DNA replication corresponds to the duplication of genetic material, as DNA makes a copy of itself. The two strands that make up the molecule separate and guide the formation of complementary strands that will join them.
The cell cycle can be divided into two moments: interphase and cell division, for example, mitosis. The interphase, in turn, is the longest phase as it presents DNA replication and intervals before and after the duplication of genetic material.
What is DNA replication?
DNA, which in eukaryotic cells is located in the nucleus, contains all the genetic information of a being and its duplication process is important for cell growth, reproduction and repair.
A DNA molecule is formed by two strands that complement each other. For example, if we have an F tape and another F outra, in the replication process the tapes separate and are used as molds for forming complementary tapes. Hence, the nucleotide sequence of F determines the sequence of a new F' strand and F' indicates the composition of a new F strand.
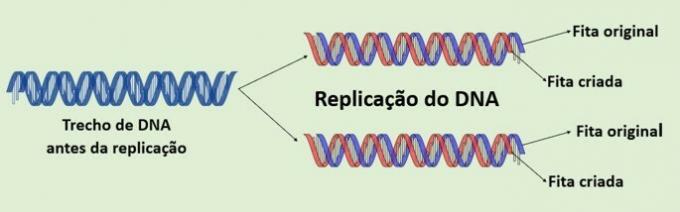
Before cells are formed in cell division, the contents of the mother cell must undergo duplication to be distributed. Therefore, with DNA replication it is guaranteed that the daughter cells will receive the same genetic information.
DNA structure
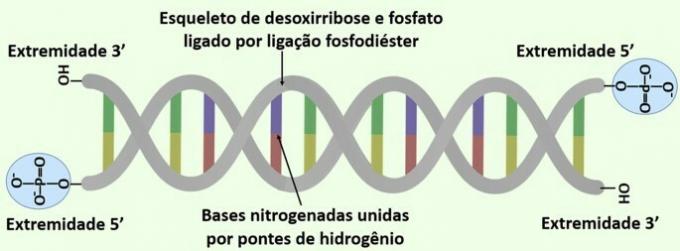
O DNA, a double strand in the form of a spiral (double helix), is a nucleic acid formed by nitrogenous bases, the pentose deoxyribose and the phosphate group. This structure is joined by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases, Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G), which form the A-T and C-G pairs.
Phosphodiester bonds hold the nucleotides together in the DNA molecule. The ends of a strand of DNA are classified as 5' and 3' as they correspond to the carbon number. of pentose where the phosphate group and the hydroxyl (OH) group that join in a bond are located. phosphodiester. At the 5' end is a free phosphate group and at the 3' end is a free hydroxyl.
know more about nucleotides and nucleic acids.
DNA replication process
In summary, DNA replication occurs in the 5’ → 3’ direction and the strands are separated by the action of enzymes, which break the bonds between the nitrogenous bases and unwind the chains, opening the double propeller.
As DNA unwinding takes place, other enzymes act by catalyzing the synthesis of two new sequences using the parent strands as a template. Each strand created joins an original strand of DNA. Therefore, the process is classified as semi-conservative.
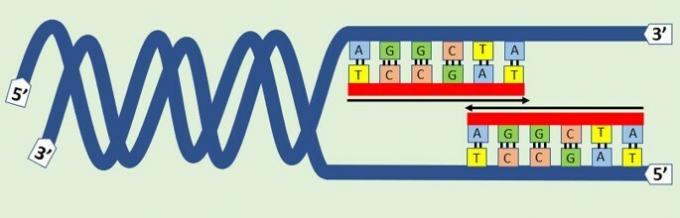
DNA is a double helix molecule and, in order to duplicate it, the first step is to unpack this structure by the action of the DNA helicase enzyme. The helicase recognizes the origin of replication and acts by breaking the hydrogen bonds in the nitrogenous bases A-T and C-G. This process occurs at various points and forms "replication bubbles".
As the bonds unravel it's like a zipper opening, so this step brings up a Y-shaped structure called a replication fork, the starting point of duplication.
The primase enzyme is responsible for synthesizing a portion of RNA, called the primer. At this stage several primers are generated and join the chain to initiate DNA synthesis.
The DNA polymerase enzyme is the replication enzyme responsible for extending the new chain by adding bases (A, C, G and T). This step is directed from the 5' end, with a phosphate group, to the 3' end, with a hydroxyl group. This phase is called continuous replication.
Between the primers attached to the original strand, several pieces of DNA are attached and are called Okazaki fragments. As the sections will need to be joined later, this phase is called delayed.
The exonuclease enzyme is responsible for removing the primers of the original tapes after forming continuous and discontinuous tapes. To avoid sequencing errors a review and, if necessary, a correction is performed by another exonuclease.
The DNA ligase enzyme causes the DNA fragments to be joined and the DNA sequenced into two continuous strands.
Exercises on DNA Replication
Use the following questions to test your knowledge of what you have just learned about DNA replication.
question 1
Why is DNA replication considered a semi-conservative process?
Reply:
Replication is considered a semi-conservative process, as DNA molecules after duplication are consisting of an original tape and another complementary tape formed using the original tape as mold.
question 2
Name at least three enzymes that play a role in DNA replication and what role they play.
Reply:
DNA helicase: unpacks the DNA structure by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the molecule's nitrogenous bases to initiate replication.
DNA primase: responsible for synthesizing the portions of DNA, called primers, which will bind to the original strand of DNA.
DNA polymerase: replication enzyme responsible for extending the new strand formed during replication.
question 3
Observe the steps in the DNA replication process.
I. Creation of replication forks
II. Free nucleotide binding
III. Synthesis and coupling of primers
IV. Linking fragments and forming a DNA strand
The correct sequence according to the order they happen in the duplication is:
a) II, I, IV and III
b) I, III, II and IV
c) III, II, IV and I
d) I, II, III and IV
Correct alternative: b) I, III, II and IV.
I. Creation of replication forks. Helicase enzymes start the process by separating the strands of DNA.
III. Synthesis and coupling of primers, which are pieces of RNA that act as duplication initiators.
II. Free nucleotide binding. Polymerase enzymes bind free nucleotides to primers.
IV. Binding of fragments and formation of a DNA strand. Binding is done by the ligase enzymes.
question 4
When separating the double helix of a DNA molecule, there is the following sequence of nitrogenous bases of one of the strands that will be used as a template: ATCGGTTA
The complementary strand sequence that will be produced to bind to the original strand is:
a) TGCCAAT
b) CGATTGGC
c) TAGCCAAT
d) GCGTTAAC
Correct alternative: c) TAGCCAAT.
Nitrogen bases always make the same pairs when they bind, that is, thymine binds to adenine (A-T) and guanine binds to cytosine (G-C).
Thus, a sequence of nitrogenous bases ATCGGTTA will bind to the sequence TAGCCAAT, as per letter c.
Get more knowledge with the contents:
- DNA and RNA
- Nitrogen bases
- DNA exercises