deal with the artificial juice chemistry is talk about all substances that are part of its composition, as well as the specification of the action of each one of them in the formulation of this industrialized product so consumed by the population. We have easy access to artificial juices of various brands and flavors on the market. There are many people who consume this type of product daily without knowing very well the components used in its manufacture.
As if it is an artificial product, what is least found in it is the fruit itself. this kind of juice it's just a mixture of sugars, colorings and preservatives without any nutritional value. Unfortunately, more than 70% of its content is sugar. However, in this text, we are not going to focus on the nutritional nature of powdered juice, but on its chemical composition.
In addition to all the important functions of each of the components of artificial juice, we will have access in this text to its structural formulas. The main components that can be part of the composition of artificial powder juice are:
a) Antioxidants
Antioxidants are chemical substances that delay the appearance of oxidative changes in a food. Examples of oxidative changes are discoloration, deterioration and rancidity.
Ascorbic acid or vitamin C
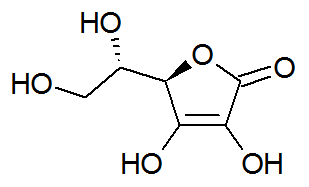
Chemical structure of ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid, popularly known as vitamin C, is a long-chain organic compound and has the following organic functions: enol, alcohol and ester.
Tocopherol or Vitamin E

Chemical Structure of Tocopherol
Tocopherol, popularly known as vitamin E, is a long-chain organic compound and has the following organic functions: phenol and ether.
b) Flavorings
Flavorings are chemical substances that can be natural or artificial. They are used in powdered juice for provide characteristic odor and taste of a particular fruit. Artificial ones are most used due to their low manufacturing cost.
In general, many of the flavorings are esters, derived from chemical reaction of esterification between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Some examples are:
Ethyl Butanoate
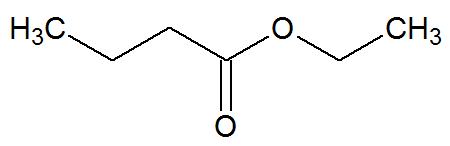
Chemical structure of ethyl nutanoate
It is the ester that mimics the taste and odor of pineapple. It originates from the esterification reaction between butanoic acid and ethanol.
octyl acetate
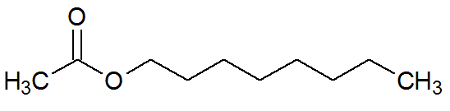
Chemical Structure of Octyl Acetate
It is the ester that mimics the taste and odor of oranges. It originates from the esterification reaction between ethanoic acid and octan-1-ol.
isobutyl ethanoate
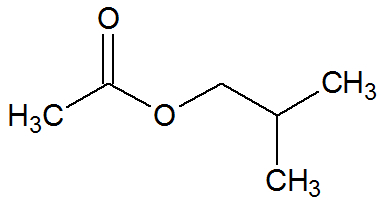
Chemical Structure of Isobutyl Ethanoate
It is the ester that mimics the flavor and odor of strawberry. It originates from the esterification reaction between ethanoic acid and 2-methyl-propan-1-ol.
c) pH regulator
These are substances added to artificial juice to avoid large variations in the product's pH before and after preparation.
fumaric acid
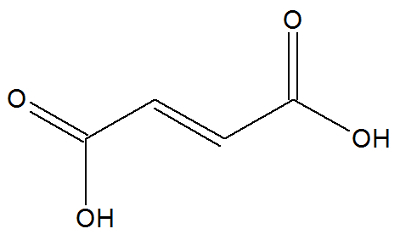
Chemical structure of fumaric acid
Fumaric acid is a long-chain organic compound and its organic function is carboxylic acid.
Citric acid
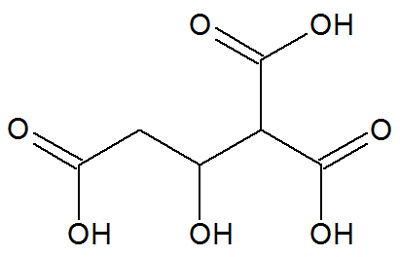
Chemical structure of citric acid
Citric acid, a long-chain organic compound, has the following organic functions: carboxylic acid and alcohol.
Potassium citrate

Chemical Structure of Potassium Citrate
Potassium citrate, a long-chain organic compound, has the following organic functions: potassium salt, carboxylic acid and alcohol.
Sodium citrate
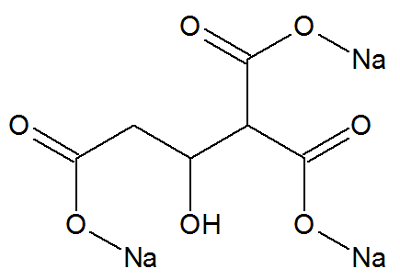
Chemical Structure of Sodium Citrate
Sodium citrate, a long-chain organic compound, has the following organic functions: carboxylic acid sodium salt and alcohol.
d) Sweeteners (sweeteners)
They are natural or artificial substances that are intended to sweeten a certain food.
Acesulfam Potassium
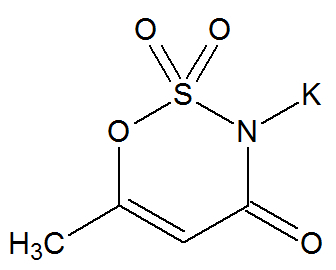
Chemical Structure of Acesulfame Potassium
Potassium acesulfame, a long-chain organic compound, has the following organic functions: amide with potassium and sulfoethoxy.
Crystal Sugar
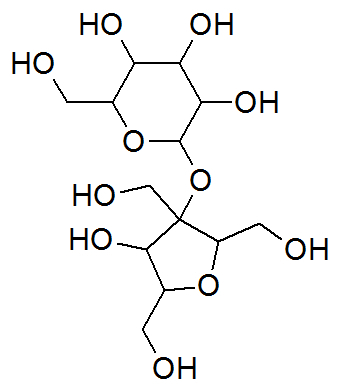
Chemical structure of sucrose
Crystal sugar, known as sucrose, a long-chain organic compound, has the following organic functions: alcohol and ether. It is the only sweetener in powdered juice of natural origin.
aspartame

