They are six the big ones Brazilian biomes (continental). Biomes are sets of ecosystems (plant and animal) with their own biological diversity.
According to IBGE, in Brazil there are six types of continental biomes it is a marine biome or aquatic. What are the Brazilian terrestrial biomes, then?
- Amazon
- thick
- Caatinga
- Atlantic forest
- wetland
- pampa
Map of Biomes of Brazil
Observe on the map where the Brazilian terrestrial biomes are located.
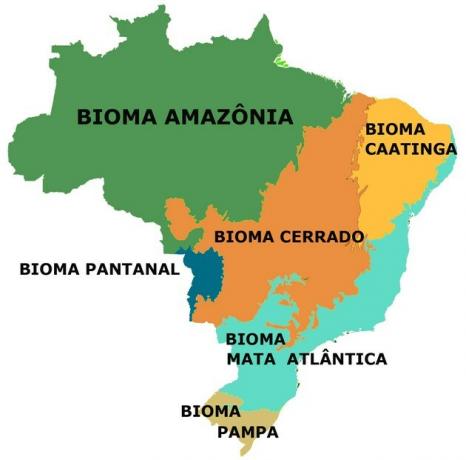
Terrestrial Biomes of Brazil
Due to its continental dimensions, the country is home to biomes as distinct from each other as tropical forests to dense vegetation. Learn a little more about this diversity:
Amazon Biome
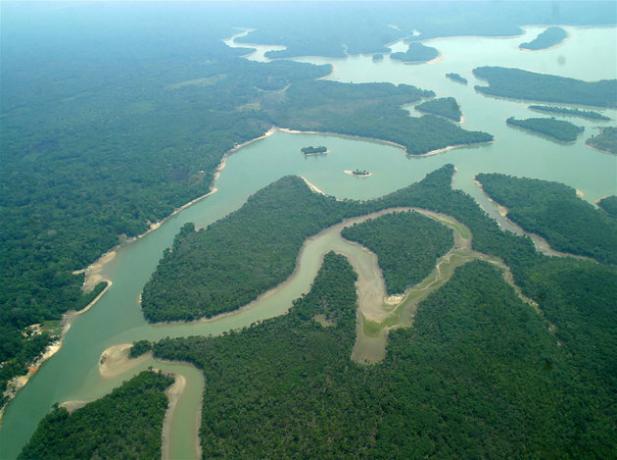

Considered the largest Brazilian Biome and the largest reserve of biological diversity in the world, the Amazon biome corresponds to almost half of the national territory.
It covers the Brazilian states of: Acre, Amapá, Amazonas, Pará, Roraima; part of Rondônia, Mato Grosso, Maranhão and Tocantins.
The climate of this region is hot and humid and its dense vegetation is characterized by Forest amazonian with large trees.
Read too:
- Amazon Animals
- Endangered Animals in the Amazon Forest
- Amazon Basin
Cerrado Biome

O thick it is considered the second largest biome in Brazil in terms of extension. It covers the states of: Maranhão, Distrito Federal, Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais and Tocantins. In addition, it occupies a small area of six other states.
The predominant climate in the cerrado is seasonal tropical, with periods of rain and drought. Its vegetation is characterized by trees with twisted trunks, grasses and shrubs. In general, trees are small and sparse.
Caatinga Biome

