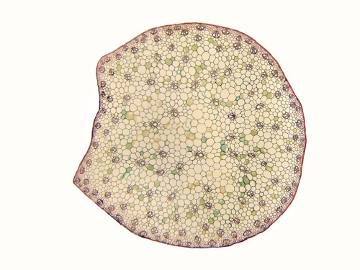
The stem is a part of the plant that mainly has the function of conduction of substances and support. It is an organ that, together with the leaves, makes up the stem system.
The stems and their leaves are closely associated in their development. The leaves sprout in the peripheral region of the stem and are arranged according to the organization of its vascular system.
The plant can grow for its entire life, thanks to meristems. Primary growth occurs longitudinally, elongating the plant, and secondary growth promotes increased width.
Stem Types
- Stem is the vertical stem. Found in trees, larger plants.
- rhizomes they are underground and grow horizontally. They are long and delicate.
- Stolons they are elongated and grow horizontally along the soil surface.
- tubers have storage function. The English potato is a well-known example of a tuber. On its surface there are small depressions from which protuberances appear, these are the buds.
- Bulbs they are small stems that are cone-shaped. They have a large yolk and many modified leaves. Examples are onion and lily.
- tendrils are a very common modification of the stem (in some cases of the leaf). They assist in support by wrapping themselves around the main support structure. Vines are an example.
See too:
- Stem Types
- Plant Parts
- Sheets
- plant cell
Occupation
The stem has two main functions: support and conduction of substances, but it can also serve as a nutritional reserve.
- Driving: the substances produced in the leaves (elaborated sap) are transported by the stem, through the phloem. These compounds are taken to all parts of the plant, where they will be consumed. The transport of raw sap (water and mineral salts) is done by the xylem, going from the roots to the leaves.
- Support: The stem supports the leaves, so they are able to receive more light to carry out photosynthesis.
- Storage: some underground stems are adapted to storage, as is the case of potato.
Structure and Development
The stem structure has apical growth, in other words, the stem grows from the apex which is a primary meristem.
O meristem is a tissue that produces undifferentiated cells that are used for plant growth, it is also called yolk.
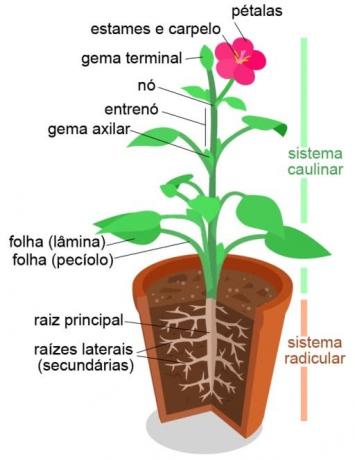
Structure of a plant's stem system
The plant embryo (before germinating) consists of a stem, one or more rudimentary leaves and an apical meristem. With its development, new sheets are formed from the apical yolk and the stem grows.
As the stem elongates, the knots and internodes differentiate. You we they are the regions of the stem from which the leaves come out. The spaces between one node and another is called get in on.
At this point, arise side yolks in the armpits of the leaves. These are protuberances that will originate the lateral branches of the stem.