Have you ever heard of rotation? This is one of the movements performed by the planet Earth, but it is also characteristic of other planets, however we will limit ourselves to talking about the terrestrial rotation.
The rotation, which is performed concomitantly with another movement (translation), is extremely important for the maintenance of life on the planet, maintaining the energy balance and chemical composition that characterizes the Wow atmosphere.
Read too: Planets of the Solar System

Rotation Motion Characteristics
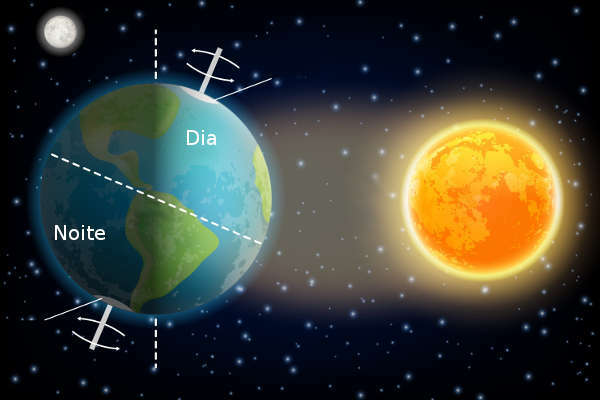
The rotation movement is the one that the Earth performs around its own axis (imaginary line that crosses the center of the Earth, going from one pole to another). This shift causes the alternation between periods of insolation in regions of the planet. Earth rotation takes place in the anticlockwise, from west to east, a characteristic that explains the sunrise in the east and the sunset in the west.
→ Duration
Earth rotation lasts approximately 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4 seconds
. This duration refers to the sidereal day and refers to a distant celestial body, such as the stars. When using the Sun as a reference for the rotation movement, the duration is on average 24 hours. This time variation is due to the movement of translation (which we will talk about later) concurrently with the movement of rotation.→ Speed
The rotation movement is performed at a speed of approximately 1,669 kilometers per hour.
Consequences of the rotation movement
The main consequence of the rotation movement is the succession of days and nights. This is possible due to the difference in lighting in the areas of the planet throughout the movement. The part of the planet that receives the highest solar incidence is in the daytime period, while the opposite part is in darkness, therefore, in the night period.
Days and nights have different durationss over the seasons. During summer the days are longer than the nights, while in winter the days are shorter and the nights longer. In spring and autumn, the days and nights are of equal length. This is possible due to the Earth's axis of inclination relative to the Sun.
During the summer, one of the hemispheres receives greater solar incidence, because the Earth is more inclined to the north or south. At the same time, the other hemisphere receives less sunlight, characterizing winter. In spring and autumn, the equal length of days and nights is also explained by the position of the Earth in relation to the Sun. The sun's rays, at this time, fall perpendicularly to the equator line, there being, therefore, no differentiation in the illumination of the hemispheres.
Another consequence of rotation is the apparent sky movement. During the rotation movement, we have the impression that the stars visible to the naked eye, like the stars, are moving from east to west. However, this is a false impression, caused by the Earth's rotation.
We must also mention the creation of the time zone system, which standardizes the world time. The creation of this system is due to the time difference in different regions of the planet. While in Japan it is already day, in Brazil it is still night. So, so that there was a pattern, the Earth was divided into 360º and 24 hours. Thus, the regions east of the Greenwich Meridian are ahead of our standard time (Brasilia time), while the regions west of this meridian lag behind our schedule.
Read too:Curiosities about the Solar System
rotational movement x translational movement

As mentioned before, the Earth's rotation occurs simultaneously with other movements performed by the Earth. One of them is the translation movement, which is the trajectory taken by the planet around the Sun, in an elliptical orbit (the path taken is not made in a circle, but in the shape of Ellipse). This circle around the Sun lasts approximately 365 days, 5 hours and 48 minutes, at an average speed of approximately 107,000 km.
This speed varies as the Earth moves away from or approaches the Sun. The removal is called aphelion, characterized by the reduction in the speed of the translation movement. When there is approximation, the speed of movement is greater, what we call perihelion.
The main consequence of the translation movement is the occurrence of the seasons of the year, linked to what we know as the solstices and equinoxes.
Solstice is nothing more than an astronomical phenomenon that marks the beginning of the summer and winter. The Earth, at the moment of the solstice, is at its maximum inclination, reaching its peak from north to south. As mentioned earlier, at the summer solstice, one of the hemispheres is more inclined in relation to the sun's rays, so it receives more light. The other is less illuminated, then the winter solstice occurs.
O equinox marks the beginning of spring and autumn. At this moment the Earth is not tilted, therefore both hemispheres are illuminated equally. While in one the spring equinox occurs; on the other, the autumnal equinox occurs. To learn more about the subject, click here: solstice and equinoheat.
Rotation of the Solar System Planets
In addition to Earth, the other planets of the Solar system they also rotate around the Sun. However, the movement duration in each of them is different. With the exception of Venus and Uranus, which rotate from east to west, that is, clockwise, the other planets rotate from west to east. See the duration of rotation of each planet.
Mercury |
58.6 earth days |
Venus |
224 days and 17 terrestrial hours |
Earth |
23 hours and 56 minutes |
Mars |
24 hours and 37 minutes by land |
Jupiter |
9 hours and 48 minutes terrestrial |
Saturn |
10 hours and 12 minutes terrestrial |
Uranus |
17 hours and 54 minutes on land |
Neptune |
19 hours and 6 minutes terrestrial |
by Rafaela Sousa
geography teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/movimento-rotacao.htm