Molecule is a stable grouping of two or more atoms, the same or different, joined through covalent bonds.
Molecular compounds are classified according to polarity.
- Apolar Molecules: there is no difference in electronegativity between atoms.
- Polar Molecules: there is a difference in electronegativity between the atoms, with a positive pole and a negative pole.
When the molecule is formed by more than one chemical element, the number of electronic clouds and ligands to the central atom determines the polarity.
nonpolar molecules
Molecules have their atoms joined by covalent bonds, that is, electrons are shared.
electronegativity it is the ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a bond, forming poles in the molecule.
The atom that attracts the electrons becomes the negative pole, by the accumulation of negative charge, and the other atom becomes the positive pole.
When a molecule is formed by atoms of a single chemical element, there is no difference in electronegativity and the molecule is apolate.

The molecules of simple substances like O2 and no2, are formed by atoms of the same element; molecules of composite substances, on the other hand, have at least two different elements.

At molecules CO2 and BeH2 they are also nonpolar due to geometry. As both have linear geometry, the atoms at the ends, oxygen and hydrogen, attract the bond's electrons towards each other, as they are more electronegative.
The attraction of the atom on the left is counterbalanced by the attraction of the atom on the right. As the bonds are the same, that is, they have the same intensity but different directions, the molecules do not form poles.
polar molecules
When a molecule is formed by different atoms there is a difference in electronegativity, but it is the molecule geometry which determines whether it will be polar or non-polar.
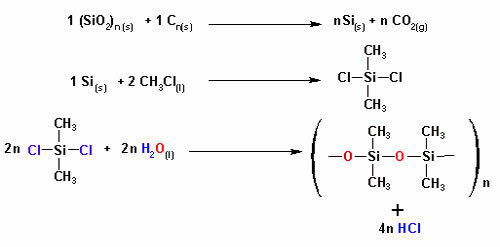
In both examples, we see that the central atoms, oxygen and nitrogen, have unpaired electron pairs that form electron clouds.
Since there are more electron clouds around the central atom than there are equal atoms attached to it, the molecule is polar.
With the formation of an electronic cloud, the molecule assumes a structure that better accommodates the atoms and, therefore, the geometry of water is angular and ammonia pyramidal.
Want to enrich your knowledge? Don't miss the texts below!
- Biomolecules
- intermolecular forces
- molecular formula
- Molecular mass
Exercise with commented feedback
1. Indicate the polarity of the molecules:
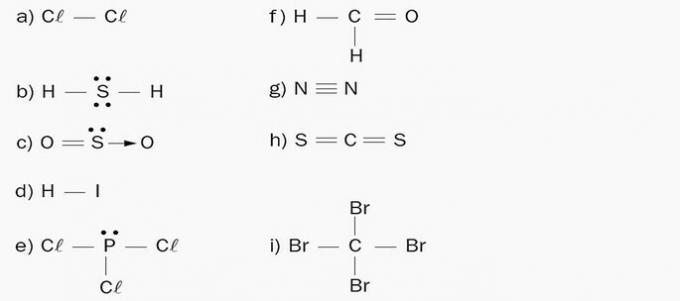
a) Apolar. The molecule is made up of a single chemical element, chlorine. As there is no difference in electronegativity, no poles are formed.
b) Polar. There are 4 electron clouds and 2 equal atoms (H) attached to the central element (S).
c) Polar. There are 3 electronic clouds and 2 equal atoms (O) attached to the central element (S).
d) Polar. The elements of the molecule have different electronegativities. A negative pole is formed in the iodine due to the accumulation of negative charge and, consequently, the hydrogen side forms a positive pole.
e) Polar. There are 4 electron clouds and 3 equal atoms (Cl) attached to the central element (P).
f) Polar. There is an asymmetric distribution of charges on the molecule, as carbon has different ligands.
g) Apolar. The molecule is diatomic and made up of atoms of the same chemical element, so there is no difference in electronegativity.
h) Apolar. The number of electron clouds is equal to the number of atoms attached to the central atom.
i) Apolar. The number of electron clouds is equal to the number of atoms attached to the central atom.
2. (Fuvest) Consider the molecules of HF, HCl, H2O, H2, O2 and CH4.
a) Classify these molecules into two groups: polar and non-polar.
| Polar | apolar |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen fluoride (HF) | Molecular hydrogen (H2) |
| Hydrogen chloride (HCl) | Molecular Oxygen (O2) |
| Water (H2O) | Methane (CH4) |
HF, HCl and H2The are polar because in the three compounds hydrogen is bound to very electronegative elements.
H2 it's the2 they are non-polar, as there is no difference in electronegativity in the molecules. the CH4 it is also non-polar because the number of electron clouds is equal to the number of elements attached to the central atom, carbon.
Property referring to the atom: electronegativity.
Molecules that are made up of atoms of only one chemical element have been classified as non-polar, as there is no difference in electronegativity.
Property related to the molecule: amount of clouds and number of equal ligands.
Molecules formed by atoms of different chemical elements were classified as polar or non-polar according to the number of electronic clouds and the amount of ligands to the central atom.
Water is polar because the central atom, oxygen, has an unpaired pair of electrons, causing there to be 3 electron clouds and 2 ligands. Therefore, the distribution of charges is asymmetric, forming poles in the molecule.
Methane is non-polar, as the central atom, carbon, has the number of ligands equal to the number of electronic clouds, making the geometry tetrahedral and there being no polarity in the molecule.
3. (Vunesp) Among the alternatives below, indicate the one with the incorrect statement:
a) Covalent bond is one that occurs through the sharing of electrons between two atoms.
b) The covalent compound HCl is polar, due to the difference in electronegativity existing between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms.
c) The compound formed between an alkali metal and a halogen is covalent.
d) The substance of formula Br2 it is non-polar.
e) The substance of formula Cal2 it's ionic.
Incorrect alternative: c) The compound formed between an alkali metal and a halogen is covalent.
a) CORRECT. This type of bond corresponds to the sharing of electrons generally between non-metals.
b) CORRECT. Chlorine has greater electronegativity than hydrogen and, therefore, attracts the pair of electrons from the bond to itself, causing a charge imbalance.
The HCl molecule is polar because a negative pole forms in chlorine due to the accumulation of negative charge and, consequently, the hydrogen side tends to have an accumulated positive charge, forming a pole positive.
c) INCORRECT. Through ionic bonds, metals are able to donate electrons and stay positively charged, forming cations; halogens, on the other hand, receive electrons and form anions, species with a negative charge.
d) CORRECT. The molecule is diatomic and made up of atoms of the same chemical element, so there is no difference in electronegativity.
e) CORRECT. In ionic bonding, electrons are donated or received by atoms. In the ionic compound, calcium donates two electrons and forms the cation Ca2+. Iodine receives electrons from calcium and forms a negatively charged species, I2-.
Be sure to check these texts on issues related to the topic of this content:
- ionic bonds
- covalent bonds
- Polarity of connections
- Simple and compound substances
- General properties of matter