O equation balancing allows us to match the number of atoms present in the chemical equation so that it becomes true and represents a chemical reaction.
Use the questions below to test your knowledge and check the answers commented after the feedback to answer your questions.
question 1
(Mackenzie-SP)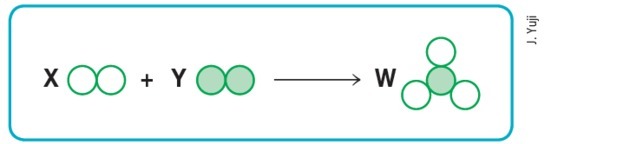
Assuming that the empty and filled circles respectively mean different atoms, then the scheme above will represent a balanced chemical reaction if we replace the letters X, Y, and W, respectively, with the values:
a) 1, 2 and 3.
b) 1, 2 and 2.
c) 2, 1 and 3.
d) 3, 1 and 2.
e) 3, 2 and 2.
Alternative d) 3, 1 and 2.
1st step: We assign letters to make the equation easier to understand.
2nd step: we add up the indices to find out who has the most atoms in the equation.
| THE | |
| B |
A and B appear only once in each member of the equation. However, if we add the indices we see that A has the highest value. Therefore, we started the balancing for him.
3rd step: We balance element A by transposing the indices and turning them into coefficients.
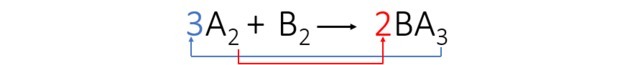
We observed that element B was automatically balanced and the coefficients of the equation are: 3, 1 and 2.
question 2
(Unicamp-SP) Read the following sentence and transform it into a (balanced) chemical equation, using symbols and formulas: “a molecule of gaseous nitrogen, containing two atoms of nitrogen per molecule, reacts with three molecules of gaseous diatomic hydrogen, producing two molecules of gaseous ammonia, which is made up of three hydrogen atoms and one of nitrogen".
Reply:
Representing the atoms described in the question, we can understand that the reaction occurs as follows:
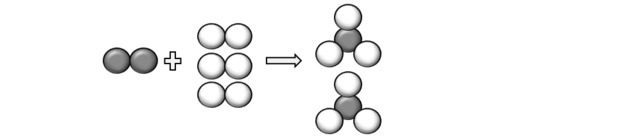
So we come to the equation:
question 3
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound that can decompose, forming water and oxygen, according to the chemical equation below.
Regarding this reaction, the correctly balanced equation is:
a) H2O2 → The2 + H2O
b) 2h2O2 → The2 + 2H2O
c) H2O2 → 2O2 + H2O
d) 2h2O2 → 2O2 + 2H2O
Correct alternative: b) 2H2O2 → The2 + 2H2O
Note that hydrogen peroxide is a chemical made up of atoms of two chemical elements: hydrogen and oxygen.
After the decomposition reaction you must have the same number of atoms of the two elements in both the reactants and the products. For this, we need to balance the equation.
Note that we have 2 hydrogen atoms in the reactant (H2O2) and two atoms in the product (H2O). However, oxygen has two atoms in the reactant (H2O2) and three atoms in the products (H2O and O2).
If we put the coefficient 2 before the hydrogen peroxide we double the number of atoms in the elements.
Note that if we put the same coefficient together with the formula for water, we will have the same amount of atoms on both sides.
Therefore, the correctly balanced chemical equation is 2H2O2 → The2 + 2H2O.
question 4
(UFPE) Consider the chemical reactions below.
We can say that:
a) all are balanced.
b) 2, 3 and 4 are balanced.
c) only 2 and 4 are balanced.
d) only 1 is unbalanced.
e) none is correctly balanced, because the physical states of the reactants and products are different.
Alternative b) 2, 3 and 4 are balanced.
Alternatives 1 and 5 are incorrect because:
- Equation 1 is unbalanced, the correct balance would be:
- Equation 5 is incorrect because the compound formed in the reaction would be H2ONLY3.
