Dynamics is the knowledge area of Physics what study the cause of the movements, analyzing and describing them according to the forces who are responsible for producing them. Dynamics is, therefore, one of the areas of mechanics, along with kinematics and statics.
See too: Forces - types, formulas and how to calculate
What are the main themes studied in the dynamics?
The main subjects of study in dynamics are Newton's laws, universal gravitation and the study of mechanical, kinetic and potential energies.
- Newton's Laws: describe the movements of bodies through the forces acting on them. Altogether, there are three laws of Newton: a law of inertia, O fundamental principle of dynamics and the law of action and reaction. Based on Newton's laws, the behavior of friction forces, buoyancy, traction, centripetal forces etc.
- universal gravitation: area of dynamics that studies the movement of celestial bodies. Besides the law of universal gravitation, which is used to calculate the force and attraction that one body exerts on another, there are also Kepler's laws, used to describe the orbitsplanetary.
- mechanical energy: the study of this form of energy relates the energies kinetics and potential, among others. Here, the principle of conservation of mechanical energy is also studied, in addition to calculations of mechanical work and power.
Dynamics formulas
Check out the main dynamics formulas and learn what each of its variables means.
→ Resultant Force
THE strengthresultant can be obtained through vector calculus. According to the Newton's 2nd Law, it is equal to the product of the body's mass and its acceleration.

→ Formula of the work of a force
The work exerted by a constant force can be calculated through the product of the applied force and the distance traveled by the body.
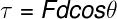
→ Kinetic energy
Kinetic energy is the amount of energy stored in any body of mass m that moves with velocity v, as shown in the following formula:
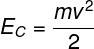
→ gravitational potential energy
Gravitational potential energy refers to the amount of energy that is stored in a mass body. m, when raised to a height h from the ground, in a region where the acceleration of gravity is equal to g. Watch:
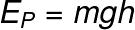
→ Mechanical energy
Mechanical energy refers to all energy related to the movement of a body or system of bodies. Mechanical energy is equal to the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy.
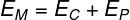
See too: Tips for solving kinematics exercises
Solved exercises on dynamics
Question 1 — Determine what is the acceleration developed by a body with a mass equal to 4.5 kg, when subjected to a force of 900 N.
a) 10 m/s²
b) 20 m/s²
c) 0.5 m/s²
d) 9 m/s²
Resolution:
Just apply Newton's 2nd law and use the data provided by the statement.
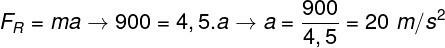
Based on the result obtained, the correct alternative is the letter B.
Question 2 — A 20 kg body is 10 m high in a region where gravity has a value of 10 m/s². Knowing that the body moves at a constant speed of 10 m/s, determine the magnitude of the mechanical energy of that body.
a) 1500 J
b) 2500 J
c) 3000 J
d) 4500 J
Resolution:
To solve the exercise, it is necessary to calculate the kinetic and potential energies and then add them up.

Through the calculation, we find that the mechanical energy of the body is 3000 J, so the correct alternative is letter C.
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher



