THE toxoplasmosis is a disease caused by a protozoan, O Toxoplasma gondii, which presents felines as the definitive host and man, in addition to some other animals vertebrates, as intermediate hosts. It's a disease with distributiongeographicworldwide, being a widespread zoonosis. It is usually an asymptomatic disease in patients without compromised immunity, however, it is especially dangerous in cases of pregnancy.
Read too:Diseases caused by protozoa
→ life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii
O Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan that infects different types of ahomeothermic animals, including birds and mammals. Felines, for example, the domestic cat, are its only definitive hosts, but other vertebrate species can act as intermediate hosts, this being the case for man.
During the cycle of Toxoplasma gondii, we observe three infective states: oocysts, tachyzoites and bradyzoites. Oocysts, which contain sporozoites, are stages formed in the intestinal cycle of the protozoan that occurs in the intestinal tract of the felids. The tachyzoite stage is found during the acute phase of the infection. The bradyzoite stage is found within tissue cysts in the chronic phase of the disease.
Cats are the only definitive hosts of the Toxoplasma gondii, therefore, they play a key role in the transmission of toxoplasmosis. |
Cats are usually infected when ingest intermediate host tissues, such as rodents and birds, with bradyzoites or even when ingesting sporulated oocysts from contaminated environments. In the cat's digestive tract, tissue cysts are ruptured and bradyzoites are released.
Later, bradyzoites invade the intestinal mucosa, differentiate and reproduce. The oocyst is immaturely formed and eliminated in the feces. Once eliminated, the sporulation process begins, resulting in the infecting oocyst.
Intermediate hosts become infected by ingesting the oocyst which may be contaminating the soil or food. The intermediate host may also ingest tissue from contaminated intermediate hosts. The ingested parasitic forms break up and release sporozoites (when oocyst was ingested) or bradyzoites (when tissue with tissue cysts was ingested) that invade nucleated cells.
Every parasite inside the cell is a tachyzoite. The tachyzoite then divides asexually several times until the cell breaks down. This process occurs successively and the tachyzoites migrate to various organs through the systemvascular.
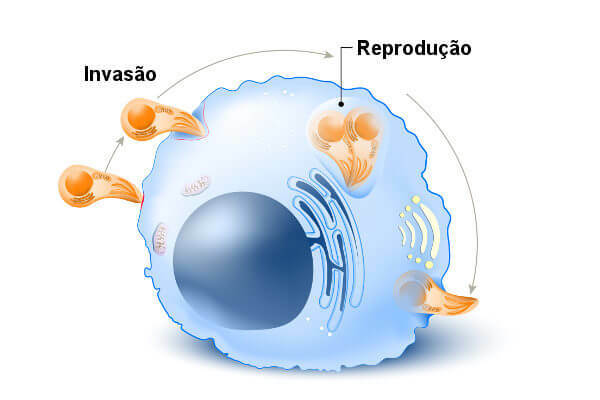
Observe the invasion of Toxoplasma in the cell and its further replication.
The formation of bradyzoites occurs when the intermediate host begins to develop immunity. With the development of immune response, the tachyzoites transform into bradyzoites and present a slower division and start to form the cyststissue.
Read too:Protozoa
→ Toxoplasmosis transmission
Toxoplasmosis is transmitted to humans, mainly due to the ingestion of oocysts, which may be present in the soil, water and foods of plant origin, or through the ingestion of meat with cysts tissue. In case of men, we cannot fail to mention that the transmission can also be congenital, that is, passed from mother to baby during pregnancy.

Cat feces are responsible for releasing oocysts into the environment.
→ Toxoplasmosis symptoms
In most cases, toxoplasmosis is a disease asymptomatic, that is, it does not cause symptoms. However, in a smaller number of individuals, some clinical manifestations may occur, such as weaknesswithoutfever and lymphadenopathy (change in lymph nodes).
Lymphadenopathy may be accompanied by fever, muscle pain, malaise, headache, pain when swallowing food, skin irritation, and hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen). In immunocompromised patients, the encephalitis (inflammation in the brain), myocarditis (inflammation in the heart muscle) and pneumonitis (inflammation of the lung).
→ ocular toxoplasmosis
Ocular toxoplasmosis is caused by Toxoplasma gondii when infecting the eye region. What is often observed in these situations is that the protozoan, when infecting this area, triggers scars that result in a decreased clarity of vision (reduces visual acuity).
The individual with ocular toxoplasmosis may still have pain in the eyes and have the pressureintraocularhigh, in addition to the emergence of fliessteering wheels (spots on vision). It is worth emphasizing that, sometimes, ocular toxoplasmosis manifests itself in an atypical way, which can make the correct diagnosis difficult. Treatment depends on the eye injury and the patient's health.
→ Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy
In pregnancy, infection by Toxoplasma gondii can cause serious problems for the child, since the mother can infect the fetus. In congenital toxoplasmosis, the Toxoplasma gondii is passed by transfertransplacental to the baby, triggering a series of problems, especially in those infected in the early stages of pregnancy.
It is estimated that approximately 40% of pregnant women with acute toxoplasmosis transmit the Toxoplasma to the baby. |
Congenital toxoplasmosis can trigger, for example, visual and neurological abnormalities, intrauterine growth restriction, prematurity, macro or microcephaly, jaundice, among others problems. It is noteworthy that most babies with congenital toxoplasmosis are born without symptoms, however, late sequelae they are frequent in untreated congenital toxoplasmosis.
Due to the risks that toxoplasmosis can cause in pregnancy, it is essential to carry out tests during the prenatal period. These tests allow for the detection of the problem and the carrying out of a treatment that can prevent contamination of the fetus.
readalso:Microcephaly
→ Toxoplasmosis treatment
Toxoplasmosis is not treated in patients who are not in poor health. In pregnant women, spiramycin is used, which reduces the chances of transmitting toxoplasmosis to the baby. When fetal infection is confirmed, treatment is based on the use of sulfadiazine, pyrimethamine and folinic acid. Patients with compromised immunity or who have developed complications also need specialized attention.
→ Prevention of toxoplasmosis
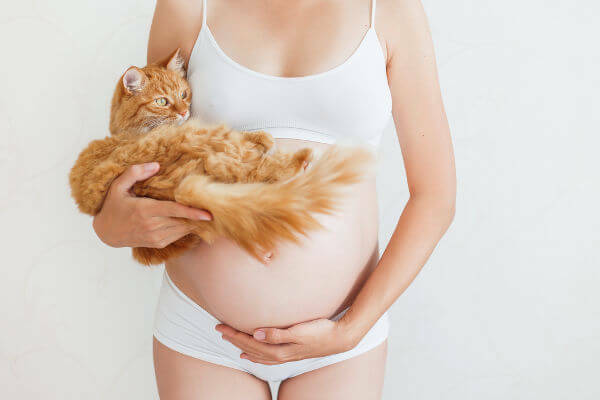

During pregnancy, it is recommended that the woman does not clean the litter box with cat feces.
Toxoplasmosis can be prevented with some very simple measures, such as:
Sanitize fruits and vegetables well.
Drink treated or boiled water.
Cook food well.
Do not eat raw or rare meat.
Freeze the meat at an internal temperature of -12º C.
Do not use the same household utensils used in meat to prepare vegetables.
Avoid contact with feline feces.
Feed cats with feed to avoid infection. It is important never to feed raw or rare meat to cats.
Change the cat litter box daily.
Pregnant women and individuals with weakened immunity should only handle the soil with gloves.
Always wash your hands thoroughly after handling sand and cats.
By Ma. Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos