DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that have different structures and functions. While DNA is responsible for storing the genetic information of living beings, RNA acts in the production of proteins.
These macromolecules are subdivided into smaller units, the nucleotides. The forming unit is composed of three components: phosphate, pentose and nitrogen base.
The pentose present in DNA is deoxyribose, whereas in RNA it is ribose and, therefore, the acronym DNA means deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA is ribonucleic acid.
The 7 main differences between DNA and RNA
DNA and RNA are polymers whose functions are to store, transport and use genetic information. Below are the main differences between them.
| differences | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
| type of sugar | Deoxyribose (C5H10O4) | Ribose (C5H10O5) |
| Nitrogen bases | Adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine |
Adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil |
| Occupation | Storage of genetic material | protein synthesis |
| Structure | Two strands of spiral nucleotides | a nucleotide strand |
| Synthesis | self-replication | Transcription |
| Synthetic Enzyme | DNA polymerase | RNA polymerase |
| Location | Cell core | Cell nucleus and cytoplasm |
Learn more about Nitrogen Bases.
Summary on DNA and RNA
You nucleic acids they are macromolecules formed by the union of phosphoric acid with pentose, sugar with five carbons, and nitrogenous, pyrimidine (cytosine, thymine and uracil) and puric (adenine and guanine) bases.
The two major groups of these compounds are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). See below for information about each of them.
DNA: what it is, structure and function
O DNA it is a molecule that transmits encoded genetic information from a species to its successors. It determines all the characteristics of an individual and its composition does not change from one region of the body to another, neither with age or environment.
In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick presented, through an article in the magazine nature, the double helix model for DNA structure.
Watson and Crick's description of the helical model was based on the study of nitrogenous bases by Erwin Chargaff, who using the chromatography technique managed to identify and quantify them.
Images and X-ray diffraction data obtained by Rosalind Franklin, who worked with Maurice Wilkins at the King's College London, were decisive for the pair to reach the presented model. The historic “Photo 51” was crucial evidence for the great discovery.
In 1962, Watson, Crick and Wilkins received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for the described structure. Franklin, who had died four years earlier, was not recognized for his work.

THE structure of the DNA is formed by:
- Phosphate skeleton (P) and sugar (D) alternate, which fold into a double helix.
- Nitrogenous bases (A, T, G and C) linked by hydrogen bonds, which protrude out of the chain.
- Nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds.
At functions of the DNA are:
- Transmission of genetic information: The nucleotide sequences belonging to the strands of DNA encode information. This information is transferred from a mother cell to daughter cells by the process of DNA replication.
- Protein coding: the information that DNA carries is used to produce proteins, the genetic code being responsible for the differentiation of the amino acids that make them up.
- RNA synthesis: DNA transcription produces RNA, which is used to make proteins through translation.
Before cell division, DNA is duplicated so that the cells produced receive the same amount of genetic material. The breakage of the molecule is done by the enzyme DNA-polymerase, splitting the two strands and remaking itself into two new DNA molecules.
Also read aboutDNA replication.
RNA: what it is, structure and function
O RNA is a polymer whose ribonucleotide strand elements are covalently linked.
It is the element between DNA and protein production, that is, DNA restructures itself to form RNA, which in turn encodes protein production.
THE structure of RNA is formed by:
- Ribonucleotides: ribose, phosphate and nitrogenous bases.
- Puric bases: adenine (A) and guanine (G).
- Pyrimid bases: cytosine (C) and uracil (U).
At functions of RNA are related to their types. Are they:
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): formation of ribosomes, which act to bind amino acids into proteins.
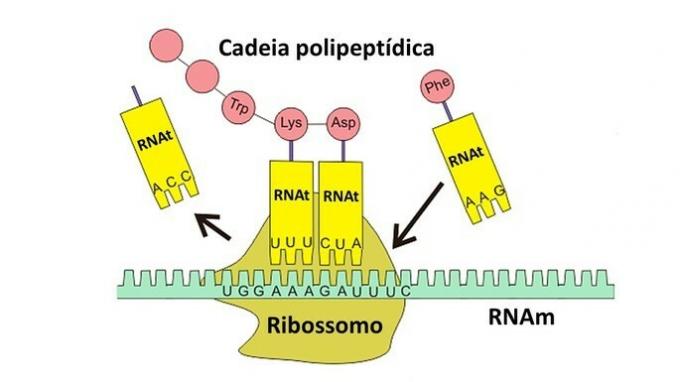
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): transmission of the genetic message to the ribosomes, indicating which amino acids and which sequence should make up the proteins.
- Transport RNA (tRNA): targeting amino acids inside cells to the site of protein synthesis.
For protein synthesis to occur, some stretches of DNA are transcribed into messenger RNA, which carries the information to the ribosome. The transporter RNA is responsible for bringing amino acids for protein production. The ribosome manufactures the polypeptide chain according to the decoding of the received message.
Know more:
- Protein synthesis
- Genetic Code
- DNA exercises