The Sun is a star that is 1,392,700 km, that is, it is 109 thousand times larger than the Earth. The Earth is 12 742 km, which means that inside the Sun it would be possible to place 1.3 million Earth planets.
But despite being much larger than Earth compared to other stars, this star is not that big. The largest known star, VY Canis Majoris, is about 2,000 times larger than the Sun.
The Sun contains almost the entire mass of the solar system, about 99.8%. It is because of their mass that the planets orbit around them.
The main features of the Sun
Pasta: 1,989 x 1030 kg (300,000 times the Earth's mass)
Lightning: 6.96 x 108 km, the same as 695 500 km (100 times the radius of the Earth)
medium density: 1.409 kg/m3
Distance from Earth: 1,496 x 108 km, the same as 149 600 000 km
luminosity: 3.9 x 1026 watts = 3.9 x 1033 ergs/s
surface temperature: 5,500 degrees Celsius
core temperature: 15 million degrees Celsius
Age: 4.6 billion years
Chemical composition (mass): 91.2% hydrogen, 8.7% helium, 0.078% oxygen and 0.043% carbon
rotation period: 25.67 days in the equator and 33.40 days in the polar regions
The distance from Earth to Sun
The Sun is about 150 million km from Earth, the equivalent of 8 light minutes away (1 light minute is 17,987,547 kilometers).
This distance is surprising, even more if we think that even so the Sun is the star that is closest to our planet.
Because of the distance, sunlight does not reach us immediately; it takes 8 minutes and 18 seconds to reach Earth.
Gigantic numbers: age and temperature of the sun
Studies indicate that the Sun, like the Earth, is about 4.5 billion years old.
As for the temperature, it varies between 5.5 thousand and 15 million degrees Celsius, respectively the temperatures of the photosphere and the core. Interestingly, the photosphere is cooler than the Sun's outermost layer, the Crown.
What is the Sun made of?
The Sun is composed largely of hydrogen and helium.
In percentage terms, its mass is composed as follows: 91.2% hydrogen, 8.7% helium, 0.078% oxygen and 0.043% carbon.
In number of particles, the chemical composition is as follows: 71% hydrogen, 27% helium, 1.2% oxygen and 0.6% carbon.
The 6 layers of the sun
The structure of the Sun is made up of six layers, from the outside to the inside, respectively:
- Crown
- Chromosphere
- Photosphere
- convective layer
- radiative layer
- Core
The photosphere is the surface of the sun, while the sun atmosphere it is composed of: chromosphere and crown. O interior of the sun, in turn, is composed of: convective layer, radiative layer and core.
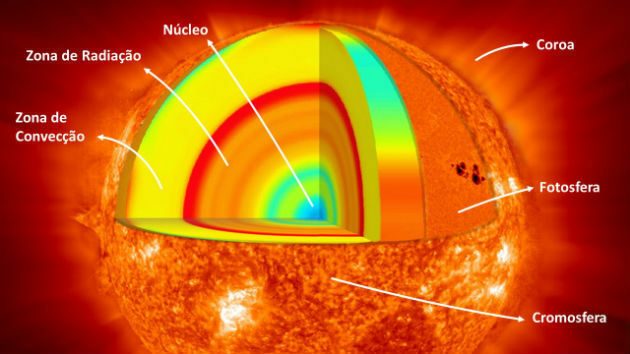
1. Crown
Also called Corona, it is an extensive, rarefied layer outside the photosphere. From it comes the solar wind, which are streams of charged particles that blow at a speed of 1 600 000 km/h. As a result of solar winds, the Sun gradually loses its mass.
2. Chromosphere
Narrow layer (10 000 km thick), rarefied and external to the photosphere. It is reddish and is visible only in eclipses.
3. Photosphere
It's the layer we see because it emits sunlight. It is 500 km thick.
In this layer are found dark spots, known as sunspots, which are magnetic storms that appear every 11 years, precisely as a result of changes in the Sun's magnetic field.
The central part of the photosphere is called the umbra, and it is the darkest. It is surrounded by penumbra, the lightest region.
4. convection zone
Also called the convective layer, it is the layer inside the photosphere that surrounds the radiative zone. In it, energy is diffused by convection, that is, by the movement of gas molecules.
5. radiation zone
Also called the radiative layer, it is the layer inside the photosphere where energy is diffused through radiation. The energy from the Sun's core can take more than 100,000 years to pass through this layer.
6. Core
The core is the layer where solar energy is generated through thermonuclear reactions that take place every second. This energy takes 1 million years to reach the surface of the Sun.
Curiosities about the Sun
- The Sun is 109 thousand times larger than the Earth.
- Within the Sun fit 1.3 million Earth planets.
- Sunlight takes 8 minutes and 18 seconds to reach Earth.
- The Sun is about 4.5 billion years old.
- The temperature of the Sun varies between 5,500 and 15 million degrees Celsius.
- The Essa generated in the Sun's core takes 1 million years to reach its surface.
- Parker Solar Probe is the name of the probe that came closest to the Sun, which happened in August 2018. This is a NASA mission that consists of a gradual approach to the Sun; it predicts that in 2025 the probe will reach its crown.
- One day there will be no more sun.
The question that won't remain silent: will the sun die?
When its energy sources run out, the sun will die.
In 4.5 billion years of life, the Sun has consumed about half of its hydrogen. That means he's in the middle of his life.
When the Sun has used up all of its hydrogen, helium will become its main fuel. Ending its consumption, the death of the Sun will be underway, because at that moment, the star will begin to increase in size and will swallow planets (this is what will happen to the Earth). It will get 100 times bigger, until it collapses.
Read too Sun Characteristics and What are stars?



