Matter is everything that has mass and occupies a place in space, that is, matter has volume and mass. Examples of matter are: trees, stars, air, a chair, a bicycle, etc.
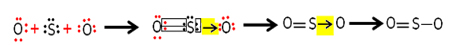
Matter is formed from the combination of chemical elements, the same or different, which are made up of particles: protons, electrons and neutrons.
The combination of these three particles form atoms, which when joined by chemical bonds, constitute the diversity of materials we know.
Difference between matter, body and object
A limited part of matter is a body. When a body receives a specific function, it becomes an object.
Example:
Composition of matter
The different types of materials that exist are due to the different forms of organization of atoms in matter. Matter can present itself as a substance or a mixture.
Substances
Pure substances are made up of only one chemical species and, therefore, their composition and properties are fixed. This type of matter can be classified as simple or composite.
A pure substance is simple when it consists of only one chemical element, for example, oxygen (O
2) of the air we breathe and the metal iron (Fe).When at least two elements come together through a chemical bond, it is characterized as a compound substance, such as water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
See too: Simple and Compound Substances
Mixtures
When pure substances come together, a mixture is formed, as they retain their individual properties.
Mixtures can be homogeneous and have only one phase, such as saline (mixture of water and sodium chloride, NaCl), or heterogeneous, in which more than one phase can be seen, such as milk (the particles are suspended in the liquid).
See too: Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures
properties of matter
The properties of matter encompass the characteristics common to all materials and the peculiarities that differentiate them.
| General Properties of Matter | |
|---|---|
| General properties are those that apply to any matter, regardless of its constitution. | |
|
|
See too: General Properties of Matter
| Specific Properties of Matter | |
|---|---|
| Specific properties are unique characteristics of a particular matter and, therefore, can be seen as a difference from others. | |
| Chemicals | Physical |
|
|
| Organoleptics | Functional |
|
|
See too: Matter Properties
relationship between matter and energy
THE energy it is used to transform or move matter. Therefore, what in the universe is not classified as matter is energy.
Examples of energy are: chemical energy, electrical energy, thermal energy, nuclear energy and mechanical energy.
Matter presents itself in three physical states: solid, liquid and gas and can undergo a physical or chemical transformation through an applied energy.
One physical transformation of matter it occurs when there is a passage from one physical state to another, as there is no change in its composition.
For example, if we add thermal energy to an ice cube, the heat will make the water go from a solid state to a liquid.
One chemical transformationof the matter it causes two substances to react and form new material. This occurs through chemical reactions, with absorption or release of energy.
For example: two gases, hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2), can unite and generate the substance water (H2O).
Learn more aboutphysical and chemical transformations of matter.