Muscle tissue is related to locomotion and other body movements.
Among its main characteristics are: excitability, contractility, extensibility and elasticity.
Muscles represent 40% of body mass. Therefore, in many animals muscle tissue is the most abundant.
Muscle tissue cells are elongated and are called muscle fibers or myocytes. They are rich in two proteins: actin and myosin.
In the study of muscle tissue, its structural elements receive a different name. Understand each of them:
Cell = Muscle Fiber;
Plasma membrane = Sarcolemma;
Cytoplasm = Sarcoplasm;
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum = Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Muscle Tissue Functions
- body movement
- stabilization and posture
- Regulation of organ volume
- heat production
Muscle tissue is classified into three types: skeletal striatum, cardiac striatum and smooth or unstriated.
Each tissue is formed by muscle fibers that have particular morphological and functional characteristics, as we will see below:
Skeletal Striated Muscle Tissue
The term skeletal is due to its location, as it is linked to the skeleton.
Skeletal striated muscle tissue has voluntary and rapid contraction.
Each muscle fiber contains several myofibrils, filaments of proteins (actin, myosin and others).
The organization of these elements makes it possible to observe transverse striations under the light microscope, which gave the name striated to the tissue.
Skeletal striated muscle fibers are shaped like long cylinders, which can be the length of the muscle to which they belong. They are multinucleated and the nuclei are located on the periphery of the fiber, close to the cell membrane.
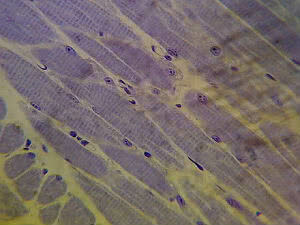
Longitudinal section of the skeletal fibers, where it is possible to observe their striations
Muscle fiber and contraction
THE Muscular contraction allows locomotion and other body movements.
Muscle fibers contract due to the shortening of myofibrils, cytoplasmic filaments rich in actin and myosin proteins, arranged along their length.
These filaments can be observed under an optical microscope, the presence of striations can be observed. transverse by alternating light bands (Band I, actin myofilaments) and dark bands (Band A, myofilaments of myosin).
This structure is called sarcomere, which represents the functional unit of muscle contraction.
A muscle cell has between tens and hundreds of sarcomeres arranged in the myofibril. Each sarcomere is delimited by two transverse discs, called Z lines.
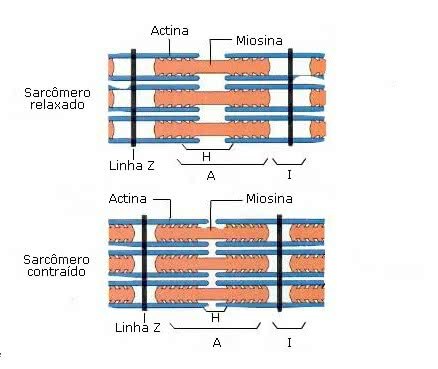 The sarcomere and its role during muscle contraction
The sarcomere and its role during muscle contraction
Briefly, muscle contraction refers to the slip of actin over myosin.
That's because actin and myosin form organized filaments that allow them to slide over each other, shortening the myofibrils and leading to muscle contraction.
In the cytoplasm of the muscle fiber it is possible to find several mitochondria, which guarantee the necessary energy for muscle contraction and glycogen granules.
Muscle fibers are held together by connective tissue. This tissue allows the contraction force, generated by each individual fiber, to act on the entire muscle.
Also, the connective tissue it nourishes and oxygenates muscle cells and transmits the force generated in contraction to neighboring tissues.
To learn more, read also: Muscle System and Muscles of the Human Body.
Cardiac Striated Muscle Tissue
It is the main tissue of the heart.
This tissue has involuntary, vigorous and rhythmic contraction.
It consists of elongated and branched cells with a nucleus or two central nuclei.
They have transverse streaks, following the pattern of organization of actin and myosin filaments. However, they do not group into myofibrils.
It differs from striated skeletal muscle tissue in that its striations are shorter and less evident.

Cardiac Muscle Tissue in longitudinal section. Striations are less apparent
Cardiac fibers are surrounded by an envelope of protein filaments, the endomysium. There is neither perimysium nor epimysium.
The cells are joined together, through their ends, by specialized structures: the intercalated discs. These junctions allow the adhesion between fibers and the passage of ions or small molecules from one cell to another.
Almost half of the cell volume is occupied by mitochondria, which reflects the dependence on aerobic metabolism and the continued need for ATP.
Connective tissue fills the spaces between cells and your blood capillaries provide oxygen and nutrients.
The heartbeat is controlled by a set of modified cardiac muscle cells, called a cardiac pacemaker or sinoatrial node. Every second, approximately, an electrical signal propagates through the cardiac musculature, generating contraction.
Smooth or Non-striated Muscle Tissue
Its main feature is the absence of striations.
Present in visceral organs (stomach, intestine, bladder, uterus, gland ducts and blood vessel walls).
It forms the wall of many organs and is responsible for internal movements such as the movement of food through the digestive tract.
This tissue has involuntary and slow contraction.
Cells are uninucleate, elongated and sharp-edged.
Unlike striated skeletal and cardiac tissue, smooth muscle tissue does not have striations. This is because the actin and myosin filaments do not organize in the regular pattern presented by striated cells.
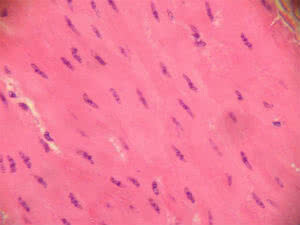
Smooth Muscle Tissue and the absence of striations
The cells are joined by gap junctions and occlusion zones.
In smooth muscle tissue, neither perimysium nor epimysium is found.
Read too:
- Human Body Tissues
- epithelial tissue