THE thyroid is gland endocrine shaped like a butterfly, with two lobes that connect in the midline. The thyroid is known mainly for producing the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), but it also produces the hormone calcitonin, which works by reducing blood calcium.
The hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine act on metabolism, and changes in their production lead to health problems. Hypothyroidism is characterized by a reduced secretion of T3 and T4, when these hormones are produced in excess, it is called hyperthyroidism.
Read more: Endocrine system — made up of glands and tissues that release substances known as hormones
Thyroid summary
The thyroid is located at the base of the neck and has two lobes, which are located on either side of the trachea.
It is an endocrine gland, therefore, it secretes hormones that are released into the bloodstream.
It produces triiodothyronine and thyroxine, known respectively as T3 and T4, and related to the body's metabolism.
When it produces large amounts of T3 and T4 hormones, we have a case of hyperthyroidism.
When it produces too few T3 and T4 hormones, we have a case of hypothyroidism.
It also produces calcitonin, a hormone that works by reducing calcium levels in the body.
Thyroid
the thyroid is an endocrine gland composed of two lobes, which are arranged on each side of the trachea and are connected in the midline. It is located in the anterior part of the neck, below the region called the Adam's apple. She is made up of thousands of follicles, small spheres that are between 0.2-0.9 mm in diameter. In an adult person, the thyroid has between 20-30 grams.
thyroid functions
The thyroid, as pointed out, is an endocrine gland, that is, responsible for release secretions known as hormones directly into the bloodstream. The thyroid produces the hormones triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4) and calcitonin.
thyroid hormones
The thyroid is a gland that produces different hormones, the triiodothyronine (T3) and Thethyroxine (T4) the best known. These two hormones are related to the maintenance of metabolic processes in the body, exerting effects on all systems of the body. Human Body.
Another important hormone produced by the thyroid is calcitonin, which acts by inhibiting the resorption of bone tissue, thereby decreasing calcium levels in the blood. Its secretion is activated by increasing the concentration of calcium in blood plasma.
Read more: Pancreas — an important gland in our body responsible for producing the hormones insulin and glucagon
Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism
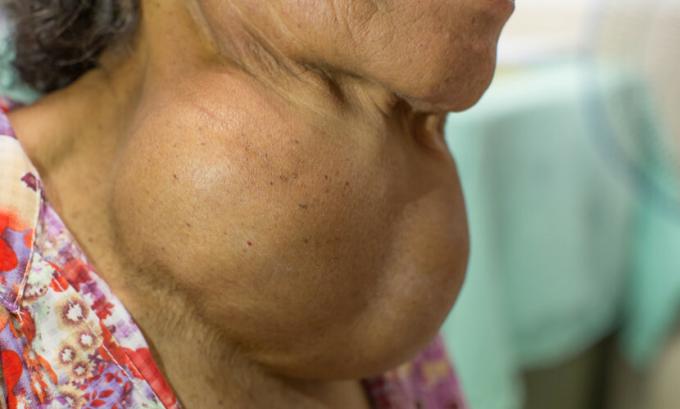
Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are two problems that affect the thyroid gland.
hypothyroidism: characterized by a reduction in the production of T3 and T4 hormones. This reduction leads to symptoms such as excessive tiredness, skin dryness, hair loss, weight gain, slowing of the heart beat, irregular menstruation, constipation, memory loss and depression.
Hyperthyroidism: It is a more common condition in women. It is important to highlight that, in newborns, hyperthyroidism can be diagnosed through the foot test. It differs from hypothyroidism by presenting, unlike it, an excessive production of T3 and T4 hormones. Hyperthyroidism can trigger a rapid heartbeat, shaky hands, loss of appetite, nervousness, anxiety, irritation, hair loss, considerable weight loss, among others problems.
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can cause a condition known as goiter. THE goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid and can be detected through physical examination.
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can be treated. Usually, medication is used in order to maintain adequate hormone levels, and, in some cases, treatment is carried out for the patient's entire life. Thyroid dysfunctions should be monitored and treated by an endocrinologist.

