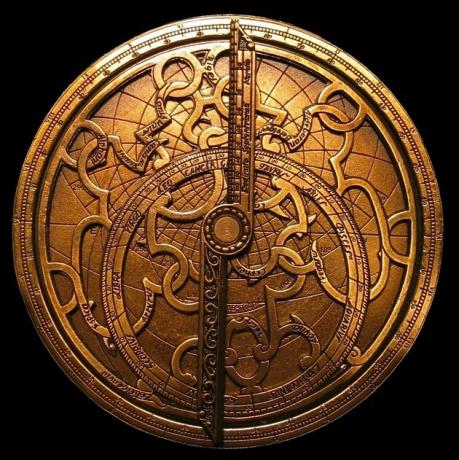
O astrolabe it is a measuring instrument that was invented by the Arabs and perfected by the Greeks.
Initially it was used on land, but was adopted by sailors in order to calculate the distances of sea routes.
It is estimated that there may be around two hundred functions for this instrument. Among which stand out to know the time, specify the seasons, calculate the height of mountains or the depth of a well, etc.

Origin of the Astrolabe
The astrolabe has an uncertain origin, but it developed from the mathematical studies of researchers such as Euclid, Theon of Alexandria, Claudius Ptolemy, Hypatia of Alexandria and many others.
If the creation of the astrolabe is imprecise, its improvement and use of the metal were given by Abraão Zacuto (1450-1522).
Probably born in Salamanca (Spain), Zacuto took refuge in the Portuguese court after the expulsion of the Jews from Spain, at the same time as the Great Navigations.
In Lisbon, he was adviser to the court of King Dom João II (1455-1495) and perfected the astronomical tables, as well as the astrolabe that was used by Vasco da Gama and Pedro Alvares Cabral on his travels across the Atlantic.
Astrolabe Functioning
The astrolabe represents the moving celestial vault. In this way, it is made up of several parts that depict latitudes, stars and constellations.
The instrument consisted of the first attempt to transpose the curved surface of the sky to a plane. It can be built with simple materials such as paper and brass.
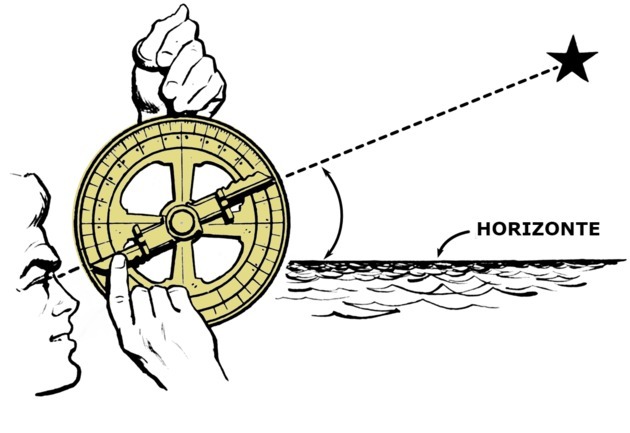
Let's see how we might see the time from the use of an astrolabe on the Midsummer Solstice.
The first thing to do is to find a star on the horizon, which will be the reference point. Suppose we choose the star Spica (Spike), from the constellation Virgo. By measuring it, we will obtain the degree of the angle of the triangle, which for our example was 30º.
That done, we go around the astrolabe to find, in the spider, the point corresponding to that star.
We rotated until it coincided with the 30º latitude of one of the eardrums.
We turn the ruler so that it coincides with the Summer Solstice and we will get the hours that mark at that moment.
Importance of the Astrolabe for Navigation
The nautical astrolabe was essential for navigators, as it made it possible to calculate distances in a practical way with just one instrument and knowledge of geometry.
It was no longer necessary to carry the tables with astronomical calculations that would give information about latitude and longitude. All that was needed was the astrolabe and the maps that could be carried easily by the user.
There was a sailor who had to measure latitude every day at solar noon in order to know where they were at sea.
Along with the sextant and the compass, the astrolabe was very important in making navigation safer.
Parts of an Astrolabe
Let's see what the parts of an astrolabe are:
In the center is engraved the maximum point of the sun, the zenith, whose maximum height is reached in the Summer Solstice.
As the elliptical rotates, the astrolabe marks 15 degrees for each hour elapsed. Thus, we will be able to accurately know the time of day and night.
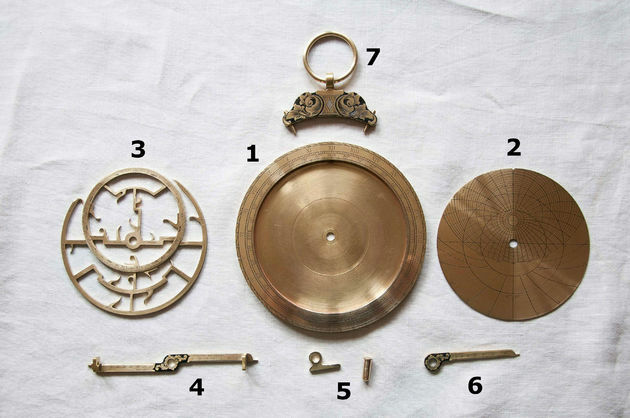

- Mater - the disk that will contain all the plates that form the astrolabe.
- Eardrums - one for each latitude. On it are engraved the circles of altitude of the celestial sphere.
- Spider – a hollow disc where each of its points represents the position of the stars and the sun in the celestial vault. Its position varies from the Summer Solstice to the Winter Solstice.
- alidade - located at the rear. It contains two displays that will serve to measure the height of celestial objects.
- pins - which secure the needle to the Mater and allow it to rotate.
- Needle (or ruler) - which will tell us the result of the measures we take.
- shoulder strap - allows the user to hang and carry it more easily.
Curiosities
- The oldest known astrolabe is an example designed by the astronomer Nastulus, in the year 927, in Baghdad.
- The instrument arrived in Europe via Muslim Spain, Al-Andalus, in the 12th century.
- There are a multitude of types of astrolabes such as flat, spherical, Islamic, maritime, universal, etc.
read more:
- wind rose
- European Maritime Expansion
- discovery of america
- arab culture
- Modern age