To form the H2ONLY4 should be included in the equation the oxidation of SO2.
question 5
(Mackenzie-SP) Heated to 800 °C, calcium carbonate decomposes into calcium oxide (virgin lime) and carbon dioxide. The correctly balanced equation, which corresponds to the described phenomenon, is:
(Given: Ca — alkaline earth metal.)
Alternative c)
Calcium is an alkaline earth metal and to have stability calcium needs 2 electrons (Ca2+), which is the oxygen charge (O2-).
Thus, a calcium atom binds to an oxygen atom and the compound formed is CaO, which is quicklime.
The other product is carbon dioxide (CO2). Both are formed by calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
Putting it into an equation:
We note that the amounts of atoms are already correct and do not need balancing.
question 6
(UFMG) The equation is not balanced. Balancing it with the smallest possible numbers, the sum of the stoichiometric coefficients will be:
a) 4
b) 7
c) 10
d) 11
e) 12
Alternative e) 12
Using the trial method, the balancing order will be:
1st step: As the element that appears only once in each member and has the highest index is calcium, we started the balancing for it.
2nd step: We follow the balancing by the radical PO43-, which also only appears once.
3rd step: we balance the hydrogen.
With this, we observe that automatically the amount of oxygen was adjusted and the balance of the equation is:
Remembering that when the coefficient is 1 you don't need to write it in the equation.
Adding the coefficients we have:
question 7
Combustion is a type of chemical reaction in which energy is released in the form of heat.
In the complete combustion of a substance formed by carbon and hydrogen, carbon dioxide and water are formed.
Observe the hydrocarbon combustion reactions and answer which of the equations below is incorrectly balanced:
a) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
b) C3H8 +502 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
c) C4H10 +13/3O2 → 4CO2 + 5h2O
d) C2H6 + 7/2O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
Incorrect answer: c) C4H10 +13/3O2 → 4CO2 + 5h2O
To balance the chemical equations, let's first look at which element appears only once in each member of the equation.
Note that carbon and hydrogen form only one reactant and one product in each equation presented.
So let's start balancing with hydrogen, as it has a greater number of atoms.
Therefore, the order of balancing will be:
- Hydrogen
- Carbon
- Oxygen
Hydrogen
As the product has 2 hydrogen atoms, we insert a number as a coefficient that multiplied by 2 results in the number of hydrogen atoms in the reactant.
a) CH4 + O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
b) C3H8 + O2 → CO2 + 4H2O
c) C4H10 + O2 → CO2 + 5H2O
d) C2H6 + O2 → CO2 + 3H2O
Carbon
Balancing is done by transposing the carbon index in the reactant and using it as a coefficient on the product that has atoms of this element.
a) CH4 + O2 → 1CO2 + 2H2O
b) C3H8 + O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
c) C4H10 + O2 → 4CO2 + 5h2O
d) C2H6 + O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
Oxygen
Adding the number of oxygen atoms in the formed products we find the number of atoms of the element that must be reacting.
For that, we must put as coefficient a number that multiplied by 2 results in the number of oxygen atoms in the products.
a) CH4 + O2 → 1CO2 + 2H2O
2x = 2 + 2
2x = 4
x = 2
So the correct equation is: CH4 + 2O2 → 1CO2 + 2H2O.
b) C3H8 + O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
2x = 6 + 4
2x = 10
x = 5
So the correct equation is: C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
c) C4H10 + O2 → 4CO2 + 5h2O
2x = 8 + 5
2x = 13
x = 13/2
So the correct equation is: C4H10 + 13/2O2 → 4CO2+ 5h2O
d) C2H6 + O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
2x = 4 + 3
2x = 7
x = 7/2
So the correct equation is: C2H6 + 7/2O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
Correctly balanced equations are:
a) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
b) C3H8 +502 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
c) C4H10 + 13/2O2 → 4CO2 + 5h2O
d) C2H6 + 7/2O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
Thus, alternative c) C4H10 +13/3O2 → 4CO2 + 5h2The thing is, it doesn't have the correct balance.
question 8
(Enem 2015) Limestones are materials composed of calcium carbonate, which can act as sorbents for sulfur dioxide (SO2), an important air pollutant. The reactions involved in the process are the activation of limestone, through calcination, and the fixation of SO2 with the formation of a calcium salt, as illustrated by the simplified chemical equations.
