Awhapada dos guimarães is an area located in state of Mato Grosso, between the cities of Cuiabá and Chapada dos Guimarães, being one of the main tourist destinations in the region. It has a typically tropical climate and relief formed by low terrain, hills and plateaus. Inserted in the Cerrado, the Chapada dos Guimarães is home to an important part of the biodiversity of this biome, in addition to being the source of some of the rivers that feed the Pantanal and other areas of the territory national.
In view of its importance for the maintenance of the local ecosystem and the environment, the Chapada dos Guimarães became a national park in 1989. ICMBio is responsible for its administration and management.
Read too: Caatinga — a uniquely Brazilian biome
Summary about the Chapada dos Guimarães
Chapada dos Guimarães is located in the state of Mato Grosso, between the capital, Cuiabá, and the city of Chapada dos Guimarães.
It was classified as a national park in 1989, and has an area of 32,630 hectares.
Its climate is tropical alternately dry and rainy, with high temperatures most of the year.
Its fauna and flora are typical of the Cerrado, the biome in which this national park is located.
The chapadas, forms delimited by the escarpments, are the main relief feature found in the Guimarães plateau.
It shelters the sources of rivers, some of which feed the Pantanal, and part of the biodiversity of the thick, a biome threatened by fires and increasing deforestation.
Important archaeological sites in the state of Mato Grosso are located in the Chapada dos Guimarães.
It attracts thousands of tourists every year, mainly interested in its natural beauties, such as the Véu da Noiva waterfall.
Location of Chapada dos Guimarães
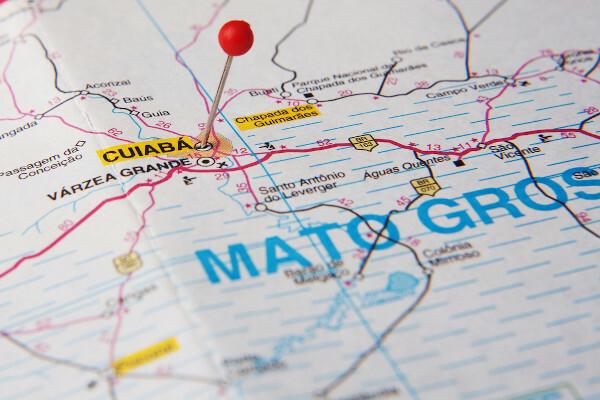
The Chapada dos Guimaraeshe is located nthe state of Mato Grosso, at Midwest region of Brazil. Its area is inserted within the limits of two municipalities in Mato Grosso:
cuiabá;
Chapada dos Guimaraes.
Characteristics of the Guimarães plateau
Chapada dos Guimaraes National Park extends over 32,630 hectares in the south-central region of the state of Mato Grosso, comprising a large area of the state capital, Cuiabá, and the homonymous municipality of Chapada dos Guimarães. The park was established in the year 1989, and is currently under the administration of the Chico Mendes Institute for Conservation and Biodiversity (ICMBio).
→ Climate of the Guimarães plateau
The Guimarães plateau is part of a region oftropic climatel, which undergoes small local changes due to the influence of factors such as relief.
The typical tropical climate of the state of Mato Grosso and the Guimarães plateau is characterized by alternation between a dry season and a rainy season, which takes place in the months of spring It is summer predominantly. To the temperatures are high for most of the year, ranging from highs of 35°C to lows of 17°C. the volume of rains is 1300 mm in the lower regions of the relief and 1600 mm in the areas of greater altitude.|1|
→ Fauna of the Chapada dos Guimarães
The fauna of the Chapada dos Guimarães hastypical animalss from the Brazilian Cerrado, housing a significant portion of the biodiversity of this biome. It is composed of 76 species of mammals, 44 species of fish and 242 species of birds, according to ICMBio.

Among the animals found in the Chapada dos Guimarães are:
Some of the animals found in the Guimarães plateau | ||
macaw |
Ocelot |
seriema |
ema |
tapir |
leather-coated hawk |
Guara wolf |
giant anteater |
butterflies |
Jaguar |
tortoise |
giant armadillo |
→ Vegetation and flora of the Chapada dos Guimarães
The vegetation present in the Guimarães plateau is typical of the biome Wwrong, the second largest biome in Brazil, wheretreees medium-sized shrubs and grasses. It also identifies some areas of forest and ciliary kills, being the second type of vegetation found near the margins of the rivers.