THE Caatinga occupies much of the northeast region of the country. It covers the states of: Ceará, Bahia, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Piauí, Rio Grande do Norte, Alagoas and Sergipe.
In addition, this type of biome is present in small parts of the states of Maranhão and Minas Gerais.
Typical of the semi-arid climate, located in the northeastern hinterland, the caatinga presents a medium-sized shrubby vegetation, with twisted branches and leaves adapted to the dry periods. Cactus are characteristic of the Caatinga.
read more:
- Caatinga climate
- Caatinga animals
- Caatinga flora
- Caatinga Characteristics
Atlantic Forest Biome
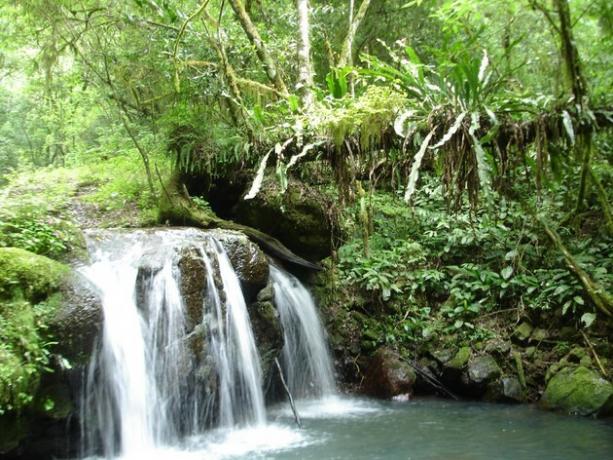

THE Atlantic forest occupies the coastal strip from north to south of the country. Thus, it encompasses the totality of three Brazilian states: Espírito Santo, Rio de Janeiro and Santa Catarina; large part of Paraná and small portions of eleven states.
The predominant climate is tropical-humid with high temperatures and rainfall. The vegetation in this biome is marked by the presence of large and medium-sized trees forming a dense and closed forest.
Pantanal Biome
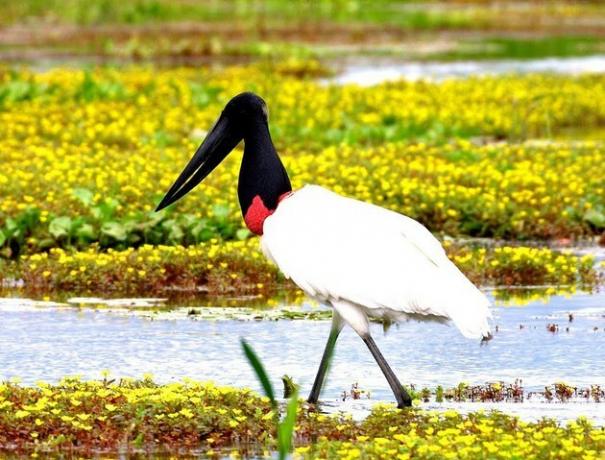

O Pantanal Biome, considered the smallest in the country, covers two Brazilian states, namely: Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul.
The predominant climate is continental tropical with high temperatures and rainfall, with a rainy summer and a dry winter.
The wetland vegetation is marked by grasses, medium-sized trees, low plants and shrubs. The name of this biome refers to the swampy regions present, that is, the swamps.
Pampa Biome

O pampa it is the only Brazilian biome present only in one federative unit. It occupies more than half of the territory of Rio Grande do Sul.
The climate is subtropical with the four seasons of the year well defined and its vegetation is marked by the presence of grasses, shrubs and small trees.
In addition, this biome is made up of large pasture areas, where large herds develop.
aquatic biomes
Aquatic biomes correspond to freshwater environments (lakes, rivers, streams...) and saltwater (seas and oceans). They are as rich in species diversity as terrestrial ones and also need to be conserved.
Most of our planet, more than 70%, is made up of salt water. The marine biome is classified according to the depth of the water and the regions illuminated or not by sunlight.
Freshwater biomes include streams, lakes, lakes, glaciers, underground reservoirs and rivers.
Curiosities
- Together, the Amazon and Atlantic Forest biomes cover 100% of eight Brazilian states.
- The Amazon Biome and the Pantanal Biome together occupy more than half of Brazil.
- The largest floodplain in the world is the Mato Grosso wetland.
- Currently, the Atlantic Forest corresponds to only 7% of its original area.
Learn more, read also:
- What is a biome?
- World Biomes
- terrestrial ecosystem
- Exercises on Brazilian Biomes
- Deforestation in Brazil