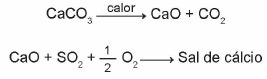
Considering the reactions involved in this desulfurization process, the chemical formula of the calcium salt corresponds to:
Alternative b)
As the reaction is balanced, the atoms contained in the reactants must be in the same quantity in the products. Thus,
The salt formed is composed of:
1 calcium atom = Ca
1 sulfur atom = S
4 oxygen atoms = O4
Therefore, the chemical formula of the calcium salt corresponds to CaSO4.
question 9
(UFPI) The reaction of X with Y is shown below. Determine which equation best represents the balanced chemical equation.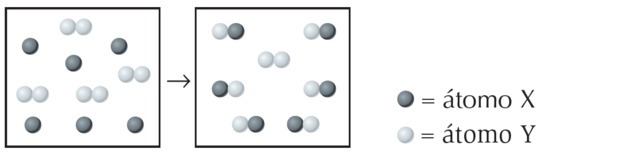
Alternative a)
In the figure we observe that the species X is a single atom while Y is diatomic, that is, it is formed by joining 2 atoms. So X reacts with Y2.
The product formed is represented by XY, the equation being unbalanced:
We balance the equation as follows:
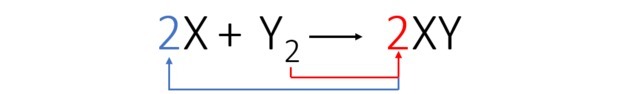
According to the balanced equation, the figure below shows us how the reaction occurs and its proportion.
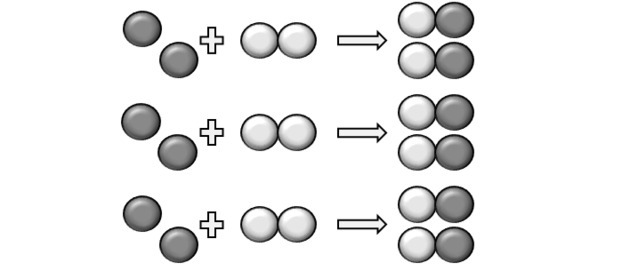
For a reaction to occur there must be a fixed ratio and therefore some compound may not react. This is what the figure shows, because in the product we see that a Y2 did not react.
question 10
(Enem 2010) Mobilizations to promote a better planet for future generations are increasingly frequent. Most means of mass transport are currently powered by burning a fossil fuel. As an example of the burden caused by this practice, it is enough to know that a car produces, on average, about 200g of carbon dioxide per km traveled.
Global Warming Magazine. Year 2, 8. Publication of the Instituto Brasileiro de Cultura Ltda.
One of the main constituents of gasoline is octane (C8H18). Through the combustion of octane it is possible to release energy, allowing the car to start moving. The equation that represents the chemical reaction of this process demonstrates that:
a) oxygen is released in the process, in the form of O2.
b) the stoichiometric coefficient for water is 8 to 1 octane.
c) in the process there is water consumption, so that energy is released.
d) the stoichiometric coefficient for oxygen is 12.5 to 1 octane.
e) the stoichiometric coefficient for carbon dioxide is 9 to 1 octane
Alternative d) the stoichiometric coefficient for oxygen is 12.5 to 1 octane.
When balancing the equation we find the following coefficients:
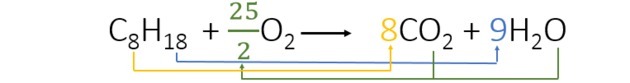
- We started the balancing by hydrogen that appears only once in each member and has a higher index. Since there are 18 reacting hydrogen atoms, there are 2 in the product, so we need to add a number that multiplied by 2 gives 18. So 9 is the coefficient.