Almost 660 plant species make up the flora of the Chapada dos Guimarães, according to ICMBio. Trees such as jatobás, ipês and buritis can be found in this national park. Fruit species such as the persimmon, mangabeira, jabuticabeira and cashew trees are also identified, as well as different varieties of grass.
→ Relief of the Chapada dos Guimarães

The Guimarães plateau is located on the northwest edge of the Paraná sedimentary basin, a geological structure that was formed through the erosion of very old rocks from the interior of the Brazilian territory.
The relief that characterizes the national park is constituted by low and hilly terrain, little accident, and by the slaps, which are extensive flat and elevated areas delimited by escarpments (steep slopes that mark the abrupt transition from a higher area to another lowered area).|2|
See too: Iguazu Falls — a set of 275 waterfalls located on the border between Brazil and Argentina
Importance of Chapada dos Guimarães
The Chapada dos Guimaraes houses an important portion of the biodiversity of the biome Cerrado, which is threatened for the logging growing and by burned caused by human action for the opening of new areas of agricultural production. As we have seen, there are hundreds of species of plants and animals that live in this natural reserve and depend directly on it for their survival.
The rainfall regime and the relief provide the formation of watercourses in the Chapada dos Guimarães region. this national park home to the source of important rivers that flow through the state of Mato Grosso and neighboring areas, supplying not only the local biomes but also the Pantanal, which extends through the south of Mato Grosso and the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, close to the border with Bolivia and the Paraguay.
Many archaeological sites are present in the Guimarães plateau, where it is possible to identify fossils, remnants of animal and plant life from a distant past, and paintings rock formations, which allow us to know a little more deeply about the process of formation of the state of Mato Grosso and the interior of Brazil, which demonstrates its bigsocio-historical importance. Furthermore, along with natural landscapes, these elements are tourist attractions for the region, which demonstrates its big economic importance.
Tourism in the Chapada dos Guimarães
The Chapada dos Guimaraes is one of the main tourist destinations in the state of Mato Grosso. The national park is responsible for attracting thousands of visitors annually to the region, being of fundamental importance for the tertiary sector from the municipalities of Cuiabá and Chapada dos Guimarães, which have part of their income derived from tourist activities carried out in the reserve.
![Blue lagoon inside the Aroe Jari cave complex, in the Guimarães plateau. [1]](/f/4f8496cfc1bc76a4d6d543052a9e8df0.jpg)
The natural landscapes formed by waterfalls, caves, lakes and forests are the main attractions of the Chapada dos Guimarães. Like this, some of the most visited places they are:
Véu da Noiva waterfall;
Stone Town;
cave circuit;
circuit of the waterfalls;
hill of São Jerônimo;
path of the walls;
valley of the river Claro;
Viewpoint Morro dos Ventos.
Preservation of the Chapada dos Guimarães
The preservation of the Guimarães plateau is essential for maintaining the environmental balance and for protecting an important part of the Cerrado's biodiversity. Despite this, this preservation encounters some difficulties arising from the fact that the Chapada dos Guimarães is located in a region that has farming one of its economic pillars. The opening of new areas for the practice of this activity has caused an increase in the rates of Cerrado deforestation and intensification of the occurrence of fires, harmful both to the vegetation and to the air.
Thinking about this need for preservation, the Chapada dos Guimarães was turned into Pbow nnational on April 12, 1989, and is currently administered by ICMBio. The classification of any area as a national park makes it a conservation and preservation unit. environment, thus ensuring the ecosystem balance, the maintenance of archaeological sites and the realization of tourism sustainable.
Grades
|1| It is |2| ROSS, Jurandyr Luciano Sanches. Chapada dos Guimarães: Edge of the Paraná Basin. Magazine of the Geography Department – USP, Volume 28 (2014), p. 180-197. Available here.
image credit
[1] Caio Pederneiras / Shutterstock
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography Teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/brasil/chapada-dos-guimaraes.htm
