What became known in posterity as the “Seven Wonders of the World” was a set of works made by man, who were named and listed by the Greeks for the purpose of presenting “the seven things worthy of being views”. The works were distinguished by their beauty, grandeur, sumptuousness and magnitude.
Even though it was the Greeks who listed the "Ta hepta Thaemata", as they called them, only one was located in Greece, the "Statue of Zeus", the others were in other locations. the Colossus of Rodhes in Asia Minor; the Temple of Artemis and the Mausoleum of Helicarnassus in Ephesus; The Pyramids of Giza and the Lighthouse of Alexandria, Egypt; and The Hanging Gardens of Babylon, in present-day Iraq.
Let's know a little more about these wonders:

The Great Pyramid of Giza
Built by the Egyptians about 4,500 years ago, it is the only ancient wonder still in existence. Built around 2,500 a. Ç. as a funerary monument to King Cheops, it is the largest of the three pyramids at Giza. According to the Greek historian Herodotus, 100,000 men worked for 20 years to build the pyramid. Its construction reveals a great knowledge of geography, astronomy, geology, mathematics and other sciences on the part of the Egyptian builders.

Hanging Gardens of Babylon
Supposedly created by king Nebucodonosor in 605 a. Ç. to present his wife, Queen Amyitis, in the city of Babylon, in Mesopotamia, the Hanging Gardens consisted of an architectural structure of terraces that contained a multitude of species of fauna and flora. It is not known for sure whether the Hanging Gardens of Babylon existed, however, archaeological excavations carried out in the 19th century have found possible signs of their existence.

The Statue of Zeus
Measuring 10 to 15 meters high and located in the temple of Olympia in Greece, the statue was built in gold and ivory for eight years, around 450 BC. Ç. The sculptor Phidias depicted Zeus sitting on his throne, indicating his superiority over the other gods of the Greek pantheon. The statue was transported to the center of the Eastern Roman Empire, Constantinople, and there it was destroyed in a fire around 470 AD. Ç.

the temple of Artemis
The Temple to the goddess Artemis, of Ephesus (present-day Turkey), was built, rebuilt and enlarged several times over the centuries, until around 262 AD. a., was destroyed during the barbarian invasion of the godos. Possible remains can be found today in the British Museum.
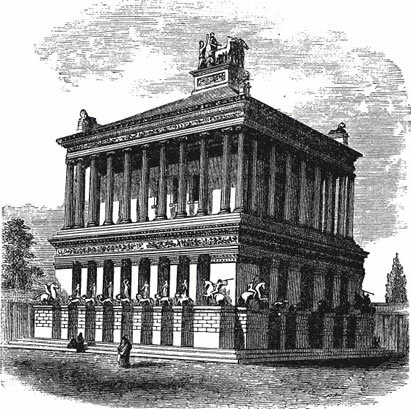
The Mausoleum of Halicarnassus
Built around 350 BC C., at the behest of Queen Artemisia, with the intention of sheltering the mortal remains of her husband and brother, King Mausolus, the mausoleum was also located in Turkey. It was destroyed around the 15th century by constant earthquakes and its remains were used in other constructions.

The Colossus of Rhodes
The Colossus of Rhodes was a 33 meter bronze statue, built in Greece around 300 BC. C., to honor the god Helios (god of the Sun) due to the aid in the victory over the army of Demetrius Pollorcetes. The statue remained standing for 50 years, when it was destroyed by an earthquake that devastated the city of Rhodes in 226 BC. Ç.

Lighthouse of Alexandria
Made of marble and mortar, the lighthouse was built by the Greek architect Sóstratus de Cnidus, around 250 BC. C., to guide sailors on their night voyages. It withstood several earthquakes, but began to collapse around the fourth century.
By Tales Pinto
Graduated in History
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/historia/sete-maravilhas-mundo.htm