- Then we add the coefficient 8 in front of the CO2 to have 8 carbons in each member of the equation.
- Finally, just add the amount of oxygen in the product and find the value that multiplied by 2 gives us 25 oxygen atoms. So we chose 25/2 or 12.5.
Thus, for the combustion of 1 octane 12.5 oxygen is consumed.
question 11
(Fatec-SP) An essential characteristic of fertilizers is their water solubility. Therefore, the fertilizer industry transforms calcium phosphate, whose solubility in water is very low, into a much more soluble compound, which is calcium superphosphate. This process is represented by the equation:
where the values of x, y, and z are, respectively:
a) 4, 2 and 2.
b) 3, 6 and 3.
c) 2, 2 and 2.
d) 5, 2 and 3.
e) 3, 2 and 2.
Alternative e) 3, 2 and 2.
Using the algebraic method, we form equations for each element and equate the number of atoms in the reactant with the number of atoms in the product. Therefore:
Balanced equation:
question 12
Balance the equations below using the trial method.
Reply:
The equation is made up of the elements hydrogen and chlorine. We balance the elements just by adding coefficient 2 in front of the product.
The equation did not need to be balanced, as the amounts of atoms are already adjusted.
Phosphorus has two atoms in the reactants, so to balance this element we adjust the amount of phosphoric acid in the product to 2H3DUST4.
After that, we observed that the hydrogen had 6 atoms in the product, we balanced the amount of this element adding coefficient 3 to the reactant that contains it.
With the previous steps, the amount of oxygen was corrected.
Looking at the equation we see that the amounts of hydrogen and bromine in the products are double what if there is in the reagents, so we add coefficient 2 to the HBr to balance these two elements.
Chlorine has 3 atoms in the products and only 1 in the reactants, so we balance putting a coefficient of 3 before the HCl.
The hydrogen had 3 atoms in the reactants and 2 atoms in the products. To adjust the quantities we transform the H index2 in coefficient, we multiply by the 3 that was already in the HCl and we arrive at the result of 6HCl.
We adjust the amounts of chlorine in the products to also have 6 atoms and get 2AlCl3.
Aluminum had 2 atoms in the products, we adjusted the amount in the reactants to 2Al.
We balance the amount of hydrogen in the product to 3H2 and we fit the amount of 6 atoms of that element in each term of the equation.
In the equation the nitrate radical (NO3-) has index 2 in the product, we transform the index into a coefficient in the reactant for 2AgNO3.
The amount of silver needed to be adjusted, as it now has 2 atoms in the reagents, so we have 2Ag in the product.
In the reactants we have 4 hydrogen atoms and to balance this element we add coefficient 2 to the HCl product.
Chlorine now has 4 atoms in the products, so we adjust the amount in the reagent to 2Cl2.
We have 6 hydrogen atoms in the reactants and to balance this element we adjust the amount of water to 3H2O.
We have 2 carbon atoms in the reactants and to balance this element we adjust the amount of carbon dioxide to 2CO2.
Oxygen needs to have 7 atoms in the reactants and to balance this element we adjust the amount of molecular oxygen to 3O2.
Looking at the equation, the nitrate radical (NO3-) has index 2 in the product. We transform the index into coefficient 2 in the AgNO reagent3.
We have 2 silver atoms in the reactants and to balance this element we adjust the amount of silver chloride in the product to 2AgCl.
We have 3 calcium atoms in the product and to balance this element we adjust the amount of calcium nitrate in the reagent to 3Ca (NO3)2.
We are then left with 6 NO radicals3- in the reactants and to balance this radical we adjust the amount of nitric acid in the products to 6HNO3.
We now have 6 hydrogen atoms in the products and to balance this element we adjust the amount of phosphoric acid in the reagent to 2H3DUST4.
Learn more about calculations with chemical equations at:
- Balancing chemical equations
- Stoichiometry
- Stoichiometric calculations
- Stoichiometry exercises
- Periodic table exercises