At hydration reactions in alkadienes they are addition reactions, that is, the components (hydronium and hydroxide) of the water molecule are added to an alkadiene.
You alkadienes are hydrocarbons that have an open chain and two double bonds (formed by a sigma and a pi) between carbons, as we can see in the following structure:

Structural formula of an alkadiene
for the hydration reaction in alkadienes is carried out, it is essential that the pi bond, present in the double bond, is broken by the influence of heat and sulfuric acid (H2ONLY4). With the breaking of the pi bond, two bond sites appear, each on one of the carbons involved in the double bond.

Emergence of binding sites with disruption of pi binding
The appearance of binding sites on the alkadiene molecule is necessary for the ions (H+ and oh-) from the water are added to the alkadiene, forming, for example, a dialcohol (alcohol with two hydroxyls).
Addition of H+ and oh- in the structure of an alkadiene
NOTE: The addition of the H+ and oh
- in the alkadiene structure follows the Markovnikov's rule, ie the H+ binds to the most hydrogenated carbon, and the OH- binds to the less hydrogenated carbon.
Example of the application of the Markovnikov rule in the hydration of alkadienes
As there are different types of alkadienes with respect to the position of the double bonds, it may be that the hydration of an alkadiene forms different compounds. See the following cases:
→ Accumulated or condensed alkadiene
It is an alkadiene that has two double bonds simultaneously involving three atoms of carbon, that is, there is no single bond separating the carbons involved in the bonds doubles.

Structural formula of an accumulated alkadiene
During the hydration reaction of an alternating alkadiene, the pi bonds are broken, being the H+ added to the more hydrogenated carbons and the OH- added to less hydrogenated carbons:
Accumulated Alkadiene Hydration Reaction Equation
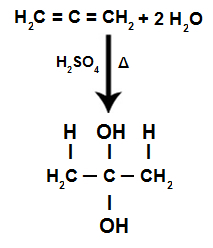
We have that in the hydration of an accumulated alkadiene, the same carbon atom receives the two hydroxyls, forming a twin alcohol, which is an unstable structure.

Structure of the twin formed alcohol
As the twin alcohol is unstable, we have the formation of a water molecule with the components of the two hydroxyls and the creation of a pi bond between carbon and oxygen.

Formation of a ketone from a twin alcohol
Therefore, the hydration reaction of accumulated alkadienes will result in the formation of a ketone.
→ Conjugated or alternate alkadiene
It is an alkadiene that has two double bonds simultaneously involving four carbon atoms, that is, there is a single bond separating the carbons involved in the bonds doubles.
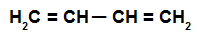
Structural formula of an alternating alkadiene
In alternating alkadienes, the resonance of their double bonds occurs. Thus, the electrons of the pi bond change position (red arrows), as in the following diagram:
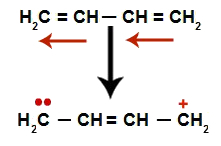
Diagram depicting the resonance in an alternating alkadiene
We have, in general, the appearance of a double bond exactly between the carbons where the two doubles were previously and the creation of two bonding sites, one on each carbon that is no longer making the double bond (in the example, carbons 1 and 4). Carbons 1 and 4 of the chain receive the H+ and the oh- from the water.

Partial hydration in alternating alkadiene
After resonance, the pi bond of the new double bond is broken, and an H+ and an oh- are added to the alkadiene molecule. The OH is added to the carbon closest to the first added OH group because it undergoes the electronic attraction of the group, which is more electronegative.

Termination of hydration in an alternating alkadiene
Because of the resonance, we say that the alternating alkadiene underwent a 1.4 hydration, forming a dialcohol.
→ Alkadiene insulated
It is an alkadiene that has two double bonds involving at least five atoms simultaneously. of carbon, that is, there are at least two single bonds separating the carbons involved in the bonds doubles.

Structural formula of an isolated alkadiene
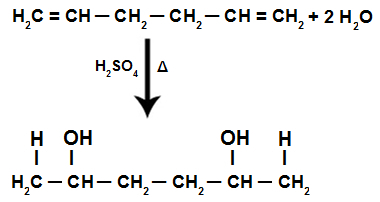
During the hydration reaction of an isolated alkadiene, the pi bonds are broken, being the H+ added to the more hydrogenated carbons and the OH- added to the less hydrogenated carbons.

Isolated alkadiene hydration reaction equation
Therefore, in the addition of an isolated alkadiene, we only have the formation of a diaalcohol.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/reacoes-hidratacao-alcadienos.htm
