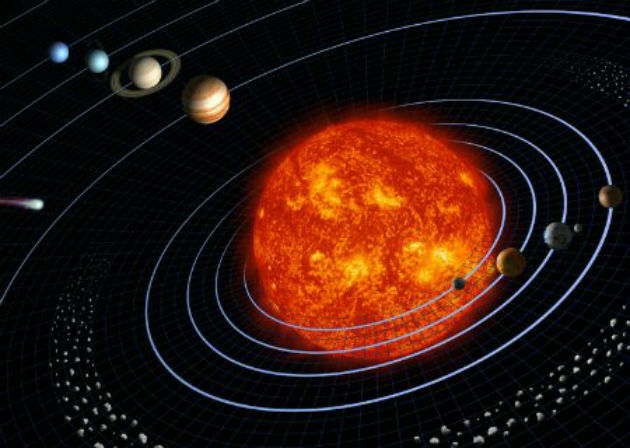
The Sun is a star located at the center of our solar system. Its gravity keeps rotating in its orbit from the biggest planets to tiny debris particles.
Huge amounts of energy are produced inside the Sun through fusion reactions of hydrogen into helium. This intense energy is our source of light and heat and without it there would be no life on Earth.
It is a yellow dwarf star and its age is about 4.6 billion years old. It is estimated that it will take around 6.5 billion years to transform into a white dwarf.
knowing the sun
- The sun's surface has a temperature of 5,500 degrees Celsius and rises towards the core where it reaches about 15 million degrees Celsius.
- Its gravitational field is very strong.
- The rotation period at the equator is 25 Earth days and at the poles it increases to 36 days.
- It is distant from Earth about 149.6 million kilometers.
- The Sun is so big that 1.3 million Earth-sized planets would fit inside it.
- The interactions between the Sun and Earth produce the seasons, weather, climate and ocean currents. terrestrial, as well as all the similar phenomena that occur in the other celestial bodies of the System Solar.
- It doesn't have a solid surface.
- Sunlight takes about eight minutes to reach Earth.
Composition and structure
The mass of the Sun corresponds to 99.8% of the mass of our solar system. It is formed by gases, and in number of particles, its composition corresponds to 71% of hydrogen and 27% of helium.
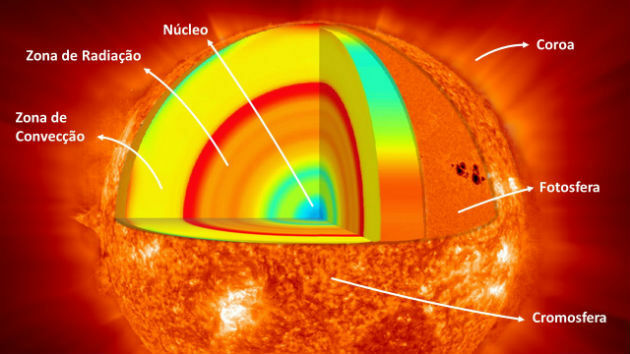
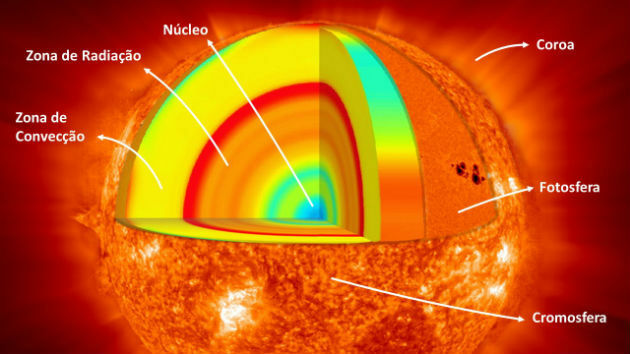
The Sun has six regions, they are:
- Core - the hottest and most massive part of the Sun. It has about 139 thousand kilometers. It is in the core region that solar energy is produced.
- radiation zone - in this area, the energy of the nucleus propagates through radiation.
- convection zone - is the portion of the Sun where convection currents of heat occur. These currents carry energy to the outside of the solar surface.
- Photosphere - is the visible part of the Earth.
- Chromosphere - is the part where the transition between the photosphere and the sun's corona occurs.
- Crown - consists of plasma. It is the luminous part of the Sun. In this region, the temperature reaches 2 million degrees Celsius.
Solar Explosions
The thermonuclear fusion reactions that take place inside the Sun produce an enormous amount of energy. This energy is carried out through the convection zone.
This escape occurs with the explosion of giant bubbles of hot plasma composed of ionized atoms that move upwards.
The solar surface, the photosphere, is about 500 kilometers thick. It is from this region that most of the Sun's radiation escapes.
Solar activities occur in cycles of approximately 11 years. They happen because of the change in polarity of their geographic poles.
During periods of increased solar activity, solar storms occur (sunspots, solar flares and coronal mass ejections), which release an enormous amount of energy and particles.
Video
Watch amazing images of a solar radiation storm captured by satellites in NASA's video.
Curiosities
The biggest and brightest star in our Solar System has inspired and influenced cultures around the world.
Ancient peoples, such as the Egyptians, Aztecs, Incas, Mayans and others, revered the movements of the Sun and the Moon and recorded them on rocks and monuments.
Seasonal calendars and monitoring were created based on the movement of sunlight. The name Sun was used by the Romans, the Greeks called it Helios.
read further:
- Sun: all about the Sun
- Solar eclipse
- Planets of the Solar System
- Natural Satellites
- stars