Hybridization of sp-type carbon2 it occurs when it has a double bond and two single bonds or a pi bond (π) and three sigma bonds (σ). In fact, sp hybridization2 it is brought about between the atoms that establish the double bond.
An example of such a molecule is formaldehyde (CH2O). Note its structure below:
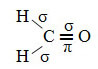
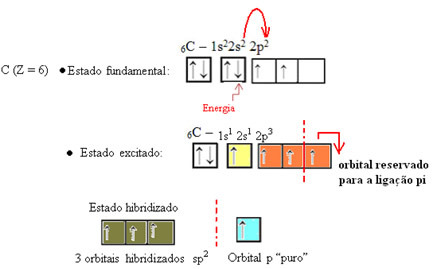
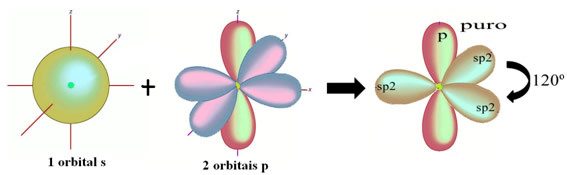
As seen in the text "sp type hybridization3”, carbon hybridization occurs when an electron from sublevel 2s receives energy and is “transported” to the 2p sublevel and, thus, originate 4 hybridized orbitals from the "mix" of atomic orbitals pure.
In the case of formaldehyde, we know that there will be a pi bond, so one of these hybridized orbitals is reserved for this bond, while the other three perform the sigma bonds:
The hydrogen atoms that make the single bond with carbon, make it with their s orbital:
The remaining "pure" p orbital double-bonds the oxygen atom and the formaldehyde molecule has the following structure:
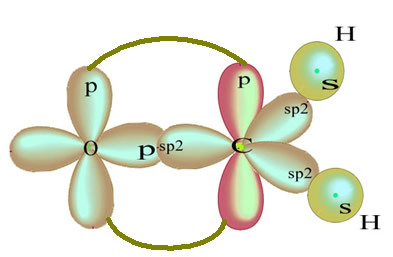
As for the type of bonds existing in this formaldehyde structure, we have:

Connections: 1 = 2 = σs-sp2
3 = σp-sp2
4 =πp-p
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/hibridizacao-tipo-sp2.htm

