THE periodic classification of elements was proposed in 1913 by Henry Monseley (1887-1915), who identified the periodic variation of many properties at regular intervals according to the number of protons in the nucleus of an element's atom chemical.
Because of the Law of Periodicity, the criterion used to organize the elements of the current Periodic Table is the ascending order of atomic number (Z).
The 118 chemical elements are arranged in groups and periods of the Periodic Table. According to the physical and chemical properties, it is possible to distinguish between metals, non metals (nonmetals) and semimetals (metalloids).

The vertical lines are the 18 groups the table and bring together elements with similar chemical properties. The horizontal lines correspond to the 7 periods and presents the elements with the same number of electronic layers.
Hydrogen is an element that is positioned above group 1 because of its electronic distribution, but it has no characteristics in common with them.
Check out the Periodic table complete and updated.
metals
Most chemical elements in the Periodic Table are classified as metals. The main characteristics of metals are:
- They have a characteristic shine;
- They are dense, malleable and ductile;
- They are good conductors of electricity and heat;
- They are present under ambient conditions in the solid state, with the exception of mercury.
The metallic elements of the Periodic Table are:
alkali metals (group1): lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium and francium.
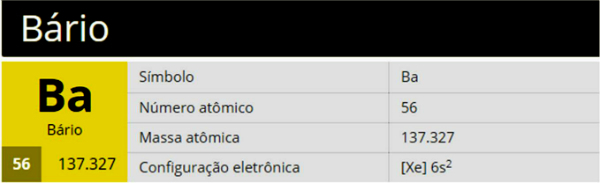
alkaline earth metals (group 2): beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium and radium.
Representative Matters, in addition to the elements of groups 1 and 2, are: aluminum, gallium, indium, thallium, nion, tin, lead, flerovium, bismuth, muscovium and livermorium.
Outer transition metals are the elements that occupy the central part of the Periodic Table:
- Group 3: scandium and yttrium.
- Group 4: titanium, zirconium, hafnium and rutherfordium.
- Group 5: vanadium, niobium, tantalum and dubnium.
- Group 6: chromium, molybdenum, tungsten and seaborgium.
- Group 7: manganese, technetium, rhenium and bohrium.
- Group 8: iron, ruthenium, osmium and hassium.
- Group 9: cobalt, rhodium, iridium and meitnerium.
- Group 10: nickel, palladium, platinum, darmstadium.
- Group 11: copper, silver, gold and roentgen.
- Group 12: zinc, cadmium, mercury and copernicium.
Internal transition metals are the elements that are part of group 3 and correspond to the elements of the lanthanide and actinide series.
The lanthanide series consists of lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium and lutetium.
The actinide series contains the elements actinium, thorium, protactinium, uranium, neptunium, plutonium, americium, curium, berkelium, californium, einsteinium, fermium, mendelevium, nobelium and laurence.
Read more about the alkali metals.
non metals
Non-metals are located in the right part of the Periodic Table and have opposite characteristics to metals, for example:
- They do not have a shiny appearance;
- They are not good conductors of electricity and heat, so they are used as insulators;
- They have low boiling and melting points, so many are found in nature in the liquid state.
You non-metallic elements of the Periodic Table are: hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, carbon, phosphorus, selenium, sulfur, halogens and noble gases.
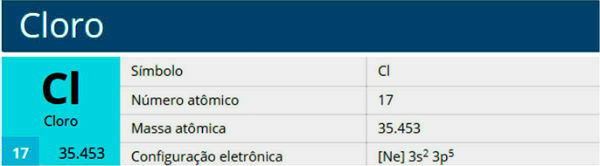
You halogens are the elements that belong to group 17: fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, tenessine and the noble gas family.
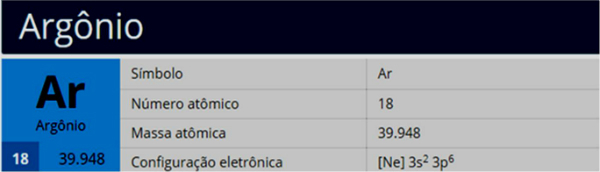
You noble gases are the elements that belong to group 18: helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon, oganesson.
Learn more about the noble gases and the halogens.
semimetals
The semimetals or metalloids are: boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium and polonium. These elements have characteristics that are intermediate between metals and nonmetals.
Also read about the periodic table families.
Representative and transition elements
Another way of classifying elements is by dividing them into representative and transition elements according to the electronic distribution of the atom.
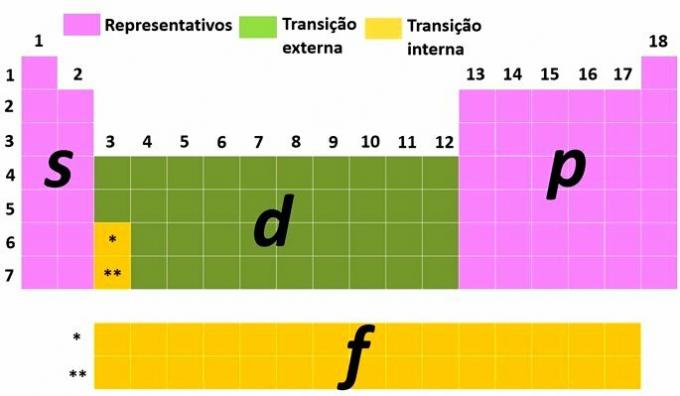
You representative elements are those that have the electronic configuration ending with the most energetic sublevel in s (groups 1 and 2) or for (groups 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 and 18).

You transition elements are separated into external transition, with the elements that have the most energetic electron in the sublevel d and those of internal transition, where the most energetic electron is in a sublevel f.

Gain more knowledge with the contents:
- periodic properties
- Periodic Table Exercises
- Exercises on Organization of the Periodic Table