electrostatics it is the part of the area of electricity that studies electrical charges without movement, that is, in a state of rest.
Electrostatic Shield
Electrostatic shielding makes the electric field null. This happens due to the distribution of excess electrical charges in a conductor. Charges of the same sign tend to move away until they come to rest.
That's what Michael Faraday proved with the Faraday's Cage. In this experiment, the chemist sat inside a cage that was subjected to an electrical discharge and left it without anything happening to him.
Also read about:
- Faraday's law
- Faraday's constant
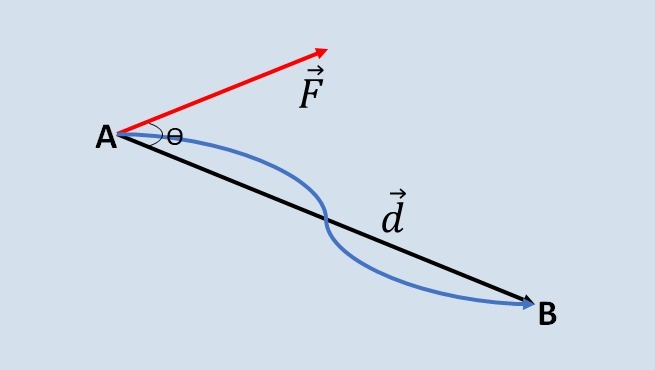
Force and Electrostatic Energy
Electrostatic force is the force of electrostatic interaction between two electrical charges through attraction and repulsion.
It is calculated by Coulomb's Law, which is expressed by the following formula:
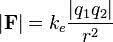
Where,
k = electrostatic constant
q1 and q2 = electrical charges
r = distance between charges
The electrostatic constant, also known as the Coulomb constant, is influenced by the environment where the electrical charges meet. Thus, the electrostatic constant influences the force value.
Usually in a vacuum, its value is 9.109 Nm2 /Ç2, but it can appear in other media, for example:
- Water 1.1.108 Nm2 /Ç2
- Benzene 2,3.109 Nm2 /Ç2
- Oil 3.6.109 Nm2 /Ç2
Electrostatic energy or electrical potential energy is energy produced by excess electrical charges in friction. It is measured by the following formula:
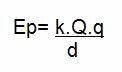
Where,
k = electrostatic constant
Q = source load
what = proof or test load
d = distance between charges
Electric field
Electric field it is the place where electrical charges are concentrated, whose intensity is measured using the formula:

Where,
AND = electric field
F = electric force
what = electric charge
Electric charge
At electrical charges they are the result of the attraction or repulsion of loads. Similar charges repel each other, while contrary ones attract.
They are measured in coulomb and the smallest of these charges that is found in nature is the elementary charge (e = 1.6 .10-19 Ç).
The electric charge formula is:
Q = n.e
Where,
Q = electric charge
no = number of electrons
and = elementary charge
Formulas
In addition to the electrostatic formulas mentioned above, the following are also used:
Electric potential

Where:
V = electrical potential
Ep = potential energy
Q = Electric charge
Potential Difference
U = vB -vThe
Where,
U = potential difference
vThe = electric potential in a
vB = electrical potential in b
Know more:
- Electric power
- Electrification Processes
- Electric current
- Electrostatics: Exercises
Electrostatics vs Electrodynamics
While Electrostatics studies electrical charges without movement, Electrodynamics studies moving loads.
Electrostatics and Electrodynamics are, therefore, areas of study in physics that are dedicated to different aspects of electricity.
In addition to these areas, there is also the Electromagnetism, which studies the capacity of electricity to attract and repress poles.
Entrance Exam Exercises
1. (UDESC-2013) Two identical spheres, A and B, made of conductive material, have charges +3e and -5e, and are placed in contact. After equilibrium, sphere A is placed in contact with another identical sphere C, which has an electric charge of +3e. Check the alternative that contains the value of the final electric charge of sphere A.
a) +2e
b) -1e
c) +1e
d) -2e
e) 0e
c) +1e
See too: Electric Charge: Exercises
2. (UFRR-2016) A rectangular plane of area A, in the international system (SI), is charged with an electric charge +Q, evenly distributed over the entire surface. What will be the electric charge density in this region?
a) Variable value in coulomb/m units
b) +Q/A coulomb/m2
c) +Q coulomb/m4
d) -Q coulomb/m5
e) 10 Q coulomb/m
b) +Q/A coulomb/m2
See too: Coulomb's Law - Exercises
3. (UEL-2011) The hydrophobic character of polyurethane is associated with the electrostatic repulsion force between the molecules of the material and water molecules, a physical phenomenon that occurs between bodies with electrical charges of same sign. It is correct to state that the electrostatic repulsion force
a) it has the opposite direction to the electrostatic attraction force between electrically neutral bodies
b) is greater between two bodies with the same electric charge +Q than between two bodies with the same electric charge -Q
c) will be twice as large if the distance between the loaded bodies is reduced by half
d) increases with the square of the distance between electrically charged bodies
e) is directly proportional to the amount of charge for electrically charged bodies
e) is directly proportional to the amount of charge for electrically charged bodies.
See too: electric power