To begin the study of a wave, it's good to remember the basic definition of a wave: wave is called the propagation of energy from one point to another, without the transport of matter between them..
We also saw that, regarding the propagation direction of a wave, there are three types of wave: one-dimensional, which is nothing more than a wave that propagates in a single dimension; two-dimensional, wave that propagates in two dimensions, that is, it propagates in a plane; and finally, three-dimensional, which is a wave that propagates in three dimensions.
As for nature, we can classify waves as follows:
mechanical waves
As for the nature of a mechanical wave, its main characteristic is that it only propagates in elastic media, between interconnected particles. This phenomenon only occurs in material media, as the mechanical wave needs a material media to propagate. This means that it never propagates in a vacuum.
The propagation of a mechanical wave through a material medium involves the transport of kinetic energy and potential energy and depends on two factors: the inertia and elasticity of the medium. As an example of mechanical waves, we have waves that propagate on stretched strings or springs and waves that propagate on surfaces of liquids and sounds.
Electromagnetic waves
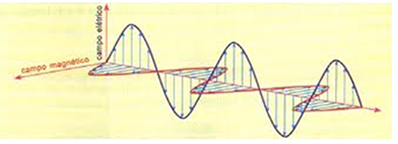
Electromagnetic waves are waves that do not need a propagation medium. They are made up of two oscillating fields, one with an electrical characteristic and the other with a magnetic characteristic. This propagation can occur both in a vacuum and in some material media. Examples of this type of wave are X-ray waves, light waves, microwaves, etc.
All electromagnetic waves have the propagation speed in common. For an electromagnetic wave, its propagation speed depends on the material medium in which it is found and also on the frequency of the emitting source.
By Domitiano Marques
Graduated in Physics
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/natureza-uma-onda.htm
