The Milky Way is among the hundreds of billions of galaxies in the Universe and where our Solar System is located.
The Latin name – Milky Way – derives from the Greek word "Kiklios Galaxies", whose meaning is milky circle.
Considering the estimated age of the Universe, the Milky Way is approximately 14 billion Earth years old.

Our Galaxy: Milky Way
Scientists believe that the Milky Way and other large galaxies formed over billions of years from interactions between smaller galaxies and, in in particular, the gradual capture of many stars from nearby dwarf galaxies (small galaxies with hundreds or thousands of times fewer stars than the Via Milk).
Structure and Location of the Solar System
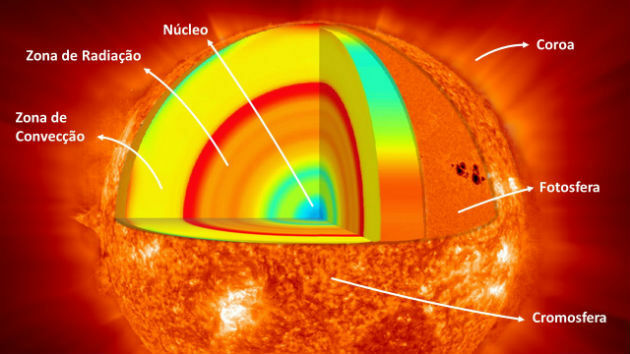
The Milky Way has approximately 200 billion stars, plus clouds of gas and dust. It is shaped like a spiral and consists of a disk with a core and a halo.
The central region of the Milky Way has a higher stellar density than the outer regions. It contains a massive central object, believed to be a huge black hole.
Its diameter is approximately 100,000 light-years and its thickness 80 thousand light years. The diameter of the core is about 30,000 light-years north-south and 40,000 light-years equatorial.
The Milky Way has spiral arms. Perseus, Sagittarius, Centaur and Cygnus being the main arms. Our solar system is located in an arm called Orion.

Location and movement of the Sun in the Milky Way
Our Sun is located 26,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way. Its speed around the galactic core is 250 km/s and it takes about 200 million years to make a complete circle around the galaxy.
Milky Way seen from Earth
It is possible to observe Earth's Milky Way in places without artificial lighting and with clear air.
On cloudless and moonless nights we clearly see a whitish band in the sky that crosses the celestial hemisphere from horizon to horizon. The brightest part is in the constellation Sagittarius.
In the Southern Hemisphere it is best observed during winter nights (June and July).

Milky Way Image
Local Group
The Milky Way belongs to a cluster of galaxies called by scientists the “Local Group”, consisting of about 50 galaxies.
Among the best-known galaxies in this group are the Milky Way, Andromeda and Triangle. The others are dwarf galaxies that orbit the Milky Way or Andromeda.
According to scientists' observations, these two galaxies are on a collision course, approaching at a speed of 480,000 kilometers per hour, and will collide in 5 billion years.
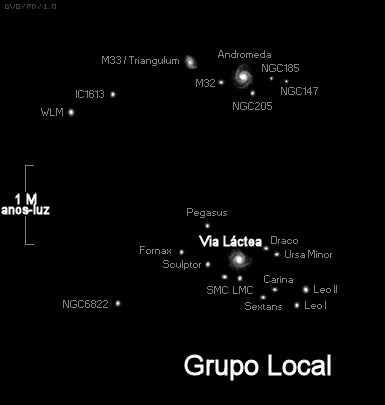
Milky Way and main galaxies that form the Local Group
Milky Way Observations
The first observations of the Milky Way were made by the Greek astronomer Democritus, who lived between 460 and 370 BC. Ç.
The first map of the galaxy was drawn up by William Herschel in 1785, he studied and measured the distribution of stars in space. Herschel counted the stars and concluded that they formed a great disk.
In 1918, the astronomer Harlow Shapey estimated the total size of the Milky Way and the position of the Solar System.
Scientists believed until the end of 1920 that the Universe was limited to the Milky Way. However, the belief was undone from the observations of Edwin Hubble, who noticed diffuse spots in space and concluded that they were, in fact, separate galaxies.
To learn more, read also:
- galaxies
- stars
- Black Hole
- Big Bang Theory
- origin of the universe
- what is universe
- Main constellations