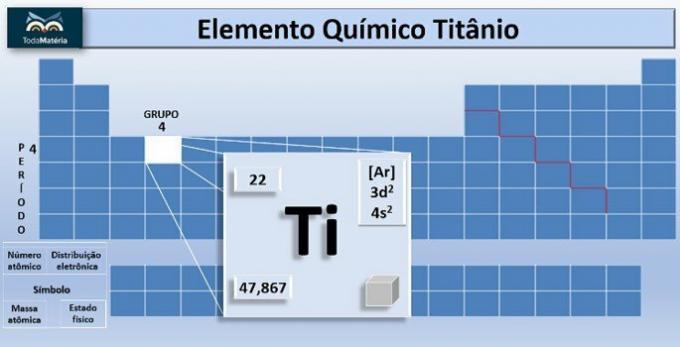
O titanium is the chemical element with symbol Ti and atomic number, that is, number of protons equal to 22. This metal is located in group 4 and 4 of the periodic table.
The atomic mass of the element is 47.867 u, and because it has 22 electrons in the atom's electrons, its electron distribution is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2.
Titanium has desirable properties for numerous applications as it is as strong as steel and much lighter.
Because it is a ductile, refractory, corrosion resistant metal, it presents mechanical resistance, thermal stability and low reactivity, it is added to metal alloys so that they have a high performance. Its biocompatibility and non-toxicity also make it useful for making bone prostheses.
The main characteristics of titanium are:
- Melting point: 1668 °C
- Boiling point: 3287 °C
- Density: 4.5 g/cm3
- Color: silver gray
- Physical state at 20 °C: solid
- Isotopes: Ti46, you47, you48, you49 and you50
This chemical element was discovered by the Englishman William Gregor in 1791 and its name, derived from the Greek titans, was later attributed by Martin Heinrich Klaproth.
Titanium is the ninth most abundant element on the planet and is found in the earth's crust in ores such as rutile (TiO2) and ilmenite (FeTiO3). Therefore, mining is the main method of obtaining this metal.
What is titanium used for?
Because it is chemically unreactive at room temperature, easily molded, has high mechanical and corrosion resistance, titanium is used as a strategic metal.
The aviation and aerospace industries are the main users of titanium for the production of parts, such as turbine and fuselage components. Other applications are the manufacture of dental prostheses, surgical implants and jewelry.
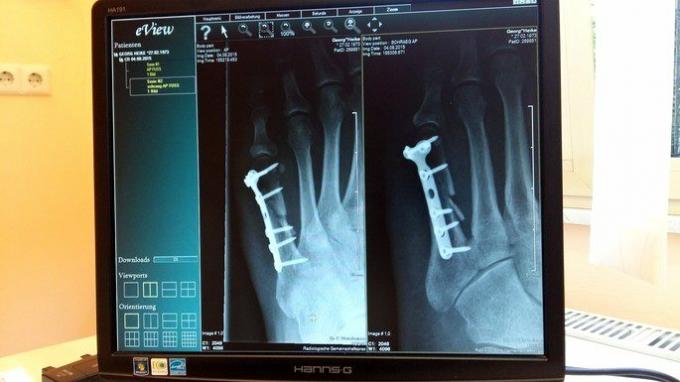
In medicine, titanium is very useful because of its compatibility with human tissues, lightness and strength. It is used for the production of implants for body parts, such as fixation screws, knee joint replacement, humerus prosthesis, hip prosthesis, among others.
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is one of the main compounds of this element, being used as a bleaching agent. Generally, high quality white inks use it to improve the visual appearance of color and gloss. Other products, such as toothpastes and sunscreens, also use the pigment. There is also application as a food coloring added in dairy products, sweets and beverages.
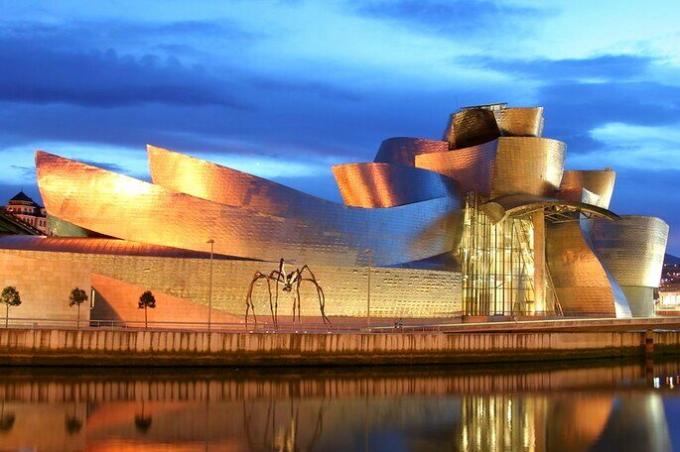
In architecture, we can see the use of titanium to cover curved structures at the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao, northern Spain.

In everyday life we can find numerous products that have titanium in their composition, such as bicycle frames, eyeglasses and tennis rackets.
In the chemical industry, titanium is used as a catalyst for reactions. In this way, it makes it possible to control the reaction speed and reduce the time for product formation without affecting the composition of the substances.
The automobile industry has studied the incorporation of titanium in the manufacture of cars to reduce their mass and, thus, reduce fuel consumption and increase their acceleration.
Gain more knowledge with the contents:
- Chemical elements
- Periodic table
- What are metals?
Bibliographic references
ATKINS, P.W.; JONES, L. Principles of chemistry: questioning modern life and the environment. 3.ed. Porto Alegre: Bookman, 2006.
FELTRE, R. Fundamentals of Chemistry: vol. single. 4th ed. Sao Paulo: Moderna, 2005.
Lee, J. D. Not so concise inorganic chemistry. Translation of the 5th ed. English. Publisher Edgard Blucher Ltd. 1999.