The main inorganic functions are: acids, bases, salts and oxides.
Inorganic compounds have different properties and are present in many situations in our daily lives. That's why this theme is discussed a lot in entrance exams, in Enem and in competitions.
To help you prepare for exams, we've created this list of 15 questions with commented resolutions and different approaches for each inorganic function.
General concepts
1. (FGV) Some compounds, when solubilized in water, generate an aqueous solution that conducts electricity. Of the compounds below:
| I. At2ONLY4 |
| II. O2 |
| III. Ç12H22O11 |
| IV. KNO3 |
| V. CH3COOH |
| SAW. NaCl |
They form an aqueous solution that conducts electricity:
a) only I, IV and VI
b) only I, IV, V and VI
c) all
d) only I and VI
e) only saw
Correct alternative: b) only I, IV, V and VI.
The conduction of electricity in solution occurs due to the formation of electrically charged species, the ions, as Arrhenius found in his experiments.
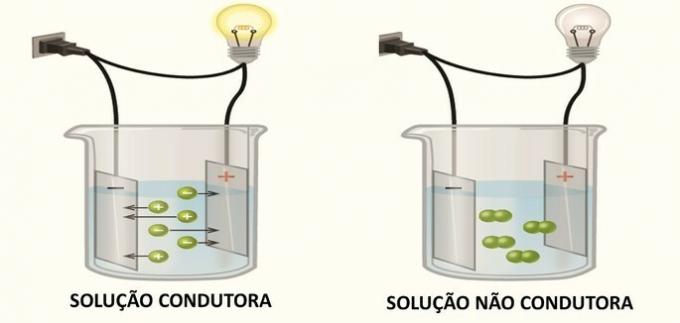
When ions are formed in solution, cations (positive charge) migrate to the negative pole and anions (negative charge) migrate to the positive pole, closing the electrical circuit and allowing the passage of chain.
Compounds that in solution generate neutral species do not conduct electricity.
According to this information we have to:
I. DRIVE
In solution, the salt dissociates and ions are formed.
II. DOES NOT DRIVE
Diatomic oxygen at room temperature is an inert molecule.
III. DOES NOT DRIVE
The formula presented is from sucrose, a molecular compound that when it comes into contact with water, its molecules disperse, but do not lose their identity.
IV. DRIVE
In solution, the salt dissociates and ions are formed.
V. DRIVE
Acetic acid is a weak acid that has a small ionized part in solution.
SAW. DRIVE
In solution, the salt dissociates and ions are formed.
2. (Mackenzie-SP)
The equation above represents a reaction
a) of ionic dissociation.
b) which has a diacid as a reactant.
c) of total ionization, forming the hydroxonium cation.
d) of ionization, producing the phosphide anion.
e) which, on full ionization, produces a monovalent anion.
Correct alternative: c) of total ionization, forming the hydroxonium cation.
Phosphoric acid is a chemical compound that ionizes when in contact with water and releases H ions+.
Ionization takes place in three steps:
| First step | |
| Second stage | |
| third step | |
| sum of steps |
The cations (H+) released react with water, forming the hydroxon ion (H3O+).
According to this reasoning we have to:
a) WRONG. Dissociation occurs in ionic compounds and phosphoric acid is a molecular compound.
b) WRONG. Phosphoric acid is a triacid because it has three ionizable hydrogens.
c) CORRECT. The hydroxonium cation, also called hydronium, is a species formed by the junction of an ionizable hydrogen with water.
d) WRONG. The anion produced is phosphate (). The phosphide formula is:
e) WRONG. The formed anion () is trivalent because it has a 3-charge.
3. Correctly associate the compounds below with their respective inorganic functions.
| I. HBr, H3DUST4 and H2CO3 | ( ) acids |
| II. CO2, ONLY2 and Al2O3 | ( ) bases |
| III. Al2(OH)3, KOH and NH4oh | ( ) salts |
| IV. NaCℓ, KNO3 and BaSO4 | ( ) oxides |
Acids are compounds that have ionizable hydrogens.
(I) acids: HBr, H3DUST4 and H2CO3
The bases have the hydroxyl ion.
