As the name implies, the main purpose of the products used as moisturizers for the body is retain water on the skin, that is, keeping the skin hydrated, preventing excessive water loss. This is necessary because the amount of water in the skin is greater than in the environment, so it tends to evaporate; in addition, the action of the soap favors dryness.
In most moisturizers, the main ingredient is the lanolin, a mixture of fatty acids (fats) and their esters, obtained as a by-product of cleaning sheep wool. Lanolin is also present in soaps and fabric softeners. Its long chains have polar ends, which can bind to water, allowing it to act as a moisturizer.
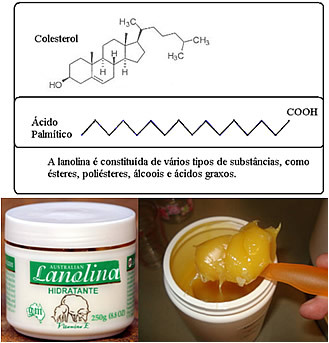
Substances used for this purpose to prevent water loss are called humectants or emollients (softeners)and are added to other products as well. For example, to prevent toothpaste from drying out (as occurs when you leave it uncapped), humectant is added, improving the product's appearance and consistency.
Humectants are also used in other cosmetics to prevent crystallization, such as skin lotions and soaps. The food industry uses them in sweets, breads, cakes, chocolates, candies, chocolates and fillings. And they are added to the glue, to prevent it from drying out quickly.
One of the most used humectants in skin moisturizers is glycerin (propan-1,2,3-triol), also called glycerol(Ç3H5(OH)3). Its structural formula is shown below:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
H2C CH ─ CH2
│ │ │
OH OH OH
Note that glycerin is a trialcohol, and thanks to this structure, oxygens activate hydrogens, so that the formation of hydrogen bonds, both between the glycerin molecules themselves, and between them and the water molecules.
At room temperature, glycerin is a viscous liquid, similar to syrup, precisely because of the hydrogen bonds, which cause its molecules to stick together.
The hydrogen bonds between glycerin and water molecules explain its use in skin moisturizers. This interaction can be represented by:
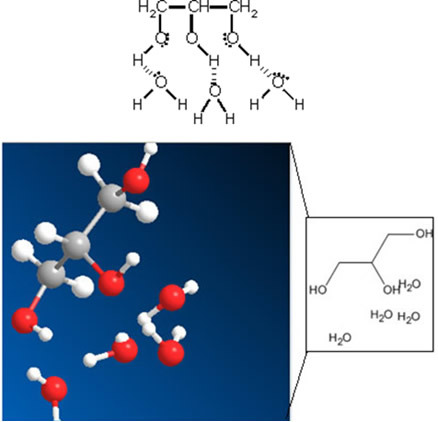
Therefore, this humectant is considered a hygroscopic substance, that is, one that absorbs water.
Another substance used in moisturizing creams and other cosmetics as a humectant is collagen.
The use of moisturizers should be carried out to restore the skin's natural moisture, whenever it is dry and after prolonged exposure to the sun.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Skin moisturizers"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/hidratantes-para-pele.htm. Accessed on July 27, 2021.
Chemistry

Transition Elements, Permanent Tattoo, Henna Tattoo, Mercury Sulfide, Cadmium Salts, Chromium Salts, Iron Salts, Titanium Oxide, Cobalt Salts, Carbon.

