to big cities, suggests the
i. importance of circulation for the dynamics of urban activities, requiring the municipality to produce solutions.
II. hegemony of the private car over collective public transport, resulting in obstacles to the fluidity of road traffic.
III. absence of legal instruments for urban planning, impeding the metropolization process.
It is correct what is stated in:
A) I, only.
B) I and II, only.
C) III, only.
D) II and III, only.
E) I, II and III.
Resolution:
Alternative B
The cartoon addresses issues of urban mobility, such as the importance of flows for urban activities and the current dependence on private vehicles, which results in the adaptation of urban spaces for the circulation of cars and the massive presence of vehicles, conditioning the lack of fluidity of traffic in the cities.
question 2
(And either)
In the 19th century, the higher price of land located in the center of cities was due to the specialization of neighborhoods and their social differentiation. Many people, who do not have the means to pay the high rents of the upscale neighborhoods, are progressively rejected for the periphery, such as the suburbs and the more remote neighborhoods.
RÉMOND, R. The 19th century. São Paulo: Cultrix, 1989 (adapted).
A geographical consequence of the spatial process described in the text is the:
A) creation of closed housing condominiums.
B) decay of the central areas of popular commerce.
C) acceleration of the process known as enclosure.
D) increase in the population's daily commute time.
E) containment of the occupation of spaces without satisfactory infrastructure.
Resolution:
Alternative D
The expansion of the urban fabric and the growth of peripheries can generate an urban mobility problem when there are no transport services. enough transport, causing an increase in the time that the population that lives in these areas takes to move from one point to another of the city.
Grades
|1| FURNISHED. Motorization rate in Brazil: see the increase in 20 years. Mobilize, [2021]. Available here.
|2| CIA. Countries: Cambodia. The World Factbook. Available here.
image credit
[1] William Perugini / Shutterstock
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography Teacher
Discover the relationship and differences between urban and rural, as well as understand the complexity of these concepts.
Understand what urban mobility is and find out what its consequences are in urban space. Also find out about the issue of urban mobility in Brazil.
Click here to learn more about the main urban environmental problems. Understand what its main consequences are for nature and for the population.
An analysis of the public transport problems in the country that served as a trigger for the recent popular uprisings.
Access and learn about the types of existing means of transport. Read about its evolution process and learn more about transport in Brazil.