Plants are beings that are part of the Plantae Kingdom, also known as the Metaphyta Kingdom. Organisms classified in this Kingdom must be:
- multicellular: Beings that have many cells;
- eukaryotes: Cells with a true nucleus that holds the DNA;
- autotrophs: Produce their own energy reserve, usually glucose, through photosynthesis. Most plants carry out photosynthesis, but some are parasitic;
- real fabrics: Cells that are grouped by similarities in function and shape.
In the past, both algae and fungi were classified in the Kingdom Plantae. However, for not meeting all the attributes, they were reclassified in other biological Kingdoms, Protista and Fungi, respectively.
Plant characteristics
According to German botanist Matthias Schleiden, all plants have cells, so they are considered living beings. This argument forms part of cell theory prepared by him and the physiologist Theodor Schwann.
Plants are usually green because of the pigment called chlorophyll. This pigment is responsible for carrying out photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, the plant captures sunlight, or artificial light, and transforms it into organic molecules with energetic function, the
glucose.
Plants are sessile beings, that is, they need to be fixed in one place. They are usually found in the soil, but can grow supported by other plants (epiphytes), rocks (lithophytes) or in water (hydrophytes).
They perform respiration, like any other organism, capturing oxygen from the atmosphere and releasing carbon dioxide. However, on the other hand, they carry out photosynthesis, which is an opposite process, that is, they capture carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
know more: plant kingdom
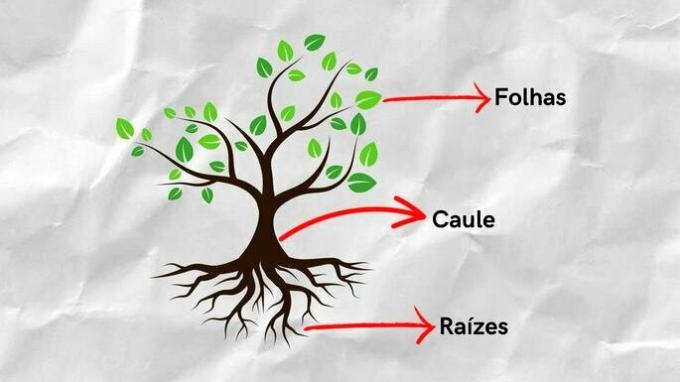
plant parts
The organisms of this Kingdom are divided into lower plants and higher plants. The basic parts of higher plants are the roots, stem and leaves, each of which has specific functions for the organism.
- roots: They help to obtain water and mineral salts from the soil;
- Stalk: Contributes to the support and transport of elaborate sap (assimilated phyto) and raw sap (water and mineral salts);
- Sheets: They carry out respiration, transpiration, guttation and photosynthesis.
Know more:
- Botany: the study of plants
- types of roots
- types of stems
- Sheets
Plant function
Plants are protective organisms of the planet earth, as they carry out the maintenance and management of environmental events at all times. They produce oxygen along with algae, protect the soil from erosion and landslides, and participate in the water cycle.
They are the producers of the food chain, that is, they feed all living beings, directly or indirectly. They serve as medicine, as they contain substances of interest medicinal for science and are used in civil construction.

The 4 types of plants: classification
At Bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms are 4 plant groups commonly studied in botany. Bryophthias and Pteridophytes are considered lower plants, so they need moisture and shade to live and reproduce, as their spores are released into the water for the birth of new organisms.
Gymnosperms and Angiosperms are superior plants, as they live independently of moisture or shade, in addition to reproducing through pollination. The types of pollination are:
- anemophilia: Pollen travels through the wind to reach the ovary;
- chiropterophilia: Pollen carried by bats to the ovary;
- ornithophily: Pollen carried by birds to the ovary;
- entomophilia: Pollen carried by insects to the ovary;
- mastophilia: Pollen carried by mammals to the ovary.
They are divided into inferior and superior not because they are better or worse, but because of important processes. evolutionary. Therefore, plants are classified according to their complexity and emergence of new attributes, such as seed, flower and fruit.
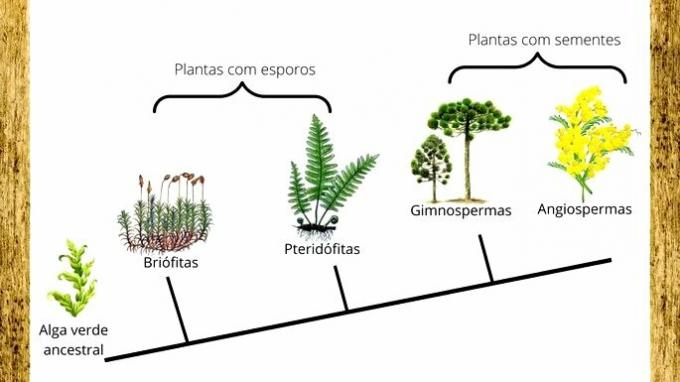
Bryophytes
Bryophytes are small plants, as they do not have sap-conducting vessels (avascular), live in shady and humid places.
your representatives, the mosses, reproduce through spores, as they do not produce seeds, which are released into the water. They are often found in closed forests, always close to water bodies.

Know more: Bryophytes
pteridophytes
Pteridophytes are currently divided into two groups, the Monilophytes and the Lycophytes. Monilophytes are represented by Ferns, and Lycophytes are all other Pteridophytes (fern, tree fern, etc.).
These are plants that, despite having sap-conducting vessels, need moisture and shade, as their reproduction also occurs by spores.

Know more: pteridophytes
gymnosperms
Gymnosperms are represented by large plants, usually trees, have sap conducting vessels and seeds.
Its pollination occurs by the wind, however, they do not produce fruits or flowers. Its best-known representatives are the Pine trees, redwoods and araucarias (Brazilian pine).

know more: gymnosperms
angiosperms
Angiosperms represent the best adapted and evolved group of plants in nature. have flowers, fruits and seeds, in addition to sap conducting vessels, in addition to a range of chemical substances of medicinal interest.
show habits herbaceous (herbs), shrubby (bushes), arboreal (trees), climber (vines) and parasite. They are usually found in soil, as well as in water, on rocks and supported by other plants.

Know more:
- angiosperms
Bibliographic references
RAVEN, P. H.; EVERT, R. F.; EICHHORN, S. AND. plant biology. 4. ed. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan, 2014. P. 18–37.
- Exercises on Kingdom Plantae (with annotated feedback)
- plant kingdom
- Botany: The study of plants
- Plant parts
- gymnosperms
- angiosperms
- Fungi questions
- pteridophytes