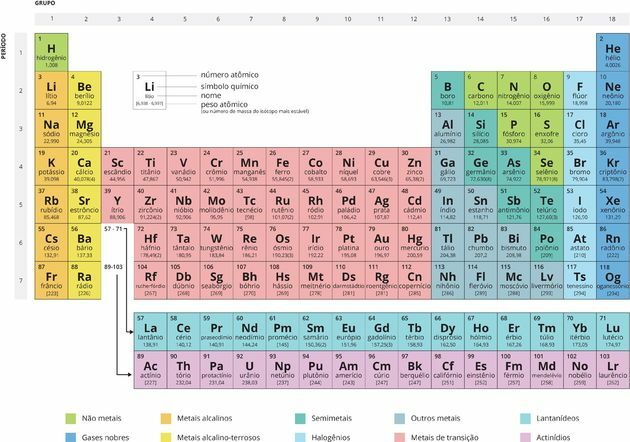
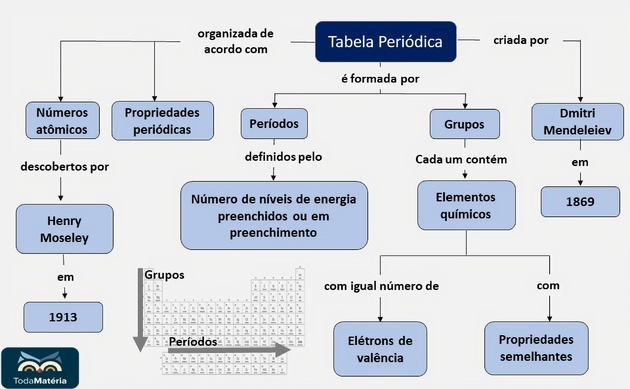
THE Periodic table is a model that groups all known chemical elements and their properties. They are arranged in ascending order of atomic numbers (number of protons).
In total, the new Periodic Table has 118 chemical elements (92 natural and 26 artificial).
Each square specifies the name of the chemical element, its symbol and its atomic number.
Periodic Table Organization
the calls Periods they are numbered horizontal lines, which have elements that have the same number of electronic layers, totaling seven periods.
- 1st period: 2 elements
- 2nd period: 8 elements
- 3rd period: 8 elements
- 4th Period: 18 elements
- 5th Period: 18 elements
- 6th Period: 32 elements
- 7th Period: 32 elements
With the organization of the periods in the table, some horizontal lines would become very long, so it is common to represent the lanthanide series and the actinide series apart from the others.
At Families or groups are the vertical columns, where the elements have the same number of electrons in the outermost shell, that is, in the
valence layer. Many elements of these groups are related according to their chemical properties.There are eighteen Groups (A and B), and the best known families are from Group A, also called representative elements:
- 1A Family: Alkaline Metals (lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium and francium).
- 2A Family: Alkaline-Earth Metals (beryl, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium and radium).
- 3A Family: Boron family (boron, aluminum, gallium, indium, thallium and nihonium).
- 4A Family: Carbon family (carbon, silicon, germanium, tin, lead and flerovium).
- 5A Family: Nitrogen family (nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, bismuth and muscovy).
- 6A Family: Chalcogens (oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, polonium, livermory).
- 7A Family: Halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine and tenessine).
- 8A Family: Noble Gases (Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon, Radon and Oganessonium).
You transition elements, also called transition metals, represent the 8 families of Group B:
- 1B family: copper, silver, gold and roentgen.
- 2B family: zinc, cadmium, mercury and copernicium.
- 3B Family: scandium, yttrium and lanthanide series (15 elements) and actinides (15 elements).
- 4B Family: titanium, zirconium, hafnium and rutherfordium.
- 5B family: vanadium, niobium, tantalum and dubnium.
- Family 6B: chromium, molybdenum, tungsten and seaborgium.
- 7B Family: manganese, technetium, rhenium and bohrium.
- 8B family: iron, ruthenium, osmium, hassium, cobalt, rhodium, iridium, meitnerium, nickel, palladium, platinum, darmstadium.
By determination of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), the groups started to be organized by numbers from 1 to 18, although it is still common to find families being described by letters and numbers as shown above.
An important difference that the new system presented by IUPAC generated is that the 8B family corresponds to groups 8, 9 and 10 in the periodic table.
Black and White Periodic Table
History of the Periodic Table
The fundamental purpose of creating a table was to facilitate the classification, organization and grouping of elements according to their properties.
Until reaching the current model, many scientists created tables that could demonstrate a way to organize the chemical elements.
The most complete Periodic Table was drawn up by the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907), in the year 1869 due to the atomic mass of the elements.
Mendeleev arranged groups of elements according to similar properties and left empty spaces for elements he believed would yet be discovered.
The Periodic Table as we know it today was organized by Henry Moseley, in 1913, by order of atomic number chemical elements, reorganizing the table proposed by Mendeleev.
William Ramsay he discovered the elements neon, argon, krypton and xenon. These elements along with helium and radon included the noble gas family in the Periodic Table.
Glenn Seaborg discovered the transuranic elements (numbers 94 to 102) and in 1944 proposed the reconfiguration of the Periodic Table, placing the series of actinides below the series of lanthanides.
In 2019, the periodic table turns 150 years old and a United Nations and UNESCO resolution was created to make this the Year International Periodic Table of Chemical Elements as a way of recognizing one of the most influential and important creations of science.
Curiosities of the Periodic Table
- The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry - IUPAC) is an NGO (Non-governmental organization) dedicated to studies and advances in Chemistry. Worldwide, the standard established for the Periodic Table is recommended by the Organization.
- 350 years ago, the first chemical element isolated in the laboratory was the phosphor by German alchemist Henning Brand.
- The Plutonium Element was discovered in the 1940s by the American chemist Glenn Seaborg. He discovered all transuranic elements and won the Nobel Prize in 1951. Element 106 was named Seaborgium in his honor.
- In 2016, new chemical elements of the table were made official: Tennessine (Ununséptio), Nihonium (Ununtrio), Moscovium (Ununpêntio) and Oganesson (Ununóctio).
- The new chemical elements synthesized are called super heavy because they contain a high number of protons, which turns out to be far superior to the chemical elements found in nature.
Periodic Table Summary
Check entrance exam questions with a commented resolution in Exercises on the Periodic Table and unpublished questions in Exercises on Organizing the Periodic Table.