At chemical bonds are the interactions that occur between atoms to become a molecule or basic substance of a compound. There are three types of links: covalents, metallic and ionic. Atoms seek, by making a chemical bond, to stabilize themselves electronically. This process is explained by octet theory, which dictates that each atom, to achieve stability, must have eight electrons in its valence shell.
Chemical Bonds and the Octet Rule
THE search for electronic stability, which justifies the realization of chemical bonds between atoms, is explained by the octet theory. Proposed by Newton Lewis, this theory states that the atomic interaction happens so that each element acquires the stability of a noble gas, that is, eight electrons in valence layer.
For this, the element give, receive or share electrons from its outermost shell, therefore making chemical bonds of an ionic, covalent or metallic character. You noble gases they are the only atoms that already have eight electrons in their outermost shell and that's why they don't react very much with other elements.
Lookalso: Electronic distribution rules: how to do it?
Types of chemical bonds
To get the eight electrons in the valence shell as predicted in the octet rule, the atoms bond together, which vary according to the need to donate, receive or share electrons and also the nature of the bonding atoms.
ionic bonds
Also known as electrovalent or heteropolar bonds, happen between metals and very electronegative elements (ametals and hydrogen). In this type of call, metals tend to lose electrons, turning into cations (positive ions), and non-metals and hydrogen gain electrons, becoming anions (negative ions).
You ionic compounds are hard and brittle, have a high boiling point and conduct electric current when they are in a liquid state or diluted in water.
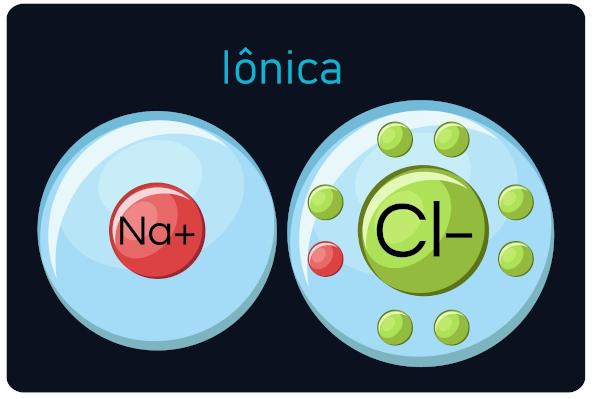
Observation: Be aware that the atom that gains electrons will become an ion with a negative sign and that the atom that loses electrons becomes a positive sign.
Examples of ionic substances:
- Bicarbonate (HCO3-);
- Ammonium (NH4+);
- Sulfate (SO4-).
To learn more about this type of chemical bond, visit our text: ionic bonds.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
covalent bonds
At covalent bonds happen by electron sharing. Due to the low electronegativity difference between the binding elements, they do not donate or receive electrons, but share electronic pairs so that they are stable according to the octet rule. This type of connection is very common in simple elements such as Cl2, H2, O2, and also in the carbon chains. the difference of electronegativity between the ligands determines whether the bond is polar or non-polar.

Read too:Polarity of molecules: how to identify?
dative covalent bond
Also called coordinate covalent bond, semipolar, dative or coordinate bond, it is very similar to the covalent bond, the difference between the two is that one of the atoms in the dative bond is responsible for sharing two electrons. In this type of connection, that occurs artificially, the molecule acquires the same characteristics as a molecule resulting from a spontaneous covalent bond.
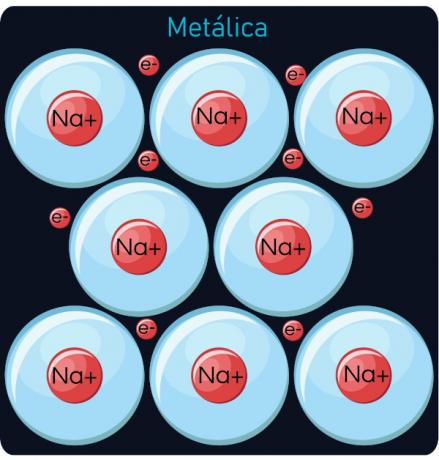
Metal links
This type of bond happens between metals, which include the elements of the 1A family (alkali metals), 2A (alkaline earth metals) and the transition metals (block B of the periodic table - group 3 to 12), forming what we call metal alloys. The differential characteristic in relation to other types of connection is the electron movement, which explains the fact that metallic materials, in solid state, are excellent electrical and thermal conductors. In addition, metallic alloys have a high melting and boiling point, ductility, malleability and shine. Examples of metal alloys are:
steel: iron (Fe) and carbon C;
bronze: copper (Cu) + tin (Sn);
brass: copper (Cu) + zinc (Zn);
gold: gold (Au) + copper (Cu) or silver (Ag).
