Normal strength (Fno), also called “support force”, is a type of contact force exerted by a body on a surface.
As an example, we can think of a block at rest on a table, where both exert the normal force on each other, perpendicular to the contact surfaces.
Note that this force is important as it prevents solid objects from being traversed by others. That's because the strength of gravity it works by pushing that object downward, while the normal force opposes it.
In addition to normal strength, we have the strength weight which acts in the vertical direction under the pull of Earth's gravitation. In this case, the normal force will be of the same intensity as the weight force, however, in the opposite direction.
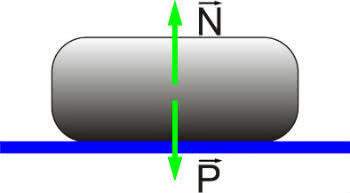 Normal Strength and Weight Strength acting on a block
Normal Strength and Weight Strength acting on a block
Read more about the topic in the article: Strength.
Formulas
To calculate the normal force of an object that is at rest in a flat surface, the following expression is used:
N = m. g
Being,
N: normal force
m: object mass
g: gravity
Remember that strength is a
vector indicated by an arrow above the letter. Note that the vectors have modulus (strength of the force exerted), direction (the line along which it acts) and direction (the side of the line on which the force was exerted).Have a question about vectors? Read the article: Vectors: Sum, Subtraction and Decomposition.
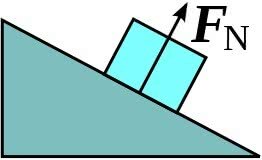 Actuation of normal force on an inclined plane
Actuation of normal force on an inclined plane
However, if that object is in a inclined plane, the formula is as follows:
N = m. g. cos(x)
Being,
N: normal force
m: object mass
g: gravity
x: object tilt angle
Learn more at inclined plane.
Examples: How to calculate normal force?
1. An object with a mass of 10 kg is at rest on a flat surface. Consider the Earth's gravity of 9.8m/s2.
N = m. g
N = 10. 9,8
N = 98 N
2. Calculate the normal force of a 5 kg object that is on a 45° inclined plane. Consider the Earth's gravity of 9.8m/s2.
N = m. g. cos 45th
N = 5. 9,8. 0,7
N = 34.3 N
Entrance Exam Exercises with Feedback
1. (PUC-RS) Let's say you are in a supermarket, waiting to weigh a quantity of apples on a spring scale whose unit of measure is the kilogram-force.
The scale reading corresponds to:
a) the modulus of the normal force, as this is the force of interaction between the apples and the scale, whose value is supposedly equal to the modulus of the weight of the apples.
b) both the value of the modulus of the weight force and the modulus of the normal force, since both constitute an action-reaction pair, according to Newton's third law.
c) the apple weight modulus, as this is the force of interaction between the apples and the scale.
d) the modulus of the resultant force on the apples.
e) the amount of apple matter.
Alternative to
2. (FUVEST-SP) A man tries to lift a 5 kg box, which is on a table, applying a vertical force of 10 N. In this situation, the value of the force that the table applies to the box is: (g=10m/s2).
a) 0 N
b) 5 N
c) 10 N
d) 40 N
e) 50 N
Alternative
3. (UFOP-MG) Which pair of forces below represents an action and reaction pair?
a) The weight of the block and the normal reaction of the table on the block.
b) The attraction force the Earth makes on a block and the attraction force the block makes on the Earth.
c) The weight of a ship and the thrust that the water makes on the vessel.
d) A horizontal force pulling a block onto a table and the friction force of the table onto the block.
Alternative b
4. (UNCISAL-AL) A glass is at rest on a horizontal table, in a place where the acceleration due to gravity is constant. It is correct to say that
a) the weight force of the cup is the reaction to the force that the table exerts on it.
b) the weight force of the cup and the normal reaction of the table on the cup cancel each other out.
c) if the glass is dragged across the table, the normal reaction of the table over the glass will change towards it.
d) if the glass is dragged over the table, the normal reaction of the table over the glass will change in intensity.
e) if a person rests their hand on the glass, the normal reaction of the table on it will decrease in intensity.
Alternative b
To learn more, read also:
- Newton's Laws
- Newton's Laws - Exercises
- Vector Quantities
- Pulleys
- Physics Formulas