Alkenes or alkenes are hydrocarbons that have a double bond in their carbon chain.
The general formula for alkenes is: CnoH2n.
Most alkenes are produced in the laboratory and few are found in nature.
Features
The main characteristics of alkenes are:
- colorless
- Insoluble in water
- Soluble in alcohol and ether
- They are more reactive than alkanes
- Melting and boiling points are higher than those of alkanes with the same number of carbon atoms
- The simplest alkene is ethylene or ethylene
Also know about:
- alkanes
- Alkynes
- alkadiene
Nomenclature
Alkenes receive the same nomenclature as other hydrocarbons.
PREFIX + INFIX + SUFFIX
The prefix indicates the amount of carbons in the main chain.
The infix is given by the term "en", which represents the double bond. The suffix is given by the letter "o", which indicates the hydrocarbon compound.
Thus, alkenes are named as suffix –eno, which indicates the double bond.
In addition, the position of the double bond must be indicated. This number precedes the name of the alkene and indicates the carbon atom where bonding begins.
The carbon chain starts to be numbered from the closest end of the double bond.
Examples
Ethene or ethylene: CH2 = CH2
Propylene or Propylene: CH2 = CH - CH3, whose equivalent formula is written as follows: CH3 — CH = CH2
1-butene: CH2 = CH - CH2 – CH3
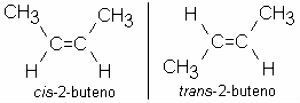
2-butene: CH3 – CH = CH – CH3
It is common for alkenes to also present isomerism:
branched alkenes
Alkenes can also be branched. In this case, the main chain is the longest and has the double bond.
Example:
5-methyl-2-hexane
Learn more about Nomenclature of hydrocarbons.
Complement your research on Hydrocarbons. Read too:
- Benzene
- Butane
- Cyclans
- Petroleum
- Organic compounds
- Aromatic Hydrocarbons
- Exercises on Hydrocarbons

