Condensation is the change from a gaseous state to a liquid state. Also called liquefaction, it is the reverse process of vaporization. In order for the steam to condense, it is necessary either to reduce its temperature or to increase the pressure to which it is subjected.
A substance in the gaseous state has neither shape nor defined volume, occupying the entire space of the volume that contains it. In this state it is easily compressed.
The atoms and molecules that make up the substance are well separated from each other and there is practically no cohesive force between their particles.
When steam loses latent heat, vibration and internal energy decrease. This reduction causes the substance to lose the characteristics of a gaseous state and start to change to a liquid state.
The condensation process can also occur by increasing the pressure exerted on the steam. By reducing the space between the particles, the cohesive force increases and the substance begins to condense.
An example of condensation is water droplets that form on the outside of a glass that contains some very cold liquid or ice.
The water vapor present in the air condenses when it comes into contact with the cold surface of the glass, making it all wet.

fractional liquefaction
Fractional liquefaction is the process that consists of separating gases from a homogeneous mixture.
The method consists of cooling or compressing the gases that make up the mixture until they pass into a liquid state.
The liquid and homogeneous mixture resulting from the condensation is placed in a distillation column. There, the mixture will undergo the process of fractional distillation, ie heat separation.
In the distillation column, the substances that make up the mixture will be subjected to areas with different temperatures. As each one has different boiling points, they change phase at different times. In this way, we managed to separate the mixture.
Read too: Separation of Mixtures and Boiling.
Condensation in the Atmosphere
The amount of water vapor in the atmosphere varies, being a decisive factor in the water cycle and temperature regulation on the planet.
There are several indices that indicate the degree of humidity in the atmosphere. The best known is the relative humidity of the air. This index represents how long the atmosphere needs to be saturated. Thus, the atmosphere is saturated when the relative humidity is equal to 100%.
The water vapor present in the atmosphere can undergo successive changes of state. It can condense when reaching higher layers and at lower temperatures.
The tiny droplets originating from this condensation, when they agglutinate around condensation nuclei (microscopic particles of dust, smoke and salt suspended in the atmosphere), form clouds.
In this way, clouds are basically composed of drops in liquid form (lower layers) or small ice crystals (higher layers).

When steam condenses near the ground, it creates fog and when it deposits on cold surfaces it forms dew.
Find out even more about how these processes happen in nature by reading the water cycle.
Phase Changes
Condensation is one of the five processes of transformation of matter. The other four processes are:
- Fusion
- Vaporization
- Solidification
- Sublimation
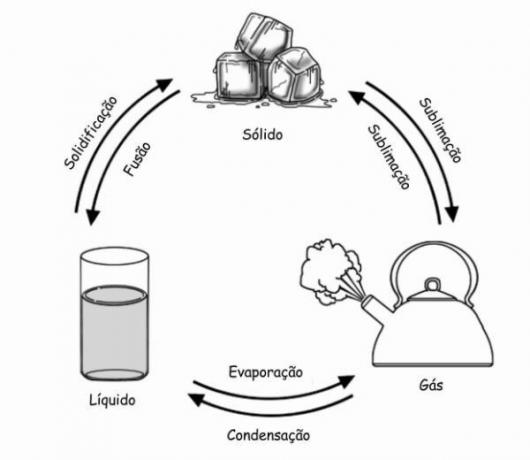
In the diagram below, we represent the three physical states of matter and their phase changes:
To learn more, read also:
- Physical State Changes
- Physical States of Water
- Physical States of Matter
- Matter Properties
- Phases diagram
- latent heat
- Evaporation
Check entrance exam questions with feedback commented on: exercises on mixing separation.