Chemical structure of aspartame
Aspartame, a long-chain organic compound, has the following organic functions: carboxylic acid, ester, amide and amine.
Sodium cyclamate
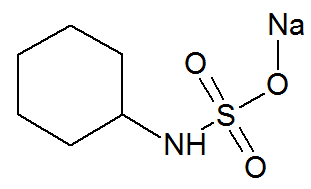
Chemical Structure of Sodium Cyclamate
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Sodium cyclamate, a long-chain organic compound, has the following organic functions: amine and sodium sulphide salt.
maltodextrin
Maltodextrin, a long-chain organic compound, has the following organic functions: alcohol and ether. It is a sweetener that is slowly absorbed by the body, providing gradual energy.

Chemical structure of Maltodextrin
Sodium saccharin

Chemical structure of sodium saccharin
Sodium saccharin, a long-chain organic compound, has the following organic functions: sodium amide and sulfur dioxide.
e) Wetting agents and Anti-wetting agents
Humectants are substances used in powdered juice in order to facilitate the dissolution of the product in water. Furthermore, they have the important function of controlling the presence and development of microbes in the product.
Anti-humectants, on the other hand, are substances added to powdered juice to prevent them from absorbing the moisture present in the air and keeping the dry appearance we are used to repairing. If it absorbed moisture from the air, we would have the occurrence of a grouping of particles that make up the product.
tricalcium phosphate
Its chemical formula is Ca3(DUST4)2. It is a substance with ionic characteristics because it has a metal in its composition. Its function in the composition of artificial juice is that of a humectant, as it helps to prevent oxidative rancidity, that is, it improves the final flavor of the product.
Silicon dioxide
Its chemical formula is SiO2. It is an ionic oxide because it has a metal in its composition. Its function is to reduce the hygroscopic capacity (absorb moisture from the air) of the artificial juice. Furthermore, it is a source of extra silicon, as silicon plays an important role in bone development.
Sodium dioctyl sulfosuccinate

Chemical Structure of Sodium Dioctyl Sulfosuccinate
Sodium dioctyl sulfosuccinate, a long-chain organic compound, has the following organic functions: ester and sulphured sodium salt. It has the ability to act as a humectant, emulsifier (facilitates material dispersion) and dispersant (helps to dissolve the product in water).
f) Thickeners - Stabilizers
The thickener is a chemical substance whose function is to increase the viscosity, texture and consistency of a processed food. The stabilizer is a substance that is added to a processed food in order to maintain the physical characteristics of the product.
arabic gum
It is a natural resin, more precisely a mixture of polysaccharide (95%), glycoprotein, polyphenols and minerals (magnesium, potassium, calcium and sodium), whose chemical composition has a wide variety of monosaccharides, such as D-galactose, L-arabinose, L-rhamnose and acid D-glucuronic.
Representation of the structure of the Arabica galactose resin
Black ovoid structures can be chains of galactose, arabinose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid units or methyl glucuronic acid.
xanthan gum
It is a heteropolysaccharide obtained by fermentation by Xanthomonas campestris bacteria. It has a main chain with glucose units linked to triglyceride branches. It is a polysaccharide whose structural formula is C35H49O29.
Sodium carboxymethylcellulose

Chemical structure of carboxymethylcellulose
Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is a polymer derived from cellulose and is formed from the reaction of cellulose with acetic acid in an alkaline medium with subsequent association with sodium cations.
d) Other Additives
Sodium Chloride
Its chemical formula is NaCl, a ionic compound. Its function in the composition of artificial juice is to help preserve the product.
cloudy
The substance with a clouding function is used in the artificial juice to act as a provider of turbidity (reduced transparency). An example of a turbidity is TiO2 (titanium dioxide), an ionic oxide.
Retinol
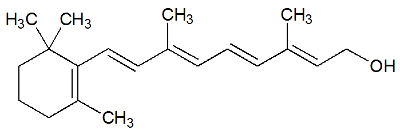
Chemical Structure of Retinol
Retinol is vitamin A, a long-chain organic compound that has the alcohol functional group. It is used in the composition of artificial juice to help replace vitamin A in the body.
calcium lactate
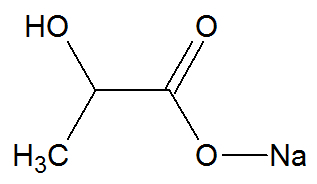
Chemical structure of calcium lactate
Sodium lactate is an organic compound that has two different organic functions in its structure: the alcohol function and the carboxylic acid salt function. It is part of the composition of powdered juice as it acts as an antioxidant and stabilizer.
Potassium phosphate
Its chemical formula is K3DUST4 and it is an ionic compound. Its function in the composition of the artificial juice is that of a stabilizer, as it helps to maintain the physical properties of the food, keeping the homogeneity of the products and preventing the separation of the different ingredients that make up its formula.
Potassium chloride
Its chemical formula is KCl. It is an ionic compound because it has a metal associated with a non-metal. Its function in the composition of the artificial juice is that of a stabilizer, as it maintains the physical properties of the food, the homogeneity of the products and prevents the separation of the different ingredients that make up its formula.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias



