Acceleration is a vector physical quantity and its unit is the m/s². Acceleration measures the change of velocity in relation to time. Therefore, we can say that acceleration is the rate of change over time the speed of a mobile.
Types of Acceleration
All acceleration is caused by the application of a non-zero net force in accordance with Newton's 2nd Law. Thus, there are several situations in which accelerations are produced by forces of different natures. Check out some of them:
Centripetal acceleration: When a body describes a circular or curvilinear trajectory, we say that it is subject to centripetal acceleration. This acceleration arises when a force is applied perpendicular to the body's velocity. To learn more about, click on here.
Gravitational acceleration: This type of acceleration arises from the attraction between masses. Massive bodies, such as planets and stars, produce large gravitational fields around them, attracting all bodies in their vicinity. To learn more, click on here.
Accelerationtangential: It is the component of acceleration that is in the same direction as the linear velocity of a mobile that performs a circular movement, this acceleration contributes to the change in body velocity.
Accelerationinloads: Electric charges and currents are subject to accelerations produced by the electromagnetic force, described by Coulomb's laws and the law of magnetic force.
See too:How to solve kinematics exercises
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Average and instantaneous scalar acceleration
Although acceleration is a greatnessvector, there are a large number of problem-situations present in the exercises that present one-dimensional movements, that is, they happen along a only direction from space. In these cases, it is not necessary to consider all vector operations to calculate the acceleration, we can consider it as a scalar (number). Average acceleration is the temporal variation of velocity for non-zero time intervals. The formula of average scalar acceleration is shown in the following figure:

The — average acceleration
ov — speed variation
t - time interval
Instantaneous acceleration, in turn, is calculated in the same way as average acceleration, however, the time interval between velocity measurements is much shorter. We say that the time span t tends to zero. Check out the formula that is used to calculate instantaneous acceleration:

Acceleration Formula
The acceleration formula is very simple to use: it is determined by the speed variation (ov) divided by the time interval (t), check out:

The — average acceleration
t -time interval
vF — final speed
vi — initial speed
In the formula just shown, v and v0 are, respectively, velocityFinal and velocityinitial of a mobile, measured in m/s (meters per second). Already t and t0 they are the momentsintimeinitial and timeFinal.
Acceleration unit
According to the international system of units (I.I.), the unit of measure of acceleration is the meter per second per second, or simply m/s² (which can also be written as m.s-2). Check out some examples to better understand the unit of measure of the acceleration quantity:
A vehicle that was at rest and starts a movement with an acceleration of 2 m/s² will have its speed increased by 2 m/s during each second of its movement.
A mobile that starts braking at 3 m/s² will have its speed decreased by 3 m/s every second.
Types of Movement According to Acceleration
There are some movement classifications related to the modulus of a rover's acceleration. Check out the most important ones:
Accelerated movement: When the speed of a body increases every second, we say that your movement is accelerated. The acceleration in this type of movement is positive.
Movementretarded: In this type of movement, the speed of the mobile decreases every second, that's why we say your movement is retarded. When the mobile's speed decreases, its acceleration is negative.
evenly varied movement: When the mobile's acceleration is constant, we say that its movement is uniformly varied. In the case that your speed increases steadily, the movement is said uniformly accelerated, if your speed steadily decreases, it is called a uniformly delayed.
uniform movement:O uniform movement characterized by not showing acceleration. In this type of movement, the speed is constant and the acceleration is null.
See too: Check out the graphics of accelerated motion
solved exercises
(Question 1) During a sprint, the cheetah can reach a speed of 104 km/h, in a time interval of approximately 9.6 seconds. Determine the average acceleration of this animal during its sprint.
Resolution
To calculate the average acceleration for the cheetah, we will use the formula for average acceleration. In addition, we must convert the speed from km/h to m/s:

Dividing the final speed of 104 km/h by the factor of 3.6, we have a final speed of 28.9 m/s. Applying the data in the previous formula, we will have the following calculation to be done:
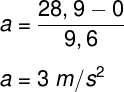
The result found indicates that the speed of the cheetah changes by 3 m/s every second.
(Question 2) Determine the final speed of a rover that starts a braking process that lasts 8 s, with a constant deceleration of 2.5 m/s², knowing that the rover's initial speed was 20 m/s.
Resolution:
To solve the exercise, it is necessary to adopt the sign of acceleration as negative, as the movement described by the statement is delayed. In doing so, we will have to solve the following calculation:

According to the acceleration provided by the exercise, the final velocity of this mobile should be zero at the end of 8 s.
By Me. Rafael Helerbrock
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
HELERBROCK, Rafael. "Acceleration"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/aceleracao.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.