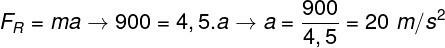Literally, antimatter is the inverse of matter. Each elementary particle that we know has an opposite particle that has exactly the same characteristics, except the electric charge, which is the reverse. O positron, for example, is the antimatter of electron, therefore, has the same mass, same rotation, same size, but electrical charge of opposite sign.
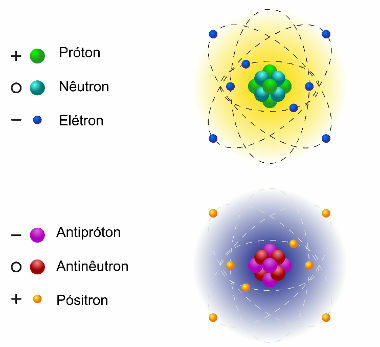
Matter and antimatter, consisting of antiparticles
Antimatter is not produced naturally on Earth. All that is known about these antiparticles comes from experiments carried out inparticle accelerators, which feature antiparticles as a product. The difficulty in producing and analyzing these materials lies in the fact that, in the encounter between matter and antimatter, annihilation always occurs, that is, one destroys the other, and the result is a great deal of energy.
Discovery
In 1928, the British physicist Paul Andrien M. Dirac revised the equation of equivalence between mass and energy proposed byEinstein and proposed that the mass should be considered with positive and negative values. Dirac's proposal made it possible to consider the possibility of the existence of antimatter.
In 1932, Carl Anderson detected the presence ofpositive electrons during an experiment with cosmic rays. The anti-electron detected was called positron and has the same characteristics as the electron, but has a positive electrical charge.
In 1955, scientists created the antiproton using a particle accelerator. Since then, studies related to antimatter have revealed antiparticles of neutrons, quarks, leptons etc.
applications
In a practical way, we can mention the PET scan exam, which uses the emission of positrons to form three-dimensional images used in the detection of tumors. The human body's electrons suffer annihilation when they encounter positrons emitted by a particular substance. The product of annihilation is the generation of gamma radiation, which is used for 3D imaging.
The large-scale annihilation that exists in the encounter of particles and antiparticles can generate exorbitant amounts of energy. An amount of 10 kilos of antimatter can generate the energy corresponding to six years of full operation of the Itaipu Power Plant! The yield of 1 g of antimatter in a car would have an approximate range of 10,000 kilometers.
The US armed forces are carrying out research for the creation of bombs made with antimatter. The annihilation generated by the contact of matter with the antimatter of the bombs could generate explosions with a destructive potential much greater than that of the nuclear warheads.
The distances that separate us from certain celestial bodies in space make any attempts at approximation impossible. A trip to the star Alpha Centauri, for example, which star after the Sun, is the closest to Earth, it would take about 80 thousand years with current technologies. If the spacecraft were powered by antimatter, the time for this trip would be significantly reduced, which could make the "walk" entirely viable.
Generation and storage of antiparticles
By accelerating atoms to very high speeds with a particle accelerator, they can be collided with a particular target. The antiparticles result from this collision and are separated by the action of magnetic fields. The storage of these elements is done in a kind of magnetic bottle, which prevents the antimatter come into contact with matter, which could lead to annihilation and destruction of antiparticles. Every year, only a trillionth of a gram of antiprotons is produced.
By Joab Silas
Graduated in Physics
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-antimateria.htm