(III) bases: Al2(OH)3, KOH and NH4oh
Salts are ionic compounds formed by cations and anions.
(IV) salts: NaCℓ, KNO3 and BaSO4
Oxides are compounds formed by the junction of oxygen with other elements, except fluorine.
(II) oxides: CO2, ONLY2 and Al2O3
Acids
4. Write the name of the following acids:
a) HCl and HBr
Hydrochloric acid and hydrobromic acid.
The above compounds represent hydrates. Acids in this class have formula HxA, where x represents the number of hydrogens (H) and A corresponds to the bound ametal.
The nomenclature of these substances is done as follows:
| H | Cl | |
| Acid | Chlorine | hydric |
| Hydrochloric acid |
| H | br | |
| Acid | Brom | hydric |
| hydrobromic acid |
b) HNO3 and HNO2
Nitric acid and nitrous acid.
The above compounds represent oxyacids with two oxidation numbers. Acids in this class have formula HxAO, being formed by hydrogen, nonmetal and oxygen.
The nomenclature of these substances is done as follows:
| H | N | O3 |
| Acid | Nitr | ich |
| Nitric acid. The Nox of nitrogen in this compound is +5. |
The lowest Nox compound is nitrous acid: HNO2.
| H | N | O2 |
| Acid | Nitr | bone |
| Nitrous acid. The Nox of nitrogen in this compound is +3. |
c) HClO, HClO2, HClO3 and HClO4
Hypochlorous, chlorous, chloric and perchloric acids.
The above compounds represent oxyacids with four oxidation numbers. Acids in this class have formula HxAO, being formed by hydrogen, oxygen and a nonmetal of the 7A family.
The nomenclature of these substances is done as follows:
| Nox +1 | Acid | hippo | element prefix | bone |
| Nox +3 | Acid | - | element prefix | bone |
| Nox +5 | Acid | - | element prefix | ich |
| Nox +7 | Acid | per | element prefix | ich |
The compounds given in the alternative are named as follows:
| H | Cl | O | |
| Acid | hippo | chlorine | bone |
| Hypochlorous acid. The Nox of chlorine in this compound is +1. |
| H | Cl | O2 |
| Acid | chlorine | bone |
| Chlorine acid. The Nox of chlorine in this compound is +3. |
| H | Cl | O3 |
| Acid | chlorine | ich |
| Chloric acid. The Nox of chlorine in this compound is +5. |
| H | Cl | O4 | |
| Acid | per | chlorine | ich |
| Perchloric acid. The Nox of chlorine in this compound is +7. |
5. (UVA-CE) HClO acids4, H2MnO4, H3DUST3, H4Saturday2O7, regarding the number of ionizable hydrogens, can be classified into:
a) monoacid, diacid, triacid, tetraacid.
b) monoacid, diacid, triacid, triacid.
c) monoacid, diacid, diacid, tetraacid.
d) monoacid, monoacid, diacid, triacid.
Correct alternative: c) monoacid, diacid, diacid, tetraacid.
The ionization of the presented acids occurs as follows:
Structural formulas show us that ionizable hydrogens are bonded to oxygen.
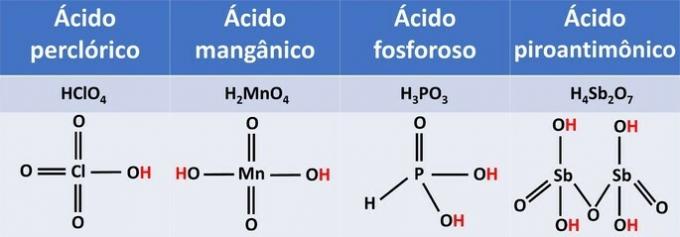
By the amount of ionizable hydrogens, acids can be classified into:
| HClO4 | an ionizable hydrogen | monoacid |
| H2MnO4 | Two ionizable hydrogens | diacid |
| H3DUST3 | Two ionizable hydrogens | diacid |
| H4Saturday2O7 | Four ionizable hydrogens | tetracid |
For oxyacids, ionizable hydrogens are those that are directly attached to oxygen. Phosphorous acid has one of its three hydrogens attached to the central element, phosphorus, and is therefore a diacid.
6. (UESPI) Let the acids be listed below, with their respective degrees of ionization in percentage (α%):
|
HClO4 (α% = 97%) |
H2ONLY4 (α% = 61%) |
H3BO3 (α% = 0,025%) |
H3DUST4 (α% = 27%) |
HNO3 (α% = 92%) |
Check the correct statement:
a) H3DUST4 is stronger than H2ONLY4.
b) HNO3 it is a mild acid.
c) HClO4 is weaker than HNO3.
d) H3DUST4 it's a strong acid.
e) H3BO3 it's a weak acid.
Correct alternative: e) H3BO3 it's a weak acid.
The value of corresponds to the degree of ionization and is calculated by:
The higher the value of , the stronger the acid because it means that more ionized species were released into solution.
According to this reasoning we have to:
a) WRONG. The higher the value of , the stronger is the acid. the H2ONLY4 has a higher degree of ionization than H3DUST4.
b) WRONG. the HNO3 it has a degree of ionization greater than 90%. It is a strong acid.
c) WRONG.4 has a higher degree of ionization than HNO3 being, therefore, stronger than he.
d) WRONG. the H3DUST4 it is a moderate acid, as it has a degree of ionization between 5% and 50%.
e) CORRECT. the H3BO3 it has a degree of ionization less than 5% and is therefore a weak acid.
Bases
7. Type the name of the following bases:
a) LiOH and Be(OH)2
Lithium hydroxide and beryllium hydroxide.
The bases presented have a fixed charge and therefore the nomenclature is made as follows:
LiOH: lithium hydroxide.
Be (OH)2: beryllium hydroxide.
b) CuOH and Cu(OH)2
Cuprous hydroxide and cupric hydroxide.
Copper has two oxidation numbers: +1 and +2. One way to name a variable nox base is as follows:
| Nox +1 | CuOH | cuprous hydroxide |
| Nox +2 | Cu(OH)2 | cupric hydroxide |
c) Sn(OH)2 and Sn(OH)4
Tin(II) hydroxide and tin(IV) hydroxide.
Tin has two oxidation numbers: +2 and +4. The nomenclature of a variable nox base can also be done as follows:
| Nox +2 | Sn(OH)2 | Tin hydroxide II |
| Nox +4 | Sn(OH)4 | Tin hydroxide IV |
8. (Fiam-SP) To combat stomach acidity caused by excess hydrochloric acid, it is customary to ingest an antacid. Of the substances below, found in people's daily lives, the most suitable for combating acidity is:
a) soda.
b) orange juice.
c) water with lemon.
d) vinegar.
e) milk of magnesia.
Correct alternative: e) milk of magnesia.
Antacids are substances used to raise the pH of the stomach, because the excess of hydrochloric acid causes a decrease in pH and, consequently, an increase in acidity.
To combat stomach acidity, it is recommended to ingest a substance with basic character, because when reacting with stomach acid, it will produce a neutralizing reaction, forming salt and water.
According to this reasoning we have to:
a) WRONG. The soda cannot be used because it contains carbonic acid in its composition.
b) WRONG. Orange cannot be used, as it contains citric acid in its composition.
c) WRONG. Lemon cannot be used, as it contains citric acid in its composition.
d) WRONG. Vinegar cannot be used, as it contains acetic acid in its composition.
e) CORRECT. Milk of magnesia should be used, as it contains magnesium hydroxide base in its composition.
The neutralization reaction formed is:
9. (Osec) A strong base must have bonded to the OH group-:
a) a very electropositive element.
b) a very electronegative element.
c) a semimetal.
d) a metal that gives 3 electrons.
e) a non-metal.
Correct alternative: a) a very electropositive element.
A strong base is one that has a high degree of dissociation, that is, free hydroxyl ions in solution.
The hydroxyl ion has a negative charge, as it manages to attract the electron towards itself when dissociating itself due to the electronegativity of oxygen.
Thus, a very electropositive element has the ability to lose electrons and give them up to the hydroxyl, remaining in the cationic form in solution.
a) CORRECT. Very electropositive elements such as alkali metals and alkaline earth metals form strong bases.
b) WRONG. An element more electronegative than oxygen would cause there to be a contest for the electron.
c) WRONG. A semimetal has great electronegativity.
d) WRONG. The hydroxyl ion has a 1- charge. a metal that gives 3 electrons would form a base with 3 hydroxyls.
Example:
e) WRONG. The strongest bases are bases formed with metals.
salts
10. Write the name of the following salts:
a-N-A2CO3
Sodium carbonate.
This is a type of neutral salt and its nomenclature is given as follows:
| anion | cation |
| At+ | |
| carbonate | sodium |
| Sodium carbonate |
b) KNaSO4
Sodium and Potassium Sulfate.
This is a type of double salt and its nomenclature is the same as the neutral salt, and the names of the two cations are written.
| anion | cations | |
| K+ | At+ | |
| Sulfate | potassium | sodium |
| Sodium and Potassium Sulfate |
c) NaHCO3
Sodium monohydrogen carbonate.
This is a type of acid salt and its nomenclature is given as follows:
| Number of hydrogens | anion | cation |
| 1 | At+ | |
| Mono | carbonate | sodium |
| Sodium monohydrogen carbonate |
The popular name for this compound is sodium bicarbonate.
d) Al(OH)2Cl
Aluminum dihydroxychloride.
This is a type of basic salt and its nomenclature is given as follows:
| Number of hydroxyls | anion | cation |
| 2 | Cl- | Al3+ |
| Di | chloride | aluminum |
| Aluminum Dihydroxychloride |
This compound is also known as dibasic aluminum chloride.
e) CuSO4. 5 hours2O
Copper Sulfate Pentahydrate.
This is a type of hydrated salt and its nomenclature is given as follows:
| anion | cation | number of water molecules |
| Ass2+ | 5 | |
| Sulfate | copper | penta |
| Copper Sulfate Pentahydrate |
11. (Unirio) Salts are also products obtained by the reaction of total or partial neutralization of the ionizable hydrogens of acids with bases or hydroxides, according to the generic reaction:
Acid + Base Salt + Water
Based on that statement, what is the only acid that doesn't have all of its related possible products?
a) hydrochloric acid only produces the neutral chloride salt.
b) nitric only produces the nitrate neutral salt.
c) phosphoric only produces the neutral phosphate salt.
d) sulfide can produce either the neutral sulfide salt or the acid salt, acid sulfide or hydrogen sulfide.
e) sulfuric can produce either the neutral sulfate salt or the acid salt, acid sulfate or hydrogen sulfate.
Incorrect alternative: c) phosphoric only produces the neutral phosphate salt.
a) CORRECT. Hydrochloric acid has only one ionizable hydrogen, which will react to form water. The salt will then be formed by the anion of the acid, in this case the chloride, and the cation of the base.
Examples:
b) CORRECT. Nitric acid has only one ionizable hydrogen, which will react to form water. The salt will then be formed by the anion of the acid, in this case the nitrate, and the cation of the base.
Examples:
c) WRONG. Phosphoric acid has three ionizable hydrogens and, therefore, it can undergo partial or total ionization. In this case, three types of salts can be formed:
- Total neutralization generating a neutral salt:
- Partial neutralization generating a acid salt:
- Partial neutralization generating a basic salt:
d) CORRECT. In total neutralization, a neutral salt is formed, and in partial neutralization, an acidic salt can be formed.
- Total Neutralization:
- Partial Neutralization:
e) CORRECT. In total neutralization, a neutral salt is formed, and in partial neutralization, an acidic salt can be formed.
- Total Neutralization:
- Partial Neutralization:
| I. At2B4O7.10h2O | THE. basic salt |
| II. Mg(OH)Cl | B. double salt |
| III. NaKSO4 | Ç. acid salt |
| IV. NaHCO3 | D. hydrated salt |
The correct association between them is:
a) AI, BIII, CIV, DII
b) AII, BIV, CIII, DI
c) AI, BII, CIII, DIV
d) AII, BIII, CIV, DI
Correct alternative: d) AII, BIII, CIV, DI
| AII. basic salt: Mg(OH)Cl | It has a hydroxyl in its structure. |
| BIII. double salt: NaKSO4 | It has two metal cations in its structure. |
| CIV. acid salt: NaHCO3 | It has a hydrogen in its structure. |
| DI. hydrated salt: Na2B4O7.10h2O | It has water molecules in its structure. |
Oxides
13. Write the name of the following oxides:
steel2 and no2O3
Carbon Dioxide and Dinitrogen Trioxide.
These oxides are molecular oxides, as oxygen is bonded to nonmetals. The nomenclature for this class is done as follows:
| number of oxygens | Number of carbons |
| 2 | 1 |
| Monocarbon Dioxide or Carbon Dioxide |
| number of oxygens | Number of nitrogens |
| 3 | 2 |
| dinitrogen trioxide |
b) Al2O3 and on2O
Aluminum oxide and sodium oxide.
These oxides are ionic oxides, as oxygen is bound to metals. Metals bound to oxygen have a fixed charge. Therefore, the nomenclature for this class is done as follows:
Al2O3: aluminum oxide
At2O: sodium oxide
b) Cu2O and CuO
Copper oxide I and copper oxide II.
These oxides are ionic oxides because oxygen is bonded to a metal. Metal bound to oxygen has a variable charge. One way to name this class is as follows:
| Nox +1 | Ass2O | copper oxide I |
| Nox +2 | CuO | copper oxide II |
c) FeO and Fe2O3
Ferrous oxide and ferric oxide.
These oxides are ionic oxides because oxygen is bonded to a metal. Metal bound to oxygen has a variable charge. The nomenclature of a variable nox oxide can also be done as follows:
| Nox +2 | FeO | ferrous oxide |
| Nox +3 | Faith2O3 | ferric oxide |
14. (UEMA) Neutral atoms of a certain representative element M have two electrons in their valence shell. The correct formulas for your normal oxide and bromide are, respectively:
(Data: O= 6A and Br = 7A.)
a) M2O and MBr
b) MO2 and MBr2
c) MO and MBr2
d) M2O2 in2br
in2O and MBr2
Correct alternative: c) MO and MBr2
The M elements have two electrons in the valence shell. To bond with other elements it can lose these two electrons and form the M cation.2+.
Oxygen belongs to the 6A family and needs 2 more electrons to acquire stability with the electronic configuration of a noble gas, as stated by the octet rule.
Likewise, bromine, which is from the 7A family, needs only 1 electron to have 8 electrons in the valence shell.
According to this information we have to:
a) WRONG. To form compound M2O and MBr, the M element should form the M cation+.
b) WRONG. Oxygen has a 2- and not a 1- charge as represented when forming the MO compound2.
c) CORRECT. According to the valence of the ions the alternative is correct.
d) WRONG. The bromide has a 1- and not a 2- charge as shown when forming compound M2Br.
e) WRONG. The element cation has a 2+ charge and not a 1+ charge as shown when forming the M compound.2O.
15. (PUC-MG) Observe the chemical reactions below:
| I. MgO + H2O |
| II. CO2 + H2O |
| III. K2O + 2HCl |
| IV. ONLY3 + 2NaOH |
The incorrect statement is:
a) Reactions II and IV involve acid oxides or anhydrides.
b) Reactions I and III involve basic oxides.
c) The salt produced in reaction IV is called sodium sulfate.
d) The salt produced in reaction III is called potassium chloride.
e) The basic character of oxides is accentuated as oxygen binds to more electronegative elements.
Incorrect alternative: e) The basic character of the oxides increases as oxygen binds to more electronegative elements.
a) CORRECT. When acidic oxides such as carbon dioxide and sulfur trioxide react with water, they form an acid in solution.
b) CORRECT. When reacting with water, basic oxides such as magnesium oxide and potassium oxide form a base in solution.
c) CORRECT. At2ONLY4 is the formula for sodium sulfate.
d) CORRECT. KCl is the formula for potassium chloride.
e) WRONG. The basic character of the oxides is accentuated as oxygen binds to more elements. electropositive, as the alkaline and earth alkaline metals, because when they react with water they generate strong bases and when reacting with acids they form salt and water.
