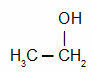Natural gas is originated by organic matter degradation (vegetable, algae and animal remains) by anaerobic bacteria in very deep layers of the earth's crust or below. It was formed over millions of years, along with the natural process of formation of the planet.
Organic matter from vegetables, from dry nature, reaches greater depths and undergoes greater heating, becoming coal, shale and methane. While the remains of algae and animals, from greasy nature, do not undergo this gradual cooking and originate the Petroleum.
In the final stages of degradation of this fatty matter, oil is transformed into a volatile condensate associated with gaseous hydrocarbons, among which methane predominates. That is why it is common to find the gas associated with oil, called associated natural gas. When there is little or no amount of oil, it is said unassociated natural gas.
See also the article about the Petroleum.
Composition
Raw natural gas has a composition defined by a series of natural factors during its formation process and the conditions of accumulation in underground reservoirs. This varies with the location of the reservoir (land or sea), the type of soil, the geology of the soil, among other factors. The components determine aspects such as the
density it's the calorific power of the gas.Unassociated natural gas has higher methane contents, and in the form associated with petroleum it contains significant amounts of ethane, propane, butane and heavier hydrocarbons. Also part of the composition are gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), hydrogen sulphide (H2S), water, hydrochloric acid (HCl) and mechanical impurities.
The composition of the natural gas that is sold varies according to the purpose for which it is intended. To acquire characteristics suitable for sale, raw natural gas passes through processing units, where impurities are removed and heavy hydrocarbons are separated. Some examples of products sold are: natural gas (with a predominance of methane or propane or ethane), natural gasoline (butane), diesel (octane), kerosene (tetradecane), among others.
Meet the Advantages of Disadvantages of Natural Gas.
Production in Brazil
In Brazil, the natural gas that is currently traded is obtained from our reservoirs, but it is also imported from Bolivia (coming through pipelines) and other suppliers in the form of liquefied natural gas (LNG), which is then transformed into gas.
Most of our oil reserves are in offshore fields, which has led drilling activities to reach ever greater depths. The Campos Basin was the first to enter into activity in the 1970s, allowing Petrobrás to develop state-of-the-art technology to operate in pre-salt and post-salt areas. The platforms are spread over several states, but mainly in the Southeast, where the Campos Basin is located (between RJ and ES) and in the Northeast. On land, production is mainly concentrated in the North and Northeast regions and, to a lesser extent, in the Southeast, in the History of Petrobras.