Organic functions group carbon compounds with similar properties.
Due to the existence of numerous substances formed by carbon, this topic is widely used in exams to test knowledge about Organic Chemistry.
Thinking about it, we gathered 10 questions Enem and entrance exams for you to test your knowledge about the different structures that characterize the functional groups.
Also use the resolutions comments to learn even more about the subject.
Entrance Exam Questions
1. (UFRGS) In organic compounds, in addition to carbon and hydrogen, the presence of oxygen is very frequent. Tick the alternative where all three compounds contain oxygen.
a) formaldehyde, acetic acid, ethyl chloride.
b) trinitrotoluene, ethanol, phenylamine.
c) formic acid, butanol-2, propanone.
d) isooctane, methanol, methoxy-ethane.
e) isobutyl acetate, methylbenzene, hexene-2.
Correct alternative: c) formic acid, butanol-2, propanone.
Functions that have oxygen in their constitution are called Oxygenated Functions.
Below are compounds that have oxygen in the functional group.
a) WRONG. Ethyl chloride has no oxygen.
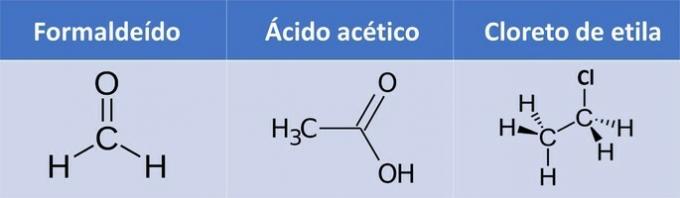
| Compound | Organic Function |
| Formaldehyde | Aldehyde: R-CHO |
| Acetic Acid | Carboxylic acid: R-COOH |
| Ethyl chloride |
Alkyl halide: R-X (X represents a halogen). |
b) WRONG. Phenylamine has no oxygen.
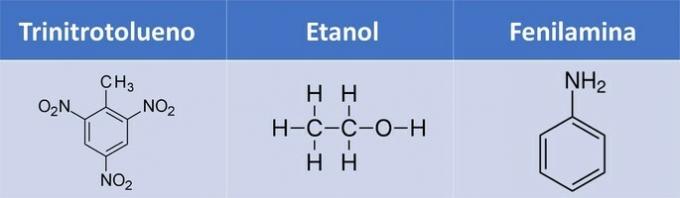
| Compound | Organic Function |
| Trinitrotoluene | Nitrocompound: R-NO2 |
| Ethanol | Alcohol: R-OH |
| Phenylamine | Amine: R-NH2 |
c) CORRECT. All three compounds have oxygen.
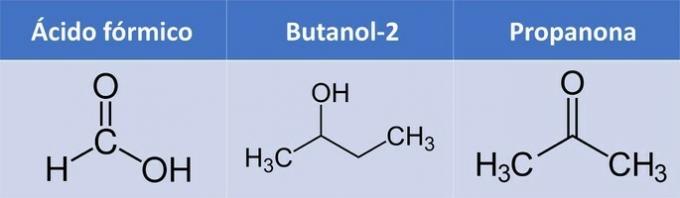
| Compound | Organic Function |
| Formic acid | Carboxylic acid: R-COOH |
| Butanol-2 | Alcohol: R-OH |
| Propanone | Ketone: R1-COLOR2 |
d) WRONG. Isooctane has no oxygen.
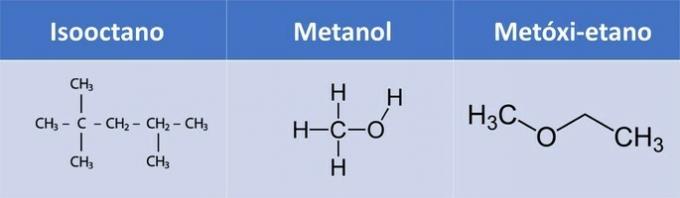
| Compound | Organic Function |
| isooctane | Alkane: CnoH2n+2 |
| Methanol | Alcohol: R-OH |
| Methoxy-ethane | Ether: R1-O-R2 |
e) WRONG. Methylbenzene and hexene-2 do not have oxygen.
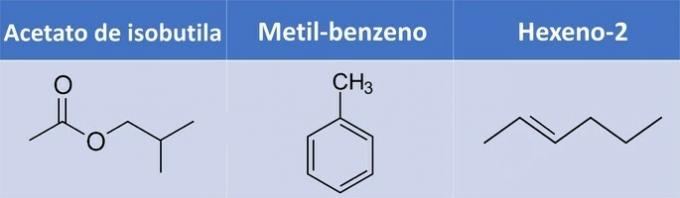
| Compound | Organic Function |
| Isobutyl acetate | Ester: R1-COO-R2 |
| Methyl benzene | Aromatic hydrocarbon |
| Hexen-2 | Alkene: CnoH2n |
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| 1. Benzene |
|
| 2. Ethoxyethane |
|
| 3. Ethyl Methanate |
|
| 4. Propanone |
|
| 5. metal |
|
The CORRECT sequence of numbers in column B, from top to bottom, is:
a) 2 - 1 - 3 - 5 - 4.
b) 3 - 1 - 2 - 4 - 5.
c) 4 - 3 - 2 - 1 - 5.
d) 3 - 2 - 5 - 1 - 4.
e) 2 - 4 - 5 - 1 - 3.
Correct alternative: b) 3 - 1 - 2 - 4 - 5.
| ( 3 ) Ester | 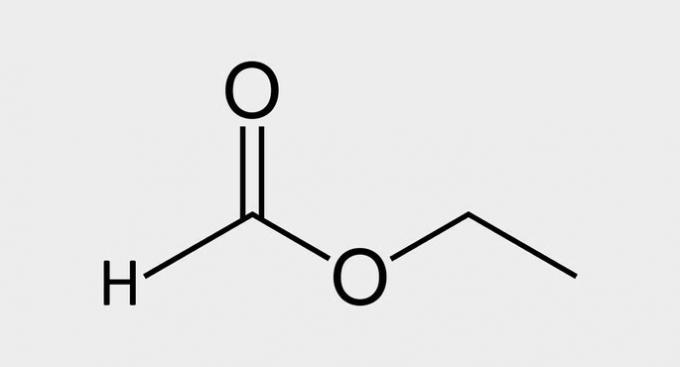 |
| Ethyl Methanate |
esters are derived from carboxylic acids, where the functional group -COOH has the hydrogen replaced by a carbon chain.
| ( 1 ) Hydrocarbon | 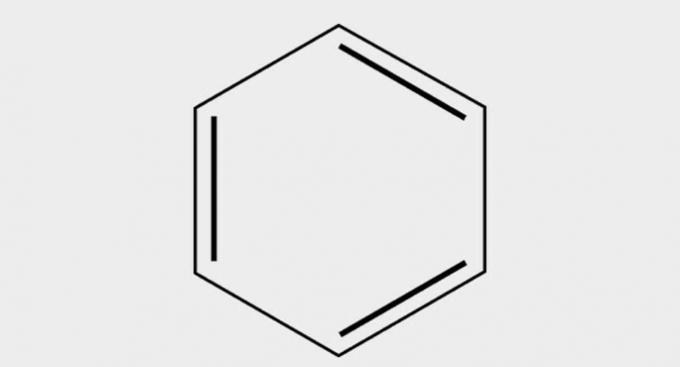 |
| Benzene |
Hydrocarbons are compounds formed by carbon and hydrogen atoms.
| ( 2 ) ether |  |
| ethoxyethane |
ethers are compounds in which oxygen is linked to two carbon chains.
| ( 4 ) Ketone |  |
| Propanone |
Ketones have the carbonyl (C=O) linked to two carbon chains.
