In astronomy, the Universe it corresponds to the set of all existing matter and energy.
It gathers the stars: planets, comets, stars, galaxies, nebulae, satellites, among others.
It is an immense place and for many, infinite. Note that from the Latin, the word university means “whole whole” or “all in one”.
Origin of the Universe
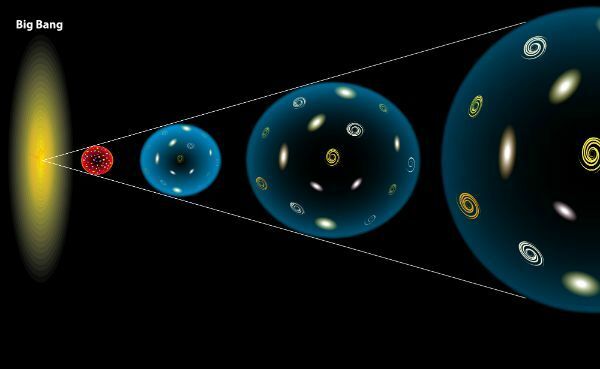
The most accepted theory and scientific and cosmological model about the origin of the universe is called "Big Bang Theory”.
In it, there was a great explosion about 14 billion years ago, thus originating several celestial bodies, and also the concept of space and time.
From there, the universe was expanding more and more, so that it was cooled giving rise to the various stars.
Some scientists consider it infinite and point to the existence of other universes.
See too: Origin of the Universe.
Main Elements of the Universe
The most relevant celestial bodies that are part of the universe are:
- planets: solid, rounded bodies that do not have their own light and heat. However, each planet has its own gravity, which revolve around a star.
- galaxies: set of planets, stars and gases. The universe has approximately 100 billion galaxies. We live in the galaxy called Milky Way, where is the solar system.
- comets: celestial bodies that have little mass and irregular orbits. The best known is the Halley's Comet.
- stars: spherical celestial bodies formed from plasma and which have their own light and heat, for example, the Sun.
- Satellites: classified into natural satellites and artificial satellites, satellites are solid celestial bodies that orbit the planets. The best known natural satellite is the Moon and the artificial is the satellite Sputnik.
Fun Facts: Did You Know?
The expression "Parallel Universe" refers to a concept of quantum physics related to the existence of other universes and other as yet unknown realities.
This concept is closely related to the incomprehension and impossibility of assimilating the dimension of the universe.
To complement your research see also other articles from Astronomy.