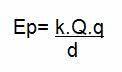Torque, or moment of a force, is the tendency that a strength it has to rotate a body on which it is applied. The torque is a vectorperpendicular to the plane formed by the vectors strength and Rayinrotation. The torque vector can be calculated using the cross product of force and distance.
Whenever a force is applied some distance from the axis of rotation of a body, that body is subject to rotation. If this body is not rotating or rotates with constant angular velocity, we say he is in balancerotational. The rotational balance indicates that the resultantFromtorques that act on a body is null and, therefore, this body rotates with constant or zero speed. In other words, when the torqueresultant about a body is null, this body notit presentsaccelerationangular.
O torque can be understood as the agentdynamic of rotations. In this way, it is to rotational movements, as force is to translational movements. If we want to make a body rotate around some point, we must torque it.
torque unit
The torque unit, according to the
International System, and the Newtontimessubway (N.m). By definition, when a body is rotated in the senseschedule, your torque is negative; otherwise, the torque applied to it has modulepositive. In addition, the direction and direction of the torque vector can be easily determined using the right hand rule. Check out the following diagram:
Torque can be determined by closing the hand towards force (F). It is determined by the direction of the thumb.
Formula
The torque modulus can be calculated by the product of force, distance and the sine of the angle that is formed between these two quantities:
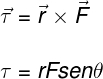
τ – torque
r - Ray
F - strength
θ – angle between r and F
In the formula above, θ is the angle formed between the radius of rotation (r) and the force (F). In the case where the force is applied with an angle of 90° to the radius (r), the sine of the angle is equal to 1. The radius (r) is determined by the distance from the application point to the axis of rotation of the body and is also known as the lever arm. The longer the lever arm on a body, the easier it is to rotate it.
Torque and Angular Moment
The torque is the agentdynamic of rotation. When we apply torque on some body, that body can gain velocityangular, going on to describe a rotational movement. We say that when a body is in rotation, it has timeangular. The angular momentum is the analogue rotational of timelinear, also known as the amountinmovement, therefore, we can understand that angular momentum is the amount of rotational motion of a body or system.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
When the resulting torque on a body is null, your timeangular remains constant, otherwise the angular momentum would change.
Similar to force, which can be written as the temporal variation of momentum, torque can be understood as the variation in angular momentum in relation to time.
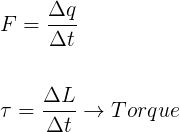
Angular momentum, in turn, can be calculated by the cross product of the body's position and its momentum. The angular momentum modulus of a rotating body is determined by:

L – angular momentum (kg.m²/s)
r – path radius (m)
Q – amount of movement (kg.m/s)
θ – angle between r and Q
Torque Examples
When we open a door, we apply force at a point away from its rotation axis, thus, we print a greater torque on it.
When pedaling on a gear bike, it is possible to notice that the greater the diameter of its crown, the greater the torque produced by each pedal stroke.
When using a screwdriver, you can see that the larger the diameter of your cable, the easier it will be to tighten or remove screws.
Torque Solved Exercises
1) A force of 50 N is applied at a 45° angle to a 0.25 m lever arm, causing a crank to rotate counterclockwise.
Data: sin 45º = √2/2
a) Determine the direction and direction of the torque exerted on the crank.
b) Calculate the torque performed on the crank.
Resolution
a) According to the right hand rule, the torque is in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the handle, and its direction points towards the plane of the door.
b) Using the torque formula and exercise data, let's do the following calculation:

2) A torque of 100 N.m is applied at a distance of 25 cm from the axis of rotation of a body. Determine the magnitude of the force perpendicular to the plane of rotation of this body and calculate the variation in angular momentum suffered by this body in a time interval of 3 s.
Resolution
To calculate the intensity of the force perpendicular to the axis of rotation, we will use the torque definition and exercise data:
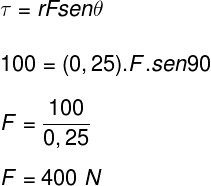
To determine the variation in angular momentum suffered by this body, let's do the following calculation:

By Me. Rafael Helerbrock
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
HELERBROCK, Rafael. "Torque"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/torque-uma-forca.htm. Accessed on July 27, 2021.