| ( 5 ) aldehyde | 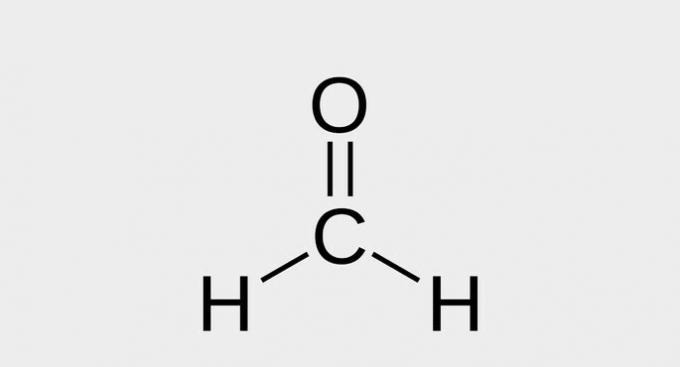 |
| metal |
Aldehydes are compounds that have the functional group -CHO.
a) Write down the structural formulas for the four amines.
Amines are compounds that were theoretically formed from ammonia (NH3), in which the hydrogen atoms are replaced by carbon chains.
According to these substitutions, amines are classified into:
- Primary: nitrogen linked to a carbon chain.
- Secondary: nitrogen linked to two carbon chains.
- Tertiary: nitrogen linked to three carbon chains.
The four amines that have the molecular formula C3H9N are isomers, as they have the same molecular mass but different structures.

Learn more at: The mine and Isomerism.
b) Which of these amines has a lower boiling point than the other three? Justify the answer in terms of structure and intermolecular forces.
Although they have the same molecular formula, amines have different structures. Below are the substances and their boiling points.
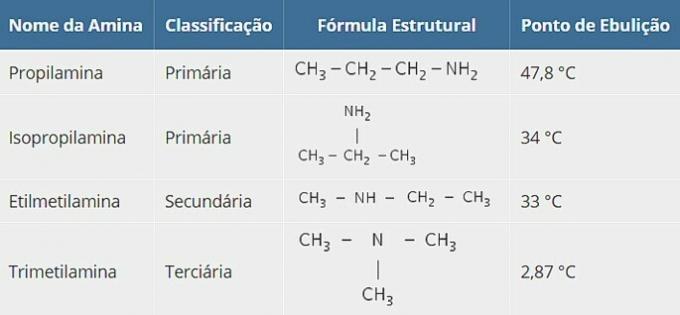
Although they have the same molecular formula, amines have different structures and this reflects the type of intermolecular forces that these substances carry.
A hydrogen bond or bridge is a strong bond type, in which the hydrogen atom is bonded to an electronegative element, such as nitrogen, fluorine, or oxygen.
Due to the electronegativity difference, a strong bond is established and the trimethylamine it's the only one that doesn't have that kind of connection.
See how hydrogen bonds in primary amines happen:
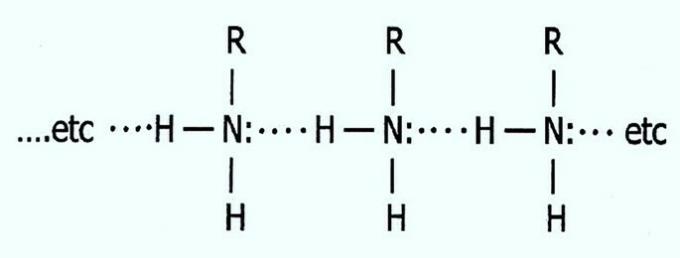
Therefore, propylamine has the highest boiling point. The strong interactions between the molecules makes it difficult to break the bonds and, consequently, the passage to the gaseous state.
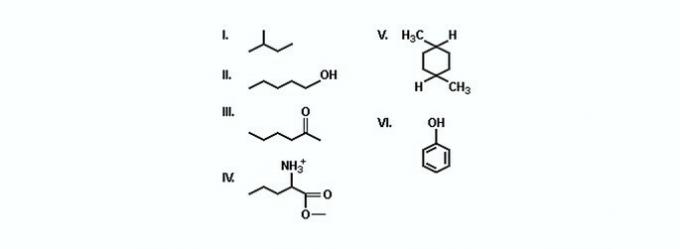
Analyze the represented compounds.
( ) Two of them are aromatic.
( ) Two of them are hydrocarbons.
( ) Two of them represent ketones.
( ) Compound V is a dimethylcyclohexane.
( ) The only compound that forms salts either by reacting with acids or bases is IV.
Correct answer: F; V; F; V; V.
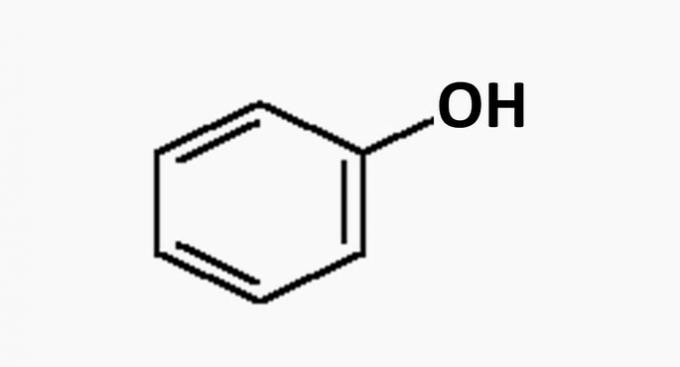
(FALSE) Two of them are aromatic.
Aromatic compounds have alternating single and double bonds. There is only one aromatic in the compounds presented, phenol.
(TRUE) Two of them are hydrocarbons.
Hydrocarbons are compounds made up of just carbon and hydrogen.
(FALSE) Two of them represent ketones.
Ketones are compounds that have a carbonyl (C=O). There is only one ketone in the compounds shown.

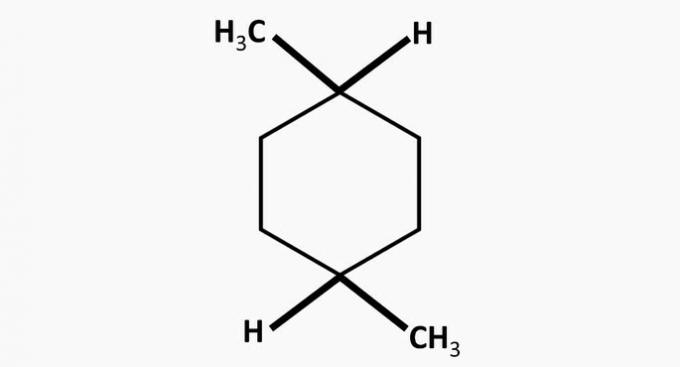
(TRUE) Compound V is a dimethylcyclohexane, a cyclic hydrocarbon with two methyl radicals.
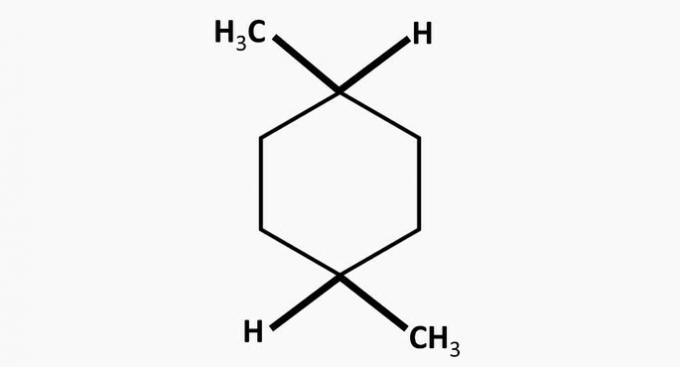
(TRUE) The only compound that forms salts either by reacting with acids or bases is IV.
The compound is an ester, whose functional group is -COO-.
5. (UFRS) Listed below are the chemical names of six organic compounds and, in parentheses, their respective applications; and later in the figure, the chemical formulas of five of these compounds. Associate them properly.
| Compounds | Structures |
|---|---|
|
1. p-aminobenzoic acid (raw material for the synthesis of the anesthetic novocaine) |
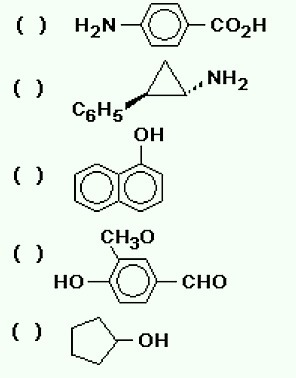 |
|
2. cyclopentanol (organic solvent) | |
|
3. 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (artificial vanilla flavor) | |
|
4. (raw material for carbaryl insecticide) | |
|
5. trans-1-amino-2-phenylcyclopropane (antidepressant) |
The correct sequence for filling the parentheses, from top to bottom, is
a) 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5.
b) 5 - 3 - 1 - 2 - 4.
c) 1 - 4 - 3 - 5 - 2.
d) 1 - 5 - 4 - 3 - 2.
Correct alternative: d) 1 - 5 - 4 - 3 - 2.
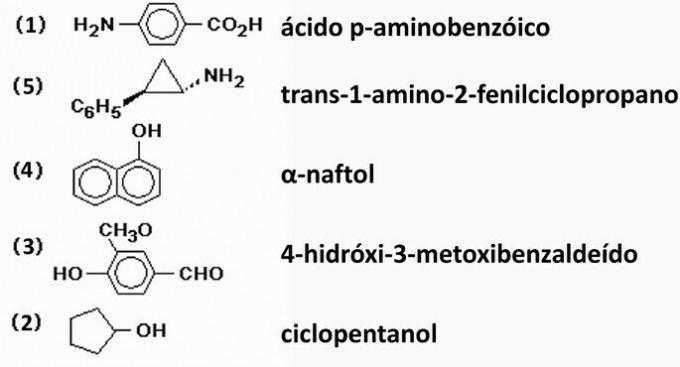
- p-aminobenzoic acid: carboxylic acid with the -COOH functional group attached to the aromatic ring with amino group.
- Trans-1-amino-2-phenylcyclopropane: cyclic hydrocarbon with two branches: amino and phenyl group.
-
-naphthol: phenol formed by two aromatic rings.
- 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde: mixed compound formed by three functional groups: aldehyde (CHO), ether (-O-) and alcohol (OH) linked to the aromatic benzene ring.
- Cyclopentanol: alcohol formed by linking hydroxyl (OH) to a cyclic chain.
Learn more at: carbon chains and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Enem questions
6. (Enem/2012) Propolis is a natural product known for its anti-inflammatory and healing properties. This material contains more than 200 compounds identified to date. Among them, some are simple in structure, such as C6H5CO2CH2CH3, whose structure is shown below.
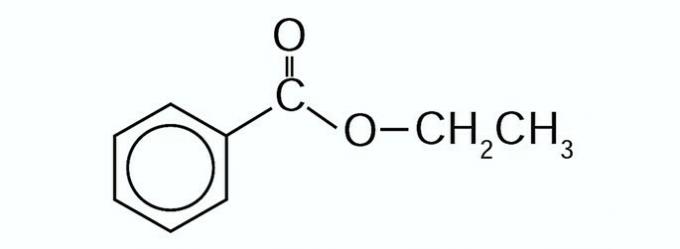
The carboxylic acid and alcohol capable of producing the ester in question through the esterification reaction are, respectively,
a) benzoic acid and ethanol.
b) propanoic acid and hexanol.
c) phenylacetic acid and methanol.
d) propionic acid and cyclohexanol.
e) acetic acid and benzyl alcohol.
Correct alternative: a) benzoic acid and ethanol.
a) CORRECT. There is the formation of Ethyl Benzanoate.
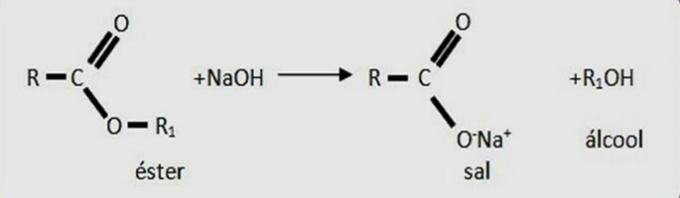
When an acid and an alcohol react in an esterification reaction, ester and water are produced.

Water is formed by the junction of the hydroxyl of the acid functional group (COOH) and the hydrogen of the alcohol functional group (OH).
The remainder of the carbon chain of the carboxylic acid and alcohol join together to form the ester.
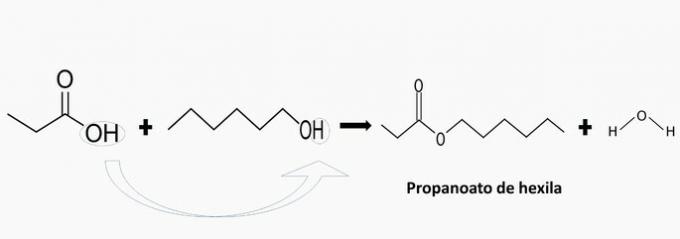
b) WRONG. There is the formation of Hexyl Propanoate.
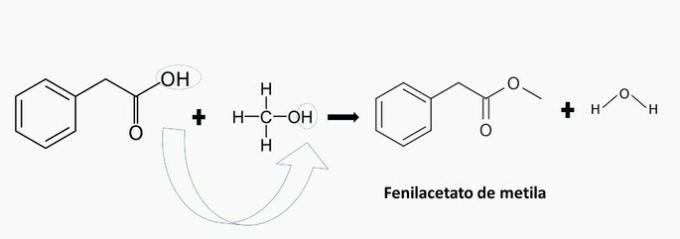
c) WRONG. There is the formation of methyl phenylacetate.
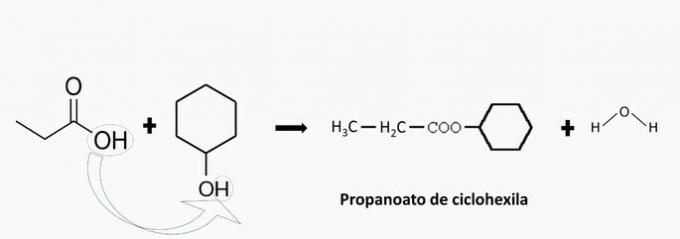
d) WRONG. There is the formation of cyclohexyl propanoate.
e) WRONG. There is no esterification as both compounds are acidic.
Learn more at: carboxylic acids and esterification.
7. (Enem/2014) You've heard this phrase: there was a chemistry between us! Love is often associated with a magical or spiritual phenomenon, but there is the action of some compounds in our body, which cause sensations when we are close to a loved one, such as a racing heart and increased frequency respiratory. These sensations are transmitted by neurotransmitters such as adrenaline, norepinephrine, phenylethylamine, dopamine and serotonin.

Available at: www.brasilescola.com. Accessed on: 1st March. 2012 (adapted).
The neurotransmitters mentioned have in common the characteristic functional group of the function
a) ether.
b) alcohol.
c) amine.
d) ketone.
e) carboxylic acid.
Correct alternative: c) amine.
a) WRONG. The ether function is characterized by an oxygen linked to two carbon chains.
Example:
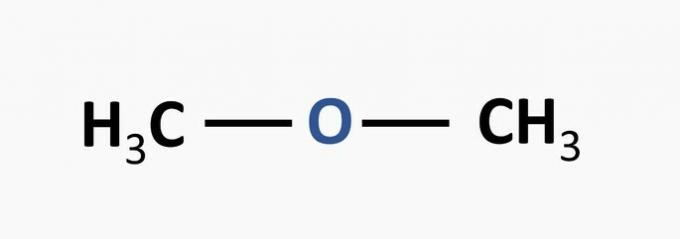
b) WRONG. The alcohol function is characterized by a hydroxyl linked to the carbon chain.
Example:
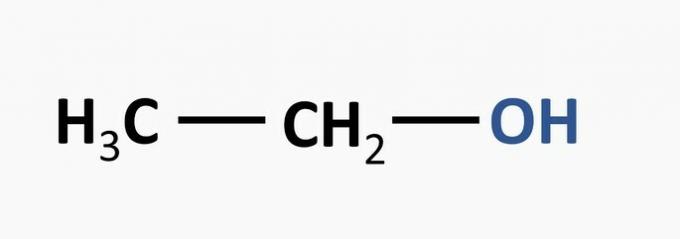
c) CORRECT. Amine function is observed in all neurotransmitters.

Neurotransmitters are chemical substances that act as biomarkers, being divided into: biogenic amines, peptides and amino acids.
Biogenic amines or monoamines are the result of enzymatic decarboxylation of natural amino acids and are characterized by the presence of nitrogen, forming a group of organic compounds nitrogenous.
d) WRONG. The ketone function is characterized by the presence of carbonyl: double bond between carbon and hydrogen.
Example:
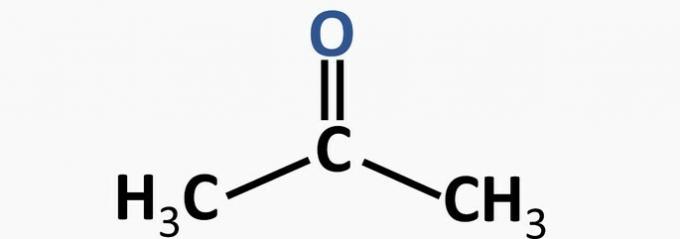
e) WRONG. The carboxylic acid function is characterized by the presence of the -COOH group.
Example:
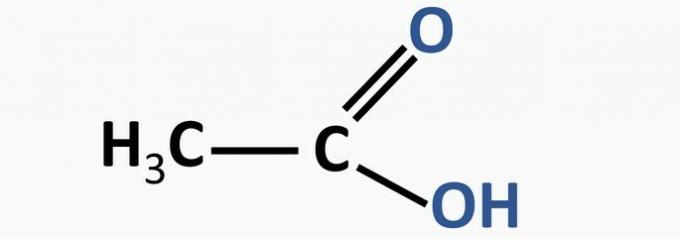
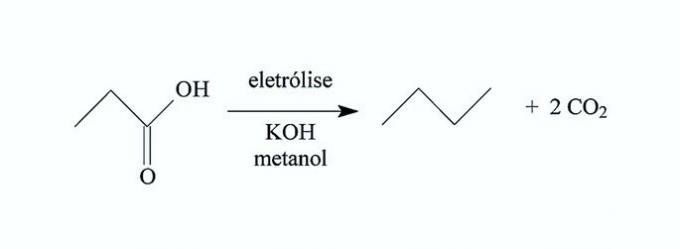
AZEVEDO, D. Ç.; GOULART, M. O. F. Stereoselectivity in electrodic reactions. New Chemistry, no. 2, 1997 (adapted).
Based on this process, the hydrocarbon produced in the electrolysis of 3,3-dimethyl-butanoic acid is the
a) 2,2,7,7-tetramethyl-octane.
b) 3,3,4,4-tetramethyl-hexane.
c) 2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-hexane.
d) 3,3,6.6-tetramethyl-octane.
e) 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-hexane.
Correct alternative: c) 2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-hexane.
a) WRONG. This hydrocarbon is produced in the electrolysis of 3,3-dimethyl-pentanoic acid.
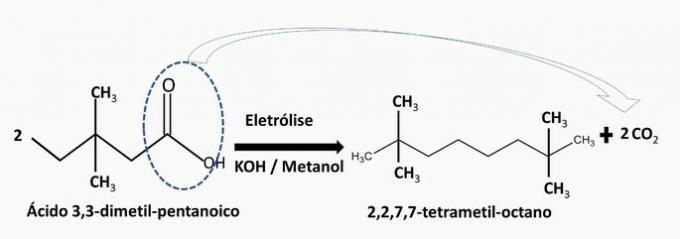
b) WRONG. This hydrocarbon is produced in the electrolysis of 4,4-dimethyl-butanoic acid.

c) CORRECT. Electrolysis of 3,3-dimethyl-butanoic acid produces 2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-hexane.

In the reaction, the carboxylic group is separated from the carbon chain and carbon dioxide is formed. By electrolysis of 2 moles of acid, the chains come together and form a new compound.
d) WRONG. This hydrocarbon is produced in the electrolysis of 4,4-dimethyl-pentanoic acid.

e) WRONG. This hydrocarbon is not produced by anodic oxidative decarboxylation.
9. (Enem/2012) The world food production could be reduced to 40% of the current one without the application of control over agricultural pests. On the other hand, the frequent use of pesticides can cause contamination in soil, surface and underground water, atmosphere and food. Biopesticides, such as pyrethrin and coronopilin, have been an alternative to reduce the economic, social and environmental damage caused by pesticides.
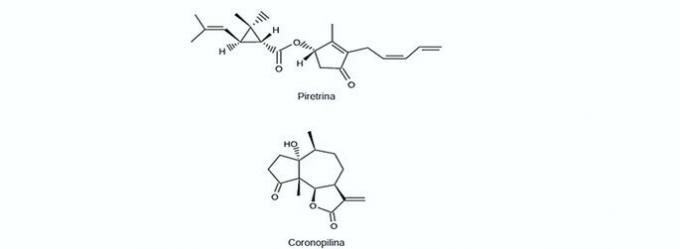
Identify the organic functions present simultaneously in the structures of the two biopesticides presented:
a) Ether and ester.
b) Ketone and ester.
c) Alcohol and ketone.
d) Aldehyde and ketone.
e) Ether and carboxylic acid.
Correct alternative: b) Ketone and ester.
The organic functions present in the alternatives are:
| carboxylic acid | Alcohol |
| Aldehyde | ketone |
| Ether | Ester |
According to the functional groups presented above, those that can be seen simultaneously in the two biopesticides are ketone and ester.
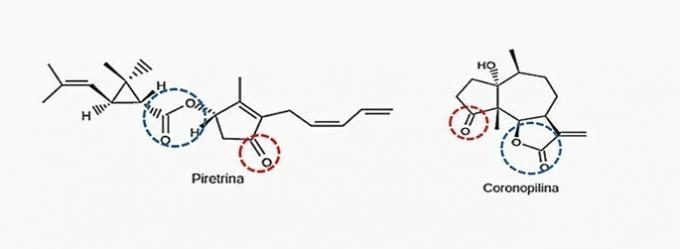
Learn more at: ketone and ester.
10. (Enem/2011) Bile is produced by the liver, stored in the gallbladder and plays a key role in lipid digestion. Bile salts are steroids synthesized in the liver from cholesterol, and their synthesis route involves several steps. Starting from the cholic acid represented in the figure, the formation of glycocholic and taurocholic acids occurs; the prefix glyco- means the presence of a residue of the amino acid glycine and the prefix tauro-, the amino acid taurine.
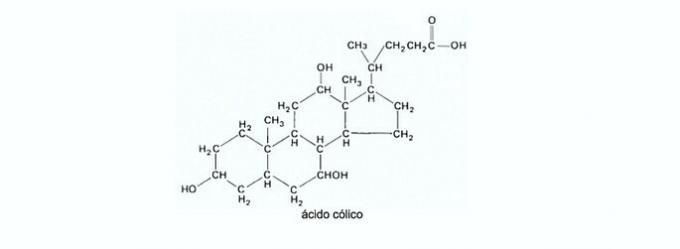
UCKO, D. THE. Chemistry for Health Sciences: an Introduction to General, Organic and Biological Chemistry. São Paulo: Manole, 1992 (adapted).
The combination between cholic acid and glycine or taurine gives rise to the amide function, formed by the reaction between the amine group of these amino acids and the group
a) carboxyl of cholic acid.
b) cholic acid aldehyde.
c) cholic acid hydroxyl.
d) cholic acid ketone.
e) cholic acid ester.
Correct alternative: a) carboxyl cholic acid.
This is the general formula for the amide function:
This group is derived from a carboxylic acid in a condensation reaction with the amine group.
During this process, there will be the elimination of a water molecule, according to the equation:

The carboxyl (-COOH) present in cholic acid is able to react with the amino group (-NH2) of an amino acid, such as glycine or taurine.

For more exercises from Organic chemistry, See too: Exercises on Hydrocarbons.