Summary
- Chemical bonds: interaction between atoms that seek electronic stability.
- Types of links: ionic, covalent and metallic.
- Octet Rule: defines that, for the atom to be stable, it must have eight electrons in its valence shell.
solved exercises
question 1 - (Mackenzie-SP) For sulfur and potassium atoms to acquire an electronic configuration equal to that of a noble gas, it is necessary that:
(Data: atomic number S = 16; K = 19).
a) sulfur receives 2 electrons and potassium receives 7 electrons.
b) sulfur gives 6 electrons and potassium receives 7 electrons.
c) sulfur yields 2 electrons and potassium yields 1 electron.
d) sulfur receives 6 electrons and potassium gives up 1 electron.
e) sulfur receives 2 electrons and potassium gives up 1 electron.
Resolution
Alternative E. Since sulfur is in the 6A or 16 family, obeying the octet rule, it needs to acquire 2 electrons to have 8 in its valence shell. Potassium, on the other hand, which belongs to the first family of the periodic table (1A or hydrogen family), to have in its valence layer the configuration of a noble gas, it needs to lose 1 electron. By combining 2 potassium atoms with 1 sulfur atom, we can establish an ionic bond in which both elements are electrically stable.
question 2 - (UFF) Breast milk is a food rich in organic substances, such as proteins, fats and sugars, and mineral substances such as calcium phosphate. These organic compounds have as main characteristic the covalent bonds in the formation of their molecules, while the mineral also has an ionic bond. Check the alternative that correctly presents the concepts of covalent and ionic bonds, respectively:
a) Covalent bonding only occurs in organic compounds.
b) Covalent bonding is done by electron transfer, and ionic bonding is done by sharing electrons with opposite spins.
c) The covalent bond is made by attraction of charges between atoms, and the ionic bond, by charge separation.
d) The covalent bond is made by joining atoms in molecules, and the ionic bond, by joining atoms in chemical complexes.
e) Covalent bonding is done by sharing electrons, and ionic bonding is done by electron transfer.
Resolution
Alternative E.
Let's look at the others:
- Alternative to: incorrect as covalent bonds also occur in inorganic compounds such as CO2.
- Alternative b: incorrect, as covalent bonds occur by sharing, and ionic bonds by electron transfer.
- Alternative c: Both covalent bonding and ionic bonding occur through the need to lose or gain electrons, not through electrostatic attraction between the nuclei.
- Alternative d: Both bonds, both covalent and ionic, occur through the union of atoms in a molecule.
question 3 - (PUC-MG) Review the table, which shows properties of three substances, X, Y and Z, under ambient conditions.
| Substance | Melting temperature (c°) | electrical conductivity | Solubility in water |
| x | 146 | none |
soluble |
| y | 1600 | high | insoluble |
| z | 800 | just melted or dissolved in water | soluble |
Considering this information, it is CORRECT to state that substances X, Y and Z are, respectively:
a) ionic, metallic, molecular.
b) molecular, ionic, metallic.
c) molecular, metallic, ionic.
d) ionic, molecular, metallic.
Resolution
Alternative C.
Substance X is molecular, as molecular bonds, also called covalents, have a low boiling point, as the difference in electronegativity between the ligands is not very tall. Generally covalent compounds do not have electrical conductivity, and solubility is variable.
We can recognize substance Y as metallic, as metals have a high melting point, are excellent electrical conductors and are insoluble in water.
Finally, substance Z is ionic, as the melting point is relatively high for this substance, which is a consequence of the crystalline arrangement of the molecule. When an ionic substance is dissolved in water or in a liquid state, it has free ions, which makes it conductive of electrons and soluble in water.
By Laysa Bernardes Marques
Chemistry teacher