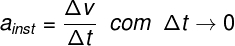Free fall is a type of movement that occurs when a body is under the influence of a force. The abandoned body, from rest, moves vertically in a downward trajectory due to the action of gravity.
Near the earth's surface, free fall is under the influence of gravity acceleration (g), considering negligible air or vacuum resistance.
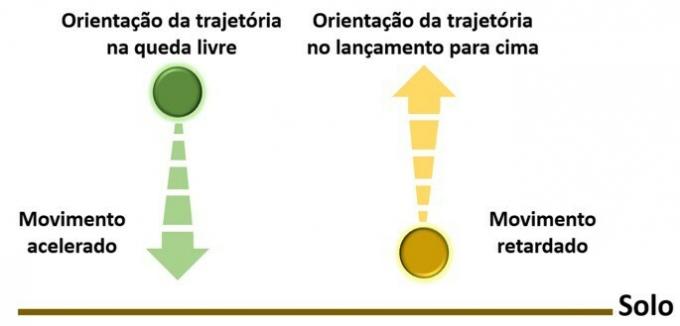
This movement is classified as uniformly accelerated. This is to say the acceleration is constant, as the speed at which the body falls increases at a rate of approximately 9.8 m/s every second.
The opposite movement, that is, the upward throw, is called uniformly delayed movement and because of the direction the acceleration is considered negative.
free fall formulas
As we've seen, free fall is a uniformly accelerated motion, because the acceleration is constant along a straight, vertical path.
When throwing a body downward from rest, the initial velocity is zero (v0 = 0). Under the action of gravity (g), it will take time (t) to travel a certain distance (h). Thus, free fall can be described by the equations:
Free Fall Speed Calculation:
Where,
v is the speed, in meters per second (m/s)
g is the acceleration of gravity, in meters per second squared (m/sec2)
t is the time interval, in seconds (s)
Free Fall Height Calculation:
Height (h) is given in meters (m).
Torricelli Equation:
Torricelli's equation is useful for calculating the rate of fall in problems without time data. Thus, we can relate height (h) to velocity (v).
Remember that the value of g varies depending on altitude and latitude. For example, the value 9.80665 m/s2 corresponds to the normal acceleration of gravity at 45º latitude and at sea level. However, it is common to approximate the value to 10 m/s2 in exercises to facilitate calculations, since close to the surface it is possible to consider it constant.
Free Fall Graphics
Graphically, the speed of movement with respect to time is expressed as an ascending straight line and the variation of position over time as a parabola.

Free Fall Exercises
question 1
Whereas a body close to the earth's surface, subject to gravity acceleration of 10 m/s2, is abandoned and after 2 seconds it hits the ground, from what height did the body free fall?
a) 10 m
b) 15 m
c) 20 m
d) 30 m
Correct alternative: c) 20 m
Note that the body has been abandoned, so the initial velocity is zero. The statement gives us 2 dice, acceleration and time, for the height to be determined. Therefore, we can use the hourly position equation:
Therefore, an abandoned body from a height of 20 meters reaches the ground in 2 seconds.
question 2
Marta knocked over a cup that was leaning on a spot. Knowing that the object took 2 seconds to reach the ground, what is the speed acquired by the cup during the movement knowing that gravity acceleration is 10 m/s2?
a) 30 m/s
b) 20 m/s
c) 15 m/s
d) 10 m/s
Correct alternative: ) 20 m/s
The speed in the free fall movement increases at a constant rate. Therefore, to determine how fast the cup hits the ground, we use the velocity formula, which relates acceleration and time.
V = g.t
V = 10. 2
V = 20 m/s
question 3
A body is dropped to the ground in free fall at a speed of 30 m/s. Neglecting air resistance and considering gravity acceleration 10 m/s2, how long did the move last?
a) 4.0 s
b) 1.0 s
c) 2.0 s
d) 3.0 s
Correct alternative: d) d) 3.0 s
To calculate the time, we use the speed formula:
Therefore, in free fall at a speed of 30 m/s, the movement lasted 3 seconds.
Get more knowledge by reading the texts below.
- Free Fall Exercises
- Vertical launch
- gravity acceleration
- gravitational force
- evenly varied movement