The periodic properties of chemical elements are the characteristics they have.
Note that the chemical elements in the periodic table have a specific location that varies according to the periodic properties they exhibit. They are sorted in ascending order of atomic number.
According to Moseley's Law:
“Many physical and chemical properties of elements vary periodically in the sequence of the atomic numbers of the elements..”
Main Periodic Properties
atomic radius
Related to the size of atoms, this property is defined by the distance between the centers of the nuclei of two atoms of the same element.
Therefore, the atomic ray corresponds to half the distance between the nuclei of two neighboring atoms, being expressed as follows:
r = d/2
Where:
r: lightning
d: internuclear distance
It is measured in picometers (pm). This measurement is a submultiple of the meter:
1 pm = 10-12 m
In the periodic table, the atomic radius increases from top to bottom in the vertical position. On the horizontal, they increase from right to left.
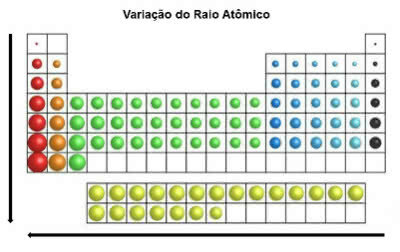
Atomic Radius Variation
The chemical element that has the largest atomic radius is Cesium (Cs).
Atomic Volume
This periodic property indicates the volume occupied by 1 mol of the element in the solid state.
It is worth noting that the atomic volume is not the volume of 1 atom, but a set of 6.02. 1023 atoms (1 mol value)
The atomic volume of an atom is defined not only by the volume of each atom, but also the spacing that exists between those atoms.
In the periodic table, atomic volume values increase from top to bottom (vertical) and from center to edge (horizontal).

Atomic Volume Variation
To calculate the atomic volume, the following formula is used:
V = m/d
Where:
V: atomic volume
m: mass of 6.02. 1023 element atoms
d: solid state element density
Absolute Density
THE density absolute, also called “specific mass”, is a periodic property that determines the relationship between the mass (m) of a substance and the volume (v) occupied by that mass.
It is calculated by the following formula:
d = m/v
Where:
d: density
m: pasta
v: volume
In the periodic table, densities values increase from top to bottom (vertical) and from edges to center (horizontal).
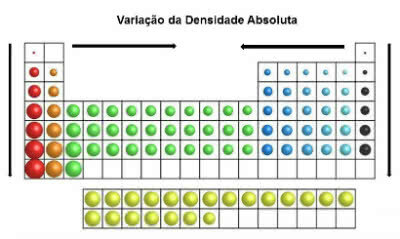
Absolute Density Variation
Thus, the densest elements are in the center and at the bottom of the table:
Osmium (Os): d= 22.5 g/cm3
Iridium (Ir): d = 22.4 g/cm3
Melting Point and Boiling Point
Another important periodic property is related to the temperatures at which elements enter into melting and boiling.
The Melting Point (MP) is the temperature at which matter passes from the solid phase to the liquid phase. The Boiling Point (PE) is the temperature at which matter passes from the liquid to the gaseous phase.
In the periodic table, the values of PF and PE vary according to the sides that are positioned in the table.
Vertically and on the left side of the table, they increase from the bottom to the top. On the right side, they increase from top to bottom. In the horizontal direction, they extend from the ends to the center.

Melting and boiling point variation
Electronic Affinity
Also called “electroaffinity”, it is the minimum energy required by a chemical element in order to remove an electron from an anion.
That is, the electronic affinity indicates the amount of energy released when an electron is received by an atom.
Note that this unstable atom is alone and in a gaseous state. With this property, it acquires stability when it receives the electron.
In contrast to atomic radius, the electroaffinity of elements in the periodic table grows from left to right, horizontally. In the vertical direction, it increases from the bottom to the top.
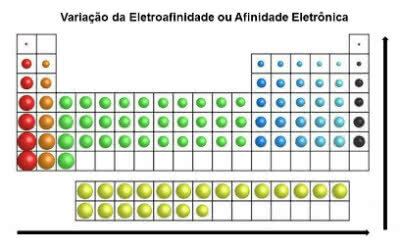
Electronic Affinity Variation
The chemical element that has the greatest electron affinity is Chlorine (Cl), with a value of 349 KJ/mol.
Ionization Energy
Also called “ionization potential”, this property is contrary to that of electronic affinity.
It is the minimum energy required by a chemical element in order to remove an electron from a neutral atom.
Thus, this periodic property indicates how much energy is needed to transfer the electron from an atom in a ground state.
The so-called “ground state of an atom” means that its number of protons is equal to its number of electrons (p+ = and-).
Thus, after removing an electron from the atom, it is ionized. That is, it gets more protons than electrons, and therefore becomes a cation.
In the periodic table, the ionization energy is contrary to that of the atomic radius. So it increases from left to right and from bottom to top.
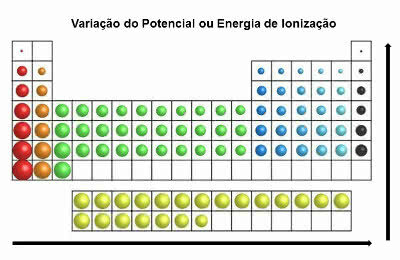
Ionization Energy Variation
The elements that have the greatest ionization potential are Fluorine (F) and Chlorine (Cl).
electronegativity
Property of atoms of elements which have a tendency to receive electrons in a chemical bond.
It occurs in covalent bonds at the time of sharing electron pairs. When receiving electrons, atoms are left with a negative charge (anion).
Remember that this is considered the most important property of the periodic table. This is because electronegativity induces the behavior of atoms, from which molecules are formed.
In the periodic table, the electronegativity increases from left to right (horizontally) and from bottom to top (vertical)
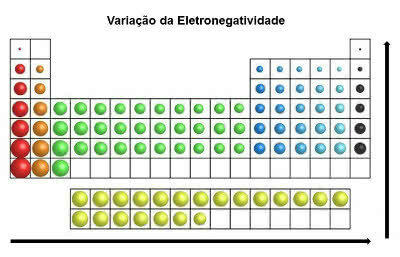
Electronegativity Variation
Thus, the most electronegative element on the periodic table is Fluorine (F). On the other hand, Cesium (Cs) and Francium (Fr) are the least electronegative elements.
electropositivity
Unlike electronegativity, this property of elemental atoms indicates tendencies to lose (or give up) electrons in a chemical bond.
When losing electrons, the atoms of the elements get a positive charge, thus forming a cation.
In the same direction as the atomic radius and contrary to electronegativity, in the periodic table a electropositivity increases from right to left (horizontal) and from top to bottom (vertical).
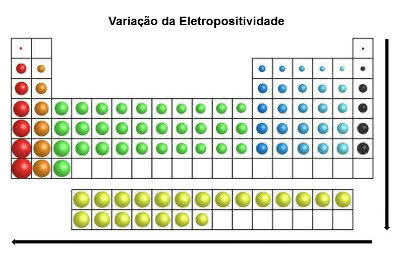
Electropositivity Variation
The chemical elements with the highest electropositivity are metals, and for this reason, this property is also called “metallic character”. The most electropositive element is Francium (Fr) with maximum tendency to oxidation.
Attention!
You "noble gases” are inert elements, as they do not carry out chemical bonds and hardly donate or receive electrons. Also, they have difficulty reacting with other elements.
Therefore, the electronegativity and electropositivity of these elements are not considered.
Read too:
- Chemical bonds
- History of the Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Families
Aperiodic Properties
In addition to periodic properties, we have aperiodic properties. In this case, the values increase or decrease with the atomic number of elements.
They receive this name, as they do not obey their position on the periodic table like the periodic ones. That is, they are not repeated at regular periods.
The main aperiodic properties are:
- Atomic Mass: This property increases as the atomic number increases.
- Specific heat: this property decreases with increasing atomic number. Remember that specific heat is the amount of heat needed to increase the temperature by 1 °C of 1g of the element.
Entrance Exam Exercises with Feedback
1. (PUC-RJ) Consider the statements about group IA elements of the Periodic Table
I. They are called alkali metals.
II. Its atomic rays grow with the atomic number.
III. Its ionization potential increases with atomic number.
IV: Its metallic character increases with atomic number.
Among the statements, are true:
a) I and II
b) III and IV
c) I, II and IV
d) II, III and IV
e) I, II, III and IV
Alternative c
2. (UFMG) Comparing chlorine and sodium, the two chemical elements that form table salt, you can say that chlorine:
a) is denser.
b) is less volatile.
c) has a greater metallic character.
d) has lower ionization energy.
e) has a smaller atomic radius.
Alternative and
3. (UFC-CE) The photoelectric effect consists of the emission of electrons from metallic surfaces, through the incidence of light of appropriate frequency. This phenomenon is directly influenced by the ionization potential of metals, which have been largely used in the manufacture of photoelectronic devices, such as: public lighting photocells, cameras photographic etc. Based on the variation in the ionization potential of the elements in the Periodic Table, mark the alternative that contains the metal most likely to exhibit the photoelectric effect.
a) Fe
b) Hg
c) Cs
d) Mg
e) Ca
Alternative c
Check entrance exam questions with a commented resolution in Exercises on the Periodic Table and unpublished questions on the subject in Exercises on Organizing the Periodic Table.
Read too:
- Periodic table
- Eletronic distribution
- Chemical elements
- Intermolecular Forces
