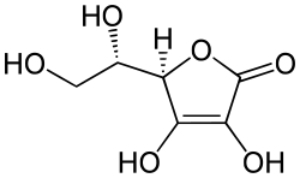
Vitamin C or ascorbic acid is a water-soluble, unstable and easily oxidized substance, whose bonds can be broken by oxygen, alkaline bases and high temperatures.
In its natural state, vitamin C is found in crystal or powder form, with a hue ranging from white to yellow.
The human being is not able to synthesize vitamin C and therefore must obtain it through food.
What is it for?
Vitamin C has a series of functions and benefits for the body, including:
- Assists the body's immune response;
- Prevention of flu and infections;
- It participates in the production of collagen, being important in the healing of wounds, fractures and in the control of gingival bleeding;
- Participates in lymphocyte maturation;
- Maintains the integrity of blood vessels;
- Facilitates the absorption of iron in the intestine;
- Due to its ability to give and receive electrons, vitamin C has a strong antioxidant action that protects the cells from free radical damage, helping to prevent some cancers and diseases cardiovascular;
- Essential in the formation of norepinephrine;
- Participates in skeletal growth and remodeling.
Foods with Vitamin C

Vitamin C is found mainly in fruits citrus fruits (orange, lemon, acerola and kiwi) and red fruits (strawberry, blackberry, raspberry, blackberry and blueberry). Some exotic fruits are also sources of vitamin C
Other vegetables are also sources of vitamin C such as tomatoes, carrots, garlic, peppers and kale.
Know more about:
- Vitamins
- Nutrients
Hypovitaminosis
Vitamin C deficiency in the body can lead to muscle weakness, anemia and problems with the immune system.
THE lack of vitamin C can also cause scurvy. Symptoms of the disease are painful, spongy gums, loose teeth, fragile blood vessels, joint swelling, and anemia.
These symptoms are due to a deficiency in collagen hydroxylation, resulting in defective connective tissue.
As it is water-soluble, excess vitamin C is eliminated through the urine, and therefore there are no side effects associated with hypervitaminosis.
Read too